Abstract
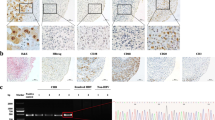
The prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in China is high. Four percent of patients with HBV infection can present with polyarthritis and positive rheumatic factor similar to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here, we investigated the association between HBV infection and serological, radiological, or histological disease status in RA. According to HBV infection status, 223 consecutive hospitalized Chinese patients with RA were divided into the groups of chronic HBV infection, past HBV infection, and no HBV infection. Clinical data and hand radiographs were collected. Synovium was obtained by closed-needle biopsy, and serial tissue sections were stained immunohistochemically for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and cluster of differentiation (CD) markers. (1) The prevalence of HBsAg positivity and chronic hepatitis B in RA was consistent with the age-matched general Chinese population (11.2 vs. 8.7 %, 1.7 vs. 1.0 %, respectively, P > 0.05). (2) Clinical parameters, disease activity score in 28 joints, or Sharp scores showed no significant difference among the three groups in 206 RA or 140 treatment-naïve patients, both with active disease (all P > 0.05). (3) Synovial immunohistochemical staining showed negative HBsAg in ten RA patients with HBV carrier status and ten RA patients with past HBV infection. Except for higher subintimal CD3+ cell density in the past HBV infection group, Krenn’s synovitis score, mean densities of subintima positive-staining cells (CD20, CD38, CD79a, and CD68), and CD34+ microvessel counts showed no significant difference among RA patients with HBV carrier status, past HBV infection, or no HBV infection (all P > 0.05). Chronic HBV infection may have no significant effect on disease activity, synovitis, or joint destruction in RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365:2205–2219
Auger I, Roudier J (1997) A function for the QKRAA amino acid motif: mediating binding of DnaJ to DnaK. Implications for the association of rheumatoid arthritis with HLA-DR4. J Clin Invest 99:1818–1822
Kamphuis S, Kuis W, de Jager W, Teklenburg G, Massa M, Gordon G et al (2005) Tolerogenic immune responses to novel T-cell epitopes from heat-shock protein 60 in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 366:50–56
Wegner N, Wait R, Sroka A, Eick S, Nguyen KA, Lundberg K et al (2010) Peptidylarginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis citrullinates human fibrinogen and alpha-enolase: implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:2662–2672
Ganem D, Prince AM (2004) Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med 350:1118–1129
Lok AS, McMahon BJ (2007) Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 45:507–539
Liang X, Bi S, Yang W, Wang L, Cui G, Cui F et al (2009) Epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B in China—declining HBV prevalence due to hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccine 27:6550–6557
Han SH (2004) Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Liver Dis 8:403–418
Maillefert JF, Sibilia J, Toussirot E, Vignon E, Eschard JP, Lorcerie B et al (1999) Rheumatic disorders developed after hepatitis B vaccination. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38:978–983
Csepregi A, Rojkovich B, Nemesanszky E, Poor G, Hejjas M, Horanyi M (2000) Chronic seropositive polyarthritis associated with hepatitis B virus-induced chronic liver disease: a sequel of virus persistence. Arthritis Rheum 43:232–233
Scully LJ, Karayiannis P, Thomas HC (1992) Interferon therapy is effective in treatment of hepatitis B-induced polyarthritis. Dig Dis Sci 37:1757–1760
Permin H, Aldershvile J, Nielsen JO (1982) Hepatitis B virus infection in patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 41:479–482
Lim MK, Sheen DH, Lee YJ, Mun YR, Park M, Shim SC (2009) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies distinguish hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated arthropathy from concomitant rheumatoid arthritis in patients with chronic HBV infection. J Rheumatol 36:712–716
Csepregi A, Nemesanszky E, Rojkovich B, Poor G (2001) Rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis B virus: evaluating the pathogenic link. J Rheumatol 28:474–477
Maya R, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y (2008) Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and autoimmune disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34:85–102
Ram M, Anaya JM, Barzilai O, Izhaky D, Porat KB, Blank M et al (2008) The putative protective role of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection from autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun Rev 7:621–625
Vassilopoulos D, Calabrese LH (2008) Virally associated arthritis 2008: clinical, epidemiologic, and pathophysiologic considerations. Arthritis Res Ther 10:215
Momohara S, Okamoto H, Tokita N, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N (2006) Rapidly destructive knee arthropathy associated with hepatitis B. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24:111–112
