Abstract
Objectives
With galectin-3 playing an important role in inflammatory responses, elevated galectin-3 levels have been shown in patients with autoimmune diseases. However, there are limited data regarding galectin-3 expression in patients with autoinflammatory diseases such as adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD). This study aimed to investigate the extracellular galectin-3 expression and examine its association with activity parameters and disease outcome in AOSD patients.
Method
Plasma levels of galectin-3 and inflammasome downstream cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 were determined by ELISA in 42 active AOSD patients and 20 healthy controls (HC). The protein levels of galectin-3 and cytokines were determined using immunoblotting.
Results
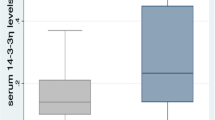
Plasma levels of galectin-3 and inflammasome downstream cytokines including IL-1β and IL-18 were significantly higher in AOSD patients (median 5.02 ng/ml, interquartile range [IQR] 3.12–7.88 ng/ml; 3.42 pg/ml, IQR 1.48–6.70 pg/ml; and 5758 pg/ml, IQR 859-11,895 pg/ml, respectively) compared with HC (1.86 ng/ml, IQR 1.09–2.89 ng/ml; 0.99 pg/ml, IQR 0.62–1.35 pg/ml; and 129 pg/ml, IQR 71-155 pg/ml, respectively, all p < 0.001). Plasma galectin-3 levels were positively correlated with clinical activity scores, inflammatory parameters values, and the levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in AOSD patients. AOSD patients with systemic pattern had significantly higher galectin-3 levels (median 6.08 ng/ml, IQR 4.01–9.54 ng/ml) compared with those with chronic articular pattern (3.56 ng/ml, IQR 3.04–4.98 ng/ml, p < 0.05). After 6-month therapy, galectin-3 levels significantly declined, paralleling the decreases in clinical activity scores and plasma levels of IL-1β and IL-18.
Conclusions
Elevated galectin-3 levels and their positive correlation with disease activity scores, inflammatory parameter, and inflammasome downstream cytokines suggest the involvement of galectin-3 in AOSD pathogenesis.
Key Points • We revealed for the first time the association of plasma galectin-3 levels with AOSD activity parameters. • We explored the link between galectin-3 levels and NLRP3-inflammasome downstream cytokines in AOSD disease. |





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H (1994) Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem 269(33):20807–20810
Dhirapong A, Lleo A, Leung P, Gershwin ME, Liu FT (2009) The immunological potential of galectin-1 and -3. Autoimmun Rev 8(5):360–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2008.11.009
Henderson NC, Sethi T (2009) The regulation of inflammation by galectin-3. Immunol Rev 230(1):160–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00794.x
Perillo NL, Marcus ME, Baum LG (1998) Galectins: versatile modulators of cell adhesion, cell proliferation, and cell death. J Mol Med (Berl) 76(6):402–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050232
Moutsatsos IK, Wade M, Schindler M, Wang JL (1987) Endogenous lectins from cultured cells: nuclear localization of carbohydrate-binding protein 35 in proliferating 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84(18):6452–6456. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.18.6452
Sato S, Hughes RC (1994) Regulation of secretion and surface expression of Mac-2, a galactoside-binding protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem 269(6):4424–4430
Ohshima S, Kuchen S, Seemayer CA, Kyburz D, Hirt A, Klinzing S, Michel BA, Gay RE, Liu FT, Gay S, Neidhart M (2003) Galectin 3 and its binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48(10):2788–2795. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11287
Kang EH, Moon KC, Lee EY, Lee YJ, Lee EB, Ahn C, Song YW (2009) Renal expression of galectin-3 in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with nephritis. Lupus 18(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203308094361
Blidner AG, Mendez-Huergo SP, Cagnoni AJ, Rabinovich GA (2015) Re-wiring regulatory cell networks in immunity by galectin-glycan interactions. FEBS Lett 589(22):3407–3418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.08.037
Tian J, Yang G, Chen HY, Hsu DK, Tomilov A, Olson KA, Dehnad A, Fish SR, Cortopassi G, Zhao B, Liu FT, Gershwin ME, Torok NJ, Jiang JX (2016) Galectin-3 regulates inflammasome activation in cholestatic liver injury. FASEB J 30(12):4202–4213. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600392RR
Simovic Markovic B, Nikolic A, Gazdic M, Bojic S, Vucicevic L, Kosic M, Mitrovic S, Milosavljevic M, Besra G, Trajkovic V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML, Volarevic V (2016) Galectin-3 plays an important pro-inflammatory role in the induction phase of acute colitis by promoting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and production of IL-1beta in macrophages. J Crohns Colitis 10(5):593–606. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw013
Chen YJ, Wang SF, Weng IC, Hong MH, Lo TH, Jan JT, Hsu LC, Chen HY, Liu FT (2018) Galectin-3 enhances avian H5N1 influenza a virus-induced pulmonary inflammation by promoting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Am J Pathol 188(4):1031–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.12.014
Kadavath S, Efthimiou P (2015) Adult-onset Still’s disease-pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and new treatment options. Ann Med 47(1):6–14. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2014.971052
Narula N, Narula T, Abril A (2015) Seizing the clinical presentation in adult onset Still’s disease. An extensive literature review. Autoimmun Rev 14(5):472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.01.007
