Abstract
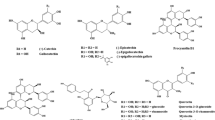
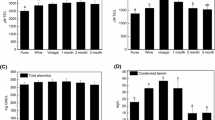
Variations in amino acid and volatile component contents, and in total flavonoid, polyphenol contents and their vitro antioxidant activities at different aging times of pomelo wine were investigated; scavenging rates against DPPH, ABTS, and ferric reducing antioxidant powers were also explored. Most amino acids reached maximum values in the third aging year; and volatile components of pomelo wine also indicated good wine quality in the third year. Total flavonoid and polyphenol contents in pomelo wine were increased and antioxidant activities enhanced during the first 3 years. Samples aged for 3 years had the highest total flavonoid and total polyphenol contents, and the strongest antioxidant activities (38.23±2.16% for DPPH· scavenging effect, 91.84±4.14% for ABTS· scavenging effect, and 0.90±0.07 mmol/L for FRAP value). These parameters gradually decreased after the 3 year period. A significant (p<0.05) correlation between antioxidant activity, and total flavonoid and polyphenol contents was identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan YQ, Xiao LF. Study on extraction of grapefruit seed oil and analysis of fatty acids by GC. Food Sci. 29: 438–440 (2008)
Tripoli E, Guardia ML, Giammanco S, Majo DD, Giammanco M. Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: A review. Food Chem. 104: 466–479 (2007)
Vanamala J, Leonardi T, Patil BS, Taddeo SS, Murphy ME, Pike LM, Turner ND. Suppression of colon carcinogenesis by bioactive compounds in grapefruit. Carcinogenesis 27: 1257–1265 (2006)
Cushnie TP, Lamb AJ. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Ag. 26: 343–356 (2005)
Ros-Chumillas M, Belissario Y, Iguaz A, López A. Quality and shelf life of orange juice aseptically packaged in PET bottles. J. Food Eng. 79: 234–242 (2007)
Serrano M, Guillén F, Martínez-Romero D, Castillo S, Valero D. Chemical constituents and antioxidant activity of sweet cherry at different ripening stages. J. Agr. Food Chem. 53: 2741–2745 (2005)
Wang SY, Chen H, Camp MJ, Ehlenfeldt MK. Flavonoid constituents and their contribution to antioxidant activity in cultivars and hybrids of rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei Reade). Food Chem. 132: 855–864 (2012)
Zozio S, Servent A, Cazal G. Changes in antioxidant activity during the ripening of jujube (Ziziphus mauritiana Lamk). Food Chem. 150: 448–456 (2014)
Prasad KN, Yang B, Dong X, Jiang G, Zhang H, Xie H, Jiang Y. Flavonoid contents and antioxidant activities from Cinnamomum species. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 10: 627–632 (2009)
Bouayed J, Hoffmann L, Bohn T. Total phenolics, flavonoids, anthocyanins and antioxidant activity following simulated gastrointestinal digestion and dialysis of apple varieties: Bioaccessibility and potential uptake. Food Chem. 128: 14–21 (2011)
Zhang R, Zeng Q, Deng Y, Zhang M, Wei Z, Tang X. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of litchi pulp of different cultivars cultivated in Southern China. Food Chem. 136: 1169–1176 (2013)
Wang HC, Hu ZQ, Wang Y, Chen HB, Huang XM. Phenolic compounds and the antioxidant activities in litchi pericarp: Difference among cultivars. Sci. Hortic-Amsterdam 129: 784–789 (2011)
Shim YS, Yoon WJ, Ha J, Seo D, Lee KW, Lee WY, Hwang JB. Method validation of 16 types of structural amino acids using an automated amino acid analyzer. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 22: 1567–1571 (2013)
Juan C, Jianquan K, Junni T, Zijian C, Ji L. The profile in polyphenols and volatile compounds in alcoholic beverages from different cultivars of mulberry. J. Food Sci. 77: 430–436 (2012)
Chang CC, Yang MH, Wen HM, Chern JC. Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J. Food Drug Anal. 10: 178–182 (2002)
Wang YF, Huang SR, Shao SH, Qian LS, Xu P. Studies on bioactivities of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) fruit peel extracts: Antioxidant activity and inhibitory potential against alphaglucosidase and alpha-amylase in vitro. Ind. Crop. Prod. 37: 520–526 (2012)
Ranilla LG, Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Shetty K. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and in vitro inhibitory potential against key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and hypertension of commonly used medicinal plants, herbs and spices in Latin America. Bioresource Technol. 101: 4676–4689 (2010)
Arnao MB, Cano A, Acosta M. The hydrophilic and lipophilic contribution to total antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 73: 239–244 (2001)
Deighton N, Brennan R, Finn C, Davies HV. Antioxidant properties of domesticated and wild Rubus species. J. Sci. Food Agr. 80: 1307–1313 (2000)
Kabelová I, Dvoráková M, Cížková H, Dostálek P, Melzoch K. Determination of free amino acids in beers: A comparison of Czech and foreign brands. J. Food Compos. Anal. 21: 736–741 (2008)
Barylko-Pikielna N, Kostyra E. Sensory interaction of umami substances with model food matrices and its hedonic effect. Food Qual. Prefer. 18: 751–758 (2007)
Cook NC, Samman S. Flavonoids-chemistry, metabolism, cardioprotective effects, and dietary sources. J. Nutr. Biochem. 7: 66–76 (1996)
Ghafar MF, Prasad KN, Weng KK, Ismail A. Flavonoid, hesperidine, total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities from Citrus species. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 9: 326–330 (2010)
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventos R M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Method. Enzymol. 299: 152–178 (1999)
Floegel A, Kim DO, Chung SJ, Koo SI, Chun OK. Comparison of ABTS/DPPH assays to measure antioxidant capacity in popular antioxidant-rich US foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 24: 1043–1048 (2011)
Thaipong K, Boonprakob U, Crosby K, Cisneros-Zevallos L, Hawkins-Byrne D. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 19: 669–675 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, M., You, Y., Zhao, X. et al. Effects of aging time on the antioxidant activity of pomelo wine. Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 1459–1465 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0188-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0188-7