Abstract
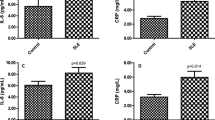
Takayasu arteritis (TA) patients with active disease often have elevated serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, which usually decline with the disease remission. The serum CRP concentration has been showed to be related to CRP gene polymorphisms in previous studies. The present study aims to investigate the associations of serum level of CRP and CRP polymorphisms with TA. A total of 178 unrelated Chinese Han TA patients and 229 unrelated Chinese Han individuals without documented disease were enrolled in our studies. After a systemic search in the HapMap database, four single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected, namely, rs1800947, rs3093077, rs1205, and rs2808630. The ligase detection reaction (LDR) was used in genotyping. CRP concentrations were determined using turbidimetric immunoassay. Genotype frequencies and allele frequencies of CRP variations were similar between TA patients and controls. CRP haplotype frequencies in patients were not significantly different from those of controls. No significant association between serum CRP concentrations and genotypes was found. Moreover, no association was found in CRP concentration between patients with types I, II, and III TA or between patients with or without pulmonary involvement. By contrast, serum CRP concentration was directly correlated with disease severity. In conclusion, CRP polymorphisms were not associated with TA susceptibility or serum CRP levels in the Chinese Han population. However, higher CRP level was correlated with a more serious disease status, which implies that CRP possibly contributes to the progression of TA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirsch MS, Aikat BK, Basu AK (1964) Takayasu’s arteritis. Report of five cases with immunologic studies. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 115:29–64
Numano F, Isohisa I, Kishi U et al (1978) Takayasu’s disease in twin sisters. Possible genetic factors. Circulation 58:173–177
Yoshida M, Kimura A, Katsuragi K et al (1993) DNA typing of HLA-B gene in Takayasu's arteritis. Tissue Antigens 42:87–90
Isohisa I, Numano F, Maezawa H et al (1978) HLA-Bw52 in Takayasu disease. Tissue Antigens 12:246–248
Lv N, Dang A, Wang Z et al (2011) Association of susceptibility to Takayasu arteritis in Chinese Han patients with HLA-DPB1. Hum Immunol 72:893-896
Dang A, Wang B, Zhang Y et al (2002) Association of the HLA-DRB1 gene with susceptibility to aortoarteritis in a Chinese Han population. Hypertens Res 25:631–634
Firooz N, Albert DA, Wallace DJ et al (2011) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 20:588-597
Hansen TK, Forsblom C, Saraheimo M et al (2010) Association between mannose-binding lectin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and the progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 53:1517-1524
Galarraga B, Khan F, Kumar P et al (2008) C-reactive protein: the underlying cause of microvascular dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:1780–1784
Elliott P, Chambers JC, Zhang W et al (2009) Genetic loci associated with C-reactive protein levels and risk of coronary heart disease. JAMA 302:37–48
Reiner AP, Barber MJ, Guan Y et al (2008) Polymorphisms of the HNF1A gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha are associated with C-reactive protein. Am J Hum Genet 82:1193–1201
Ridker PM, Pare G, Parker A et al (2008) Loci related to metabolic-syndrome pathways including LEPR, HNF1A, IL6R, and GCKR associate with plasma C-reactive protein: the Women's Genome Health Study. Am J Hum Genet 82:1185–1192
Okada Y, Takahashi A, Ohmiya H et al (2011) Genome-wide association study for C-reactive protein levels identified pleiotropic associations in the IL6 locus. Hum Mol Genet 20:1224-1231
Palomino-Morales R, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Miranda-Filloy JA et al (2009) C-reactive protein gene polymorphisms in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis from Northwestern Spain. J Rheumatol 36:341–346
Kim HA, Chun HY, Kim SH et al (2009) C-reactive protein gene polymorphisms in disease susceptibility and clinical manifestations of Korean systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 36:2238–2243
Shih PB, Manzi S, Shaw P et al (2008) Genetic variation in C-reactive protein (CRP) gene may be associated with risk of systemic lupus erythematosus and CRP concentrations. J Rheumatol 35:2171–2178