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CR et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Schiff MH, Kalden JR, Emery P, Eberl G et al (2003) A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:244–257
Aletaha D, Smolen JS (2006) The definition and measurement of disease modification in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32:9–44
Fransen J, Creemers MC, Van Riel PL (2004) Remission in rheumatoid arthritis: agreement of the disease activity score (DAS28) with the ARA preliminary remission criteria. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1252–1255
van der Heijde D (2000) How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol 27:261–263
Dienstag JL (2008) Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med 359:1486–1500
Hoofnagle JH (2009) Reactivation of hepatitis B. Hepatology 49:S156–S165
Schumacher HJ, Kulka JP (1972) Needle biopsy of the synovial membrane—experience with the Parker–Pearson technic. N Engl J Med 286:416–419
Gerlag D, Tak PP (2005) Synovial biopsy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 19:387–400
Krenn V, Morawietz L, Burmester GR, Kinne RW, Mueller-Ladner U, Muller B et al (2006) Synovitis score: discrimination between chronic low-grade and high-grade synovitis. Histopathology 49:358–364
Nanashima A, Nakayama T, Sumida Y, Abo T, Takeshita H, Shibata K et al (2008) Relationship between microvessel count and post-hepatectomy survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 14:4915–4922
Bresnihan B, Cunnane G, Youssef P, Yanni G, Fitzgerald O, Mulherin D (1998) Microscopic measurement of synovial membrane inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: proposals for the evaluation of tissue samples by quantitative analysis. Br J Rheumatol 37:636–642
Youssef PP, Smeets TJ, Bresnihan B, Cunnane G, Fitzgerald O, Breedveld F et al (1998) Microscopic measurement of cellular infiltration in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane: a comparison of semiquantitative and quantitative analysis. Br J Rheumatol 37:1003–1007
Wang Q, Chen YS, Wang XJ, Wang WJ, Wang YL, Liang XF (2007) Investigation and study of the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B and C. Modern Preventive Medicine 21:4005–4006
Kim DA, Kim TY (2010) Is screening for hepatitis necessary in diagnostic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea? J Rheumatol 37(674–675):675
Gabriel SE (2001) The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 27:269–281
Zeng QY, Chen R, Darmawan J, Xiao ZY, Chen SB, Wigley R et al (2008) Rheumatic diseases in China. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R17
Chung SJ, Kim JK, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK (2009) Reactivation of hepatitis B viral infection in inactive HBsAg carriers following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J Rheumatol 36:2416–2420
Thong BY, Koh ET, Chng HH, Chow WC (2007) Outcomes of chronic hepatitis B infection in Oriental patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann Acad Med Singap 36:100–105
Pijak M, Gazdik F (2002) Negative association between rheumatoid arthritis and both hepatitis B infection and rHBsAg vaccination. Hepatology 36:2208
Pope JE, Stevens A, Howson W, Bell DA (1998) The development of rheumatoid arthritis after recombinant hepatitis B vaccination. J Rheumatol 25:1687–1693
Rulli NE, Melton J, Wilmes A, Ewart G, Mahalingam S (2007) The molecular and cellular aspects of arthritis due to alphavirus infections: lesson learned from Ross River virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1102:96–108
Posnett DN, Yarilin D (2005) Amplification of autoimmune disease by infection. Arthritis Res Ther 7:74–84
Schumacher HR, Gall EP (1974) Arthritis in acute hepatitis and chronic active hepatitis. Pathology of the synovial membrane with evidence for the presence of Australia antigen in synovial membranes. Am J Med 57:655–664
Liaw YF (2009) Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and long-term outcome under treatment. Liver Int 29(Suppl 1):100–107
Chisari FV, Isogawa M, Wieland SF (2010) Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Pathol Biol (Paris) 58:258–266
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients and medical staff who generously contributed to this study. This work was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Research Grant (grant no. 30972742) and the Natural Science Research Grant of Guangdong Province, China (grant no. 9151008901000130) to L. Dai; Chinese National Natural Science Research Grant (no. 81001334), Guangdong Natural Science Research Grant (no. 10451008901004542), Health Department Grant of Guangdong Province (no. B2010083), Yat-Sen Scholarship for Young Scientist, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. 10ykpy19) to L-J Zhu.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chan-Juan Zou and Lang-Jing Zhu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, CJ., Zhu, LJ., Li, YH. et al. The association between hepatitis B virus infection and disease activity, synovitis, or joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 32, 787–795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2170-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2170-1