Abstract
