Abstract
Objectives
To compare the effectiveness of cyclophosphamide and rituximab in the treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis with pulmonary involvement (SSc-ILD).
Methods
Symptoms and the respiratory function parameters of 34 patients receiving cyclophosphamide and 27 patients receiving rituximab for at least 24 months between 1996 and 2018 were compared.
Results
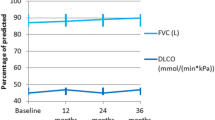
It was observed that symptoms including cough, Raynaud’s phenomenon, digital ulceration, diarrhea, and dysphagia, but not dyspnea, recovered statistically significantly more in the rituximab group (p = 0.004, p = 0.001, p = 0.006, p = 0.005, and p < 0.001, respectively; for dyspnea p = 0.11). When differences in FVC and FVC% values were compared with baseline, it was found that there was a statistically significant increase in FVC (mL) (p = 0.02) and FVC% (p = 0.002) values after 12 months of treatment in patients receiving cyclophosphamide compared with those receiving rituximab. When differences in DLCO and DLCO% values from baseline were compared, a statistically significant increase was seen in DLCO values after 15 and 24 months (p = 0.003 and p = 0.048, respectively) of treatment, also in DLCO% values after 15 and 18 months (p = 0.008 and p = 0.01, respectively) of treatment in patients receiving rituximab compared with those receiving cyclophosphamide.
Conclusion
It was observed that both cyclophosphamide and rituximab treatments were effective in controlling dyspnea and worsened pulmonary function in SSc-ILD. The effect of cyclophosphamide is more prominent on FVC and rituximab is more effective on DLCO.
Key Points • Both cyclophosphamide and rituximab treatments were effective in controlling dyspnea and worsened pulmonary function in SSc-ILD. • The effect of cyclophosphamide is more prominent on FVC and rituximab is more effective on DLCO. | |||

Similar content being viewed by others
References
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D et al (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424
Benan M, Hande I, Gul O (2007) The natural course of progressive systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung involvement. Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0302-6
de Lauretis A, Veeraraghavan S, Renzoni E (2011) Review series: aspects of interstitial lung disease: connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: how does it differ from IPF? How should the clinical approach differ? Chron Respir Dis. https://doi.org/10.1177/1479972310393758
Coghlan JG, Mukerjee D (2001) The heart and pulmonary vasculature in scleroderma: clinical features and pathobiology. Curr Opin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002281-200111000-00008
Schoenfeld SR, Castelino FV (2015) Interstitial lung disease in scleroderma. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2014.12.005
Tashkin DP, Roth MD, Clements PJ et al (2016) Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): a randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Respir Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30152-7
Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ et al. (2006) Scleroderma Lung Study Research Group. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa055120
Collins BF, Raghu G (2019) Antifibrotic therapy for fibrotic lung disease beyond idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0022-2019
Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M et al (2019) Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1903076
Sircar G, Goswami RP, Sircar D, Ghosh A, Ghosh P (2018) Intravenous cyclophosphamide vs rituximab for the treatment of early diffuse scleroderma lung disease: open label, randomized, controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key213
Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J et al (2006) A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22204
Fernández-Codina A, Walker KM, Pope JE, Scleroderma Algorithm Group (2018) Treatment algorithms for systemic sclerosis according to experts. Arthritis Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40560
Perelas A, Silver RM, Arrossi AV, Highland KB (2020) Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Lancet Respir Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30480-1
Cardelli PM, Quinn M, Bukman D, Fang Y, Colcher D, King DJ, Bebbington C, Yarranton G (2002) Binding to CD20 by anti-B1 antibody or F(ab’)(2) is sufficient for induction of apoptosis in B-cell lines. Cancer immunol immunother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-001-0247-1
Bosello SL, De Luca G, Rucco M, Berardi G, Falcione M, Danza FM, Pirronti T, Ferraccioli G (2015) Long-term efficacy of B cell depletion therapy on lung and skin involvement in diffuse systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.09.002
McGonagle D, Tan AL, Madden J, Rawstron AC, Rehman A, Emery P, Thomas S (2008) Successful treatment of resistant scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease with rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kem357
Sari A, Guven D, Armagan B, Erden A, Kalyoncu U, Karadag O, Apras Bilgen S, Ertenli I, Kiraz S, Akdogan A (2017) Rituximab experience in patients with long-standing systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease: a series of 14 patients. J Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0000000000000584
Goswami RP, Ray A, Chatterjee M, Mukherjee A, Sircar G, Ghosh P (2021) Rituximab in the treatment of systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa550
Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), (1980) Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
Mahler DA, Wells CK (1988) Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest 93:580–586
Daoussis D, Melissaropoulos K, Sakellaropoulos G et al (2017) A multicenter, open-label, comparative study of B-cell depletion therapy with rituximab for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.10.003
Daoussis D, Liossis SN, Tsamandas AC, Kalogeropoulou C, Kazantzi A, Sirinian C, Karampetsou M, Yiannopoulos G, Andonopoulos AP (2010) Experience with rituximab in scleroderma: results from a 1-year, proof-of-principle study. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep093
Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ et al (2007) 1-year treatment with cyclophosphamide on outcomes at 2 years in scleroderma lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care MED. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200702-326OC
Nannini C, West CP, Erwin PJ, Matteson EL (2008) Effects of cyclophosphamide on pulmonary function in patients with scleroderma and interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials and observational prospective cohort studies. Arthritis Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2534
van den Hombergh WMT, Simons SO, Teesselink E, Knaapen-Hans HKA, van den Hoogen FHJ, Fransen J, Vonk MC (2018) Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis in a retrospective open-label study: influence of the extent of inflammation on pulmonary function. Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4171-6
Barnes H, Holland AE, Westall GP, Goh NS, Glaspole IN (2018) Cyclophosphamide for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010908.pub2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
This is a retrospective study.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yılmaz, D.D., Borekci, S. & Musellim, B. Comparison of the effectiveness of cyclophosphamide and rituximab treatment in patients with systemic sclerosis–related interstitial lung diseases: a retrospective, observational cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 40, 4071–4079 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05785-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05785-6