Abstract
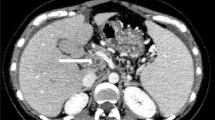
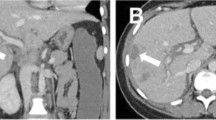
Systemic lupus erythematosus can be complicated by the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). The clinical manifestations of this syndrome most often documented thus far are recurrent deep venous thrombosis, recurrent spontaneous abortions, and cerebral vascular accidents. Abdominal ischemic events have received relatively little attention in prior reports. We report on a lupus patient with lupus anticoagulant positivity who presented with abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss who was subsequently diagnosed with gastric ulcers and pancreatitis. Computerized tomography of the abdomen in addition revealed splenic and kidney infarcts. We conclude that this patient had (ischemic) chronic pancreatitis with pseudocysts and splenic and renal infarcts probably due to secondary APS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- APS:
-
Antiphospholipid syndrome
- PPI:
-
Proton pump inhibitor
References
Stegnar M, Bozic B, Peternel P et al (1991) Prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in deep venous thrombosis and their relationship to blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Thromb Res 63:433–443
Love PE, Santoro SA (1990) Antiphospholipid antibodies: anticardiolipin and the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and non-SLE disorders. Ann Intern Med 112:682–698
Asherson RA, Khamashta MA, Ordi-Ros J (1989) Primary antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine 68:366–374
Kaul M, Erkan D, Sammaritano L, Lockshin MD (2007) Assessment of the 2006 revised antiphospholipid syndrome classification criteria. Ann Rheum Dis 66:927–930
Samarkos M, Davies KA, Gordon C, Loizou S (2006) Clinical significance of IgA anticardiolipin and anti-beta2-GP1 antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 25:199–204
Breur GS, Baer A, Dahan D, Nesher G (2006) Lupus-associated pancreatitis. Autoimmun Rev 5:314–318
Roman MJ, Shanker BA, Davis A et al (2003) Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349:2399–406
Wang CR, Hsieh HC, Lee GL, Chuang CY, Chen CY (1992) Pancreatitis related to antiphospholipid antibody syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 19:1123–1125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornelis, T., Breynaert, C. & Blockmans, D. An abdominal pain syndrome in a lupus patient. Clin Rheumatol 27, 257–259 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0711-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0711-1