Edberg JC, Wu J, Langefeld CD et al (2008) Genetic variation in the CRP promoter: association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet 17:1147–1155
Rhodes B, Merriman ME, Harrison A et al (2010) A genetic association study of serum acute-phase C-reactive protein levels in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for clinical interpretation. PLoS Med 7:e1000341
Webb M, Chambers A, AL-N A et al (2004) The role of 18 F-FDG PET in characterising disease activity in Takayasu arteritis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:627–634
Seitz M, Reichenbach S, Bonel HM et al (2011) Rapid induction of remission in large vessel vasculitis by IL-6 blockade. A case series. Swiss Med Wkly 141:w13156
Arend WP, Michel BA, Bloch DA et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1129–1134
Ishikawa K (1978) Natural history and classification of occlusive thromboaortopathy (Takayasu's disease). Circulation 57:27–35
Ueno A, Awane Y, Wakabayashi A et al (1967) Successfully operated obliterative brachiocephalic arteritis (Takayasu) associated with the elongated coarctation. Jpn Heart J 8:538–544
Li Z, Zhang Z, He Z et al (2009) A partition-ligation-combination-subdivision EM algorithm for haplotype inference with multiallelic markers: update of the SHEsis (http://analysis.bio-x.cn). Cell Res 19:519-523
Doumatey AP, Chen G, Tekola Ayele F et al (2012) C-reactive protein (CRP) promoter polymorphisms influence circulating CRP levels in a genome-wide association study of African Americans. Hum Mol Genet 21:3063-3072
Naitza S, Porcu E, Steri M et al (2012) A genome-wide association scan on the levels of markers of inflammation in Sardinians reveals associations that underpin its complex regulation. PLoS Genet 8:e1002480
Dehghan A, Dupuis J, Barbalic M et al (2011) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in >80 000 subjects identifies multiple loci for C-reactive protein levels. Circulation 123:731-738
Almeida OP, Norman PE, Allcock R et al (2009) Polymorphisms of the CRP gene inhibit inflammatory response and increase susceptibility to depression: the Health in Men Study. Int J Epidemiol 38:1049–1059
Kardys I, de Maat MP, Uitterlinden AG et al (2006) C-reactive protein gene haplotypes and risk of coronary heart disease: the Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J 27:1331–1337
Miller DT, Zee RY, Suk Danik J et al (2005) Association of common CRP gene variants with CRP levels and cardiovascular events. Ann Hum Genet 69:623–638
Komurcu-Bayrak E, Erginel-Unaltuna N, Onat A et al (2009) Association of C-reactive protein (CRP) gene allelic variants with serum CRP levels and hypertension in Turkish adults. Atherosclerosis 206:474–479
Polterauer S, Grimm C, Zeillinger R et al (2011) Association of C-reactive protein (CRP) gene polymorphisms, serum CRP levels and cervical cancer prognosis. Anticancer Res 31:2259-2264
Veen G, Giltay EJ, van Vliet IM et al (2011) C-reactive protein polymorphisms are associated with the cortisol awakening response in basal conditions in human subjects. Stress 14:128-135
Ottaviani S, Gorrini M, Scabini R et al (2011) C reactive protein and alpha1-antitrypsin: relationship between levels and gene variants. Transl Res 157:332-338
Walter MA, Melzer RA, Schindler C et al (2005) The value of [18 F]FDG-PET in the diagnosis of large-vessel vasculitis and the assessment of activity and extent of disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:674–681
Jiang L, Li D, Yan F et al (2012) Evaluation of Takayasu arteritis activity by delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Cardiol 155:262-267
Disclosures
None.
Funding source
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81170285) and the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (grant no. 20101106110012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplement Table 1
Classification of Disease Severity (PDF 52 kb)
Supplement Table 2
Haplotypes frequencies of CRP gene in Cases and Controls (PDF 11 kb)
Supplement Table 3
Association between Disease Severity and rs1205 (PDF 9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Dang, A., Lv, N. et al. Serum C-reactive protein level but not its gene polymorphism is associated with Takayasu arteritis. Clin Rheumatol 35, 673–678 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2674-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2674-3