Abstract
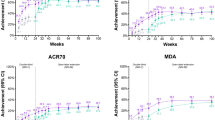
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of treatment with methotrexate (MTX), by itself or combined with other non-biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) (methotrexate, MTX with prednisolone, MTX with leflunomide, MTX with chloroquine, and MTX with sulfasalazine) on clinimetric outcomes in a retrospective cohort with a 6-month follow-up and under a Treat to Target (T2T) approach. Patients in treatment with conventional DMARDs and classified as moderate disease activity (MDA) and high disease activity (HDA) were included. Changes in disease activity score (DAS28), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), tender joint count (TJC), and swollen joint count (SJC) are compared using the Wilcoxon nonparametric test for paired data. Hypothesis contrasts were raised in order to look for differences between the different exposure groups and the outcomes defined by means of the Kruskal–Wallis (KW) nonparametric test. Follow-up was documented in 307 patients, including 250 (81.4 %) women. At the onset, 243 subjects (79.2 %) were classified as MDA and 64 (20.9 %) in HDA. A total of 247 subjects (80.4 %) presented some degree of improvement, with 156 subjects (51 %) entering remission, which is a significant number (p value = 0.047). There were no differences in the level of severity between the treatment groups (p = 0.98). This study, developed in a cohort of patients with RA with moderate or severe disease activity who were treated with MTX by itself or combined with other non-biological DMARDs under T2T strategy, showed a decrease in the severity of disease activity in 80 % of patients. The difference between monotherapy (MTX) and the combinations with other non-biological DMARDs could not be established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castrejon I, Gibson KA, Pincus T (2013) Efficacy and safety of methotrexate in combination with other non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 71(Suppl 1):S20–S28
Chan ES, Cronstein BN (2013) Mechanisms of action of methotrexate. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 71(Suppl 1):S5–S8
Aletaha D, Ward MM, Machold KP, Nell VP, Stamm T, Smolen JS (2005) Remission and active disease in rheumatoid arthritis: Defining criteria for disease activity states. Arthritis Rheum 52:2625–2636
Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Schiff MH, Kalden JR, Emery P, Eberl G, van Riel PL, Tugwell P (2003) A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:244–257
Aletaha D, Smolen J (2005) The Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI): a review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:S100–S108
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, de Wit M, Dougados M, Emery P, Gibofsky A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Haraoui B, Kalden J, Keystone EC, Kvien TK, McInnes I, Martin-Mola E, Montecucco C, Schoels M, van der Heijde D (2010) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: Recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 69:631–637
Schoels M, Knevel R, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, Breedveld FC, Boumpas DT, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, Dougados M, Emery P, van der Heijde D, Huizinga TW, Kalden J, Keystone EC, Kvien TK, Martin-Mola E, Montecucco C, de Wit M, Smolen JS (2010) Evidence for treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: Results of a systematic literature search. Ann Rheum Dis 69:638–643
Santos-Moreno, Arredondo AM, Zambrano D (2012) Improvement of disease activity in a large cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated under treat to target recommendations. J Clin Rheumat 18(9 april suppl):S5
Santos-Moreno, Arredondo AM, Zambrano D (2012) Conventional DMARD therapy and improvement of disease activity in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients treat under treat to target recommendations from a specialized rheumatology center. J Clin Rheumat 18(9 april suppl):S5
Bray K, Turpin RS, Jungkind K, Heuser G (2008) Defining success in diabetes disease management: Digging deeper in the data. Dis Manag 11:119–128
Verdecchia P, Staessen JA, Angeli F, de Simone G, Achilli A, Ganau A, Mureddu G, Pede S, Maggioni AP, Lucci D, Reboldi G (2009) Usual versus tight control of systolic blood pressure in non-diabetic patients with hypertension (Cardio-Sis): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet 374:525–533
Arguedas JA, Perez MI, Wright JM (2009) Treatment blood pressure targets for hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev Cd004349
Grigor C, Capell H, Stirling A, McMahon AD, Lock P, Vallance R, Kincaid W, Porter D (2004) Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364:263–269
Verstappen SM, Jacobs JW, van der Veen MJ, Heurkens AH, Schenk Y, ter Borg EJ, Blaauw AA, Bijlsma JW (2007) Intensive treatment with methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: aiming for remission. Computer Assisted Management in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMERA, an open-label strategy trial). Ann Rheum Dis 66:1443–1449
van Tuyl LH, Lems WF, Voskuyl AE, Kerstens PJ, Garnero P, Dijkmans BA, Boers M (2008) Tight control and intensified COBRA combination treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis: 90% remission in a pilot trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1574–1577
Symmons D, Tricker K, Roberts C, Davies L, Dawes P, Scott DL (2005) The British Rheumatoid Outcome Study Group (BROSG) randomised controlled trial to compare the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of aggressive versus symptomatic therapy in established rheumatoid arthritis. Health Technol Assess 9:iii–iv, ix-x, 1–78
