Abstract
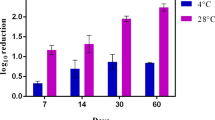
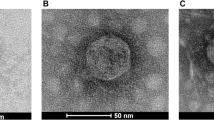
This study was designed to evaluate the effect of bacteriophage P22 on the inhibition of growth of Salmonella Typhimurium. The P22 belongs to Podoviridae family consisting of a hexagonal head and short tail. The inhibitory effect of phage in milk was noticeable at the early storage period, showing more than 3 log reduction at 4 h and day 3. The pH values of milk treated with P22 were significantly decreased from 6.7 to 6.3 after 24 h incubation at 37 °C, while no significant changes in pH values were observed for the control and bacteriophage treatment throughout the storage at 4 °C for 12 days. The slight color changes were observed in the control and bacteriophage treatment throughout the storage at 4 °C for 12 days and 37 °C for 24 h. These results provide useful information for enhancing microbiological safety and quality of milk and designing effective bacteriophage-based control in food system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao H, Zhang P, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Wang R. Bio-control of Salmonella Enteritidis in foods using bacteriophages. Viruses 7: 2847 (2015)
BermÚDez-Aguirre D, Mawson R, Versteeg K, Barbosa-CÁNovas GV. Composition properties, physicochemical characteristics and shelf life of whole milk after thermal and thermo-sonification treatments. J. Food Qual. 32: 283–302 (2009)
Bohannan BJM, Lenski RE. Linking genetic change to community evolution: insights from studies of bacteria and bacteriophage. Ecol. Lett. 3: 362–377 (2000)
Eng S-K, Pusparajah P, Ab Mutalib N-S, Ser H-L, Chan K-G, Lee L-H. Salmonella: a review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 8: 284–293 (2015)
Erskine JM. Adsorption of lactic Streptococcal bacteriophage by milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 53: 861–864 (1970)
Faille C, Cunault C, Dubois T, Bénézech T. Hygienic design of food processing lines to mitigate the risk of bacterial food contamination with respect to environmental concerns. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 46: 65–73 (2017)
García P, Martínez B, Obeso JM, Rodríguez A. Bacteriophages and their application in food safety. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 47: 479–485 (2008)
Giladi H, Goldenberg D, Koby S, Oppenheim AB. Enhanced activity of the bacteriophage lambda PL promoter at low temperature. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 92: 2184–2188 (1995)
Guenther S, Herzig O, Fieseler L, Klumpp J, Loessner MJ. Biocontrol of Salmonella Typhimurium in RTE foods with the virulent bacteriophage FO1-E2. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 154: 66–72 (2012)
Kim J, Jo A, Ding T, Lee H-Y, Ahn J. Assessment of altered binding specificity of bacteriophage for ciprofloxacin-induced antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium. Arch. Microbiol. 198: 521–529 (2016)
Labrie SJ, Samson JE, Moineau S. Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8: 317–327 (2010)
Lee S, Kim MG, Lee HS, Heo S, Kwon M, Kim G-B. Isolation and characterization of Listeria phages for control of growth of Listeria monocytogenes in milk. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 37: 320–328 (2017)
Modi R, Hirvi Y, Hill A, Griffiths MW. Effec of phage on survival of Salmonella Enteritidis during manufacture and storage of cheddar cheese made from raw and pasteurized milk. J. Food Prot. 64: 927–933 (2001)
Mungai EA, Behravesh C, Gould L. Increased outbreaks associated with nonpasteurized milk, United States, 2007–2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 21: 119–122 (2015)
O’Flaherty S, Coffey A, Meaney WJ, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP. Inhibition of bacteriophage K proliferation on Staphylococcus aureus in raw bovine milk. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 41: 274–279 (2005)
Olsen SJ, Ying M, Davis MF, Deasy M, Holland B, Iampietro L, Baysinger CM, Sassano F, Polk LD, Gormley B, Hung MJ, Pilot K, Orsini M, Van Duyne S, Rankin S, Genese C, Bresnitz EA, Smucker J, Moll M, Sobel J. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium infection from milk contaminated after pasteurization. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 10: 932–935 (2004)
Owens SL, Brewer JL, Rankin SA. Influence of bacterial cell population and pH on the color of nonfat milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 34: 329–333 (2001)
Rakhuba DV, Kolomiets EI, Dey ES, Novik GI. Bacteriophage receptors, mechanisms of phage adsorption and penetration into host cell. Polish J. Microbiol. 59: 145–155 (2010)
Smadi H, Sargeant JM, Shannon HS, Raina P. Growth and inactivation of Salmonella at low refrigerated storage temperatures and thermal inactivation on raw chicken meat and laboratory media: Mixed effect meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Global Health 2: 165–179 (2012)
Strydom A, Witthuhn CR. Listeria monocytogenes: A target for bacteriophage biocontrol. Comprehen. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 14: 694–704 (2015)
Thung TY, Jayarukshi K, Premarathne K, Mudiyanselage J, San Chang W, Loo YY, Chin YZ, Kuan CH, Tan CW, Basri DF, Jasimah Wan Mohamed Radzi CW, Radu S. Use of a lytic bacteriophage to control Salmonella Enteritidis in retail food. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 78: 222–225 (2017)
Viazis S, Akhtar M, Feirtag J, Diez-Gonzalez F. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 viability on hard surfaces by treatment with a bacteriophage mixture. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 145: 37–42 (2011)
Wong CL, Sieo CC, Tan WS, Abdullah N, Hair-Bejo M, Abu J, Ho YW. Evaluation of a lytic bacteriophage, Φ st1, for biocontrol of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in chickens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 172: 92–101 (2014)
Zinno P, Devirgiliis C, Ercolini D, Ongeng D, Mauriello G. Bacteriophage P22 to challenge Salmonella in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 191: 69–74 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A3B01008304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phongtang, W., Choi, GP., Chukeatirote, E. et al. Bacteriophage control of Salmonella Typhimurium in milk. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 297–301 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0446-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0446-6