Abstract
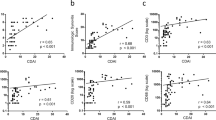
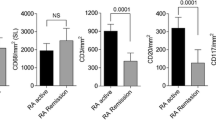
To investigate the histological changes of synovium in cases of effect attenuation occurring after the use of infliximab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we histologically assessed synovial tissue from ten methotrexate-treated RA patients and 12 infliximab-treated RA patients after arthroscopic synovectomy. The synovium was observed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain and analyzed immunohistochemically for expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), B-cell transmembrane protein, cluster of differentiation 20 (CD20), nuclear factor kappa B (NFkB), bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). H&E staining showed significant vascular proliferation in the synovium of the RA patients in the infliximab group (p < 0.05). Immunohistochemical examinations showed that TNF-α was completely blocked in patients with effect attenuation who received infliximab (p < 0.05). IL-6 was more strongly expressed in the interstitial cells of synovium of patients who received infliximab than in the cells of patients in the control group (p < 0.05). MMP-3 was expressed on the surface of synovium, and CD20 and BrdU were strongly expressed in the infliximab group compared with the control group (p < 0.05). NFkB was expressed in both groups. VEGF was decreased in the infliximab group compared with control. These findings indicate that the expression pattern of immunohistochemical findings in synovium was changed in effect attenuation cases among RA patients treated with infliximab.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris ED Jr (1990) Rheumatoid arthritis: pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 322:1277–1289
Nishimoto N (2006) Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:277–281
Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Long-Fox A, Charles P, Katsikis P, Fledmann M et al (1993) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor a. Arthritis Rheum 36:1681–1690
Nakahara H, Song J, Sugimoto M, Hagihara K, Kishimoto T, Yoshizaki K et al (2003) Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody therapy reduces vascular endothelial growth factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:1521–1529
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR et al (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1594–1602
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJ, Hazes JM et al (2005) Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 52:3381–3390
van der Heijde D, Klareskog L, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Codreanu C, Bolosiu H, Melo-Gomes J et al (2006) Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: two-year clinical and radiographic results from the TEMPO study, a double-blind, randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum 54:1063–1074
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R et al (2006) The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54:26–37
Smolen JS, Maini RN (2006) Interleukin-6: a new therapeutic target. Arthritis Res Ther 8:407
Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC et al (2006) Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum 54:2793–2806
Kremer JM, Dougados M, Emery P, Durez P, Sibilia J, Shergy W, Steinfeld S et al (2005) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with the selective costimulation modulator abatacept: twelve-month results of a phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 52:2263–2271
Lindberg J, af Klint E, Catrina AI, Nilsson P, Klareskog L, Ulfgren AK, Lundeberg J et al (2006) Effect of infliximab on mRNA expression profiles in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R179
Steinbrocker O, Traeger CH, Battman RC (1949) Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 140:659–662
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof MA, van Riel PL, Theunisse LA, Lubberts EW, van Leeuwen MA et al (1990) Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis 49:916–920
Farahat MN, Yanni G, Poston R, Panayi GS (1993) Cytokine expression in synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rhem Dis 52:870–875
Zink A, listing J, Kary S, Ramlau P, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Babinsky K et al (2005) Treatment continuation in patients receiving biological agents or conventional DMARD therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1274–1279
van der Laken CJ, Voskuyl AE, Roos JC, Stigter van Walsum M, de Groot ER, Wolbink G et al (2007) Imaging and serum analysis of immune complex formation of radiolabelled infliximab and anti-infliximab in responders and non-responders to therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:253–256
Takemura T, Kanbe K, Takeuchi K, Inoue K, Takagishi K (2005) Serum matrix metalloproteinase activity relating to cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. APLAR J Rheumatol 8:213–219
Hibi M, Murakami M, Saito M, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T et al (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell 63:1149–1157
Kanbe K, Inoue K (2006) Efficacy of arthroscopic synovectomy for the effect attenuation cases of infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 25:877–881
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) (C) (19591769) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), and grants-in-aid from the Aichi DRG Foundation, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanbe, K., Inoue, K., Inoue, Y. et al. Histological analysis of synovium in cases of effect attenuation associated with infliximab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 27, 777–781 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0850-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0850-z