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, Paulus HE, Mudano A, Pisu M, Elkins-Melton M, Outman R, Allison JJ, Suarez Almazor M, Bridges SL Jr, Chatham WW, Hochberg M, MacLean C, Mikuls T, Moreland LW, O’Dell J, Turkiewicz AM, Furst DE (2008) American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59:762–784
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gorter S, Knevel R, Nam J, Schoels M, Aletaha D, Buch M, Gossec L, Huizinga T, Bijlsma JW, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, Gabay C, Gomez-Reino J, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Martin-Mola E, McInnes I, Pavelka K, van Riel P, Scholte M, Scott DL, Sokka T, Valesini G, van Vollenhoven R, Winthrop KL, Wong J, Zink A, van der Heijde D (2010) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis 69:964–975
White D, Pahau H, Duggan E, Paul S, Thomas R (2013) Trajectory of intensive treat-to-target disease modifying drug regimen in an observational study of an early rheumatoid arthritis cohort. BMJ Open 3(7). doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003083
Vermeer M, Kuper HH, Bernelot Moens HJ, Hoekstra M, Posthumus MD, van Riel PL, van de Laar MA (2013) Adherence to a treat-to-target strategy in early rheumatoid arthritis: Results of the DREAM remission induction cohort. Arthritis Res Ther 14(6):R254. doi:10.1186/ar4099
O’Dell JR, Mikuls TR, Taylor TH, Ahluwalia V, Brophy M, Warren SR, Lew RA, Cannella AC, Kunkel G, Phibbs CS, Anis AH, Leatherman S, Keystone E (2013) Therapies for active rheumatoid arthritis after methotrexate failure. N Engl J Med 369:307–318
Moreland LW, O’Dell JR, Paulus HE, Curtis JR, Bathon JM, St Clair EW, Bridges SL Jr, Zhang J, McVie T, Howard G, van der Heijde D, Cofield SS (2012) A randomized comparative effectiveness study of oral triple therapy versus etanercept plus methotrexate in early aggressive rheumatoid arthritis: the treatment of Early Aggressive Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial. Arthritis Rheum 64:2824–2835
O’Dell JR, Haire CE, Erikson N, Drymalski W, Palmer W, Eckhoff PJ, Garwood V, Maloley P, Klassen LW, Wees S, Klein H, Moore GF (1996) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate alone, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine, or a combination of all three medications. N Engl J Med 334:1287–1291
Haagsma CJ, van Riel PL, de Jong AJ, van de Putte LB (1997) Combination of sulphasalazine and methotrexate versus the single components in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind, 52 week clinical trial. Br J Rheumatol 36:1082–1088
Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Markusse HM, van de Laar MA, Westhovens R, van Denderen JC, van Zeben D, Dijkmans BA, Peeters AJ, Jacobs P, van den Brink HR, Schouten HJ, van der Heijde DM, Boonen A, van der Linden S (1997) Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 350:309–318
Landewe RB, Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Westhovens R, van de Laar MA, Markusse HM, van Denderen JC, Westedt ML, Peeters AJ, Dijkmans BA, Jacobs P, Boonen A, van der Heijde DM, van der Linden S (2002) COBRA combination therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: Long-term structural benefits of a brief intervention. Arthritis Rheum 46:347–356
Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, Nissila M, Kautiainen H, Korpela M, Laasonen L, Julkunen H, Luukkainen R, Vuori K, Paimela L, Blafield H, Hakala M, Ilva K, Yli-Kerttula U, Puolakka K, Jarvinen P, Hakola M, Piirainen H, Ahonen J, Palvimaki I, Forsberg S, Koota K, Friman C (1999) Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised trial. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet 353:1568–1573
Dougados M, Combe B, Cantagrel A, Goupille P, Olive P, Schattenkirchner M, Meusser S, Paimela L, Rau R, Zeidler H, Leirisalo-Repo M, Peldan K (1999) Combination therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised, controlled, double blind 52 week clinical trial of sulphasalazine and methotrexate compared with the single components. Ann Rheum Dis 58:220–225
Calguneri M, Pay S, Caliskaner Z, Apras S, Kiraz S, Ertenli I, Cobankara V (1999) Combination therapy versus monotherapy for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 17:699–704
Kremer JM, Genovese MC, Cannon GW, Caldwell JR, Cush JJ, Furst DE, Luggen ME, Keystone E, Weisman MH, Bensen WM, Kaine JL, Ruderman EM, Coleman P, Curtis DL, Kopp EJ, Kantor SM, Waltuck J, Lindsley HB, Markenson JA, Strand V, Crawford B, Fernando I, Simpson K, Bathon JM (2002) Concomitant leflunomide therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite stable doses of methotrexate. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 137:726–733
Acknowledgments
We declare acknowledgments to the following: Juan Bello, MD, Danny Gomez, MD and Vanessa Giraldo, MD, as team members care for these patients. We declare that no funds or grants were received for the realization of this manuscript. The researchers would like to thank the patients who made this project possible.
Disclosure
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos-Moreno, P.I., de la Hoz-Valle, J., Villarreal, L. et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate alone and in combination with other conventional DMARDs using the T2T strategy. A cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 34, 215–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2794-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2794-9