Kastner DL, Aksentijevich I, Goldbach-Mansky R (2010) Autoinflammatory disease reloaded: a clinical perspective. Cell 140(6):784–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.002
Sidiropoulos PI, Goulielmos G, Voloudakis GK, Petraki E, Boumpas DT (2008) Inflammasomes and rheumatic diseases: evolving concepts. Ann Rheum Dis 67(10):1382–1389. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.078014
Gattorno M, Martini A (2013) Beyond the NLRP3 inflammasome: autoinflammatory diseases reach adolescence. Arthritis Rheum 65(5):1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37882
Antoniou KM, Margaritopoulos GA, Giannarakis I, Choulaki C, Fountoulakis N, Siafakas NM, Sidiropoulos P (2013) Adult onset Still’s disease: a case report with a rare clinical manifestation and pathophysiological correlations. Case Rep Med 2013:981232. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/981232
Hsieh CW, Chen YM, Lin CC, Tang KT, Chen HH, Hung WT, Lai KL, Chen DY (2017) Elevated expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and its correlation with disease activity in adult-onset still disease. J Rheumatol 44(8):1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.161354
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, Kashiwazaki S, Tanimoto K, Matsumoto Y, Ota T et al (1992) Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 19(3):424–430
Rau M, Schiller M, Krienke S, Heyder P, Lorenz H, Blank N (2010) Clinical manifestations but not cytokine profiles differentiate adult-onset Still’s disease and sepsis. J Rheumatol 37(11):2369–2376. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.100247
Mavragani CP, Spyridakis EG, Koutsilieris M (2012) Adult-onset Still’s disease: from pathophysiology to targeted therapies. Int J Inflam 2012:879020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/879020
Koca SS, Akbas F, Ozgen M, Yolbas S, Ilhan N, Gundogdu B, Isik A (2014) Serum galectin-3 level in systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 33(2):215–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2346-8
Zhang R, Sun T, Song L, Zuo D, Xiao W (2014) Increased levels of serum galectin-3 in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome: associated with interstitial lung disease. Cytokine 69(2):289–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2014.06.008
Zuberi RI, Hsu DK, Kalayci O, Chen HY, Sheldon HK, Yu L, Apgar JR, Kawakami T, Lilly CM, Liu FT (2004) Critical role for galectin-3 in airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma. Am J Pathol 165(6):2045–2053. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63255-5
Colnot C, Ripoche MA, Milon G, Montagutelli X, Crocker PR, Poirier F (1998) Maintenance of granulocyte numbers during acute peritonitis is defective in galectin-3-null mutant mice. Immunology 94(3):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2567.1998.00517.x
Chen HY, Liu FT, Yang RY (2005) Roles of galectin-3 in immune responses. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 53(6):497–504
Sun Y, Wang Z, Chi H, Hu Q, Ye J, Liu H, Cheng X, Shi H, Zhou Z, Teng J, Yang C, Su Y (2019) Elevated serum levels of interleukin-10 in adult-onset Still's disease are associated with disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 38(11):3205–3210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04642-x
Zhao Q, Guo X, Nash GB, Stone PC, Hilkens J, Rhodes JM, Yu LG (2009) Circulating galectin-3 promotes metastasis by modifying MUC1 localization on cancer cell surface. Cancer Res 69(17):6799–6806. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1096
Song L, Tang JW, Owusu L, Sun MZ, Wu J, Zhang J (2014) Galectin-3 in cancer. Clin Chim Acta 431:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.019
Thijssen VL, Heusschen R, Caers J, Griffioen AW (2015) Galectin expression in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: a systematic review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1855(2):235–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.03.003
Traber PG, Chou H, Zomer E, Hong F, Klyosov A, Fiel MI, Friedman SL (2013) Regression of fibrosis and reversal of cirrhosis in rats by galectin inhibitors in thioacetamide-induced liver disease. PLoS One 8(10):e75361. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075361
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from China Medical University Hospital (DMR-108-165) and by a grant (MOST 107-2314-B-039-053-MY3) from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PKC conceived and designed the study; acquired the clinical data; performed the data analysis, drafting, and revising of the manuscript. JLL performed the clinical assessment as well as data acquisition and statistical analysis. JPL and CKC performed the data analysis and statistical analysis. SHC, PHH, and KJY performed the clinical assessments on study subjects and acquired the clinical data. DYC conceived and designed the study, generated the original hypothesis, acquired the clinical data, performed the data analysis, and also revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The Institutional Review Board of our hospital approved this study (CMUH107-REC3-094), and each participant’s written consent was obtained according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, PK., Lan, JL., Li, JP. et al. Elevated plasma galectin-3 levels and their correlation with disease activity in adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 39, 1945–1952 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04946-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04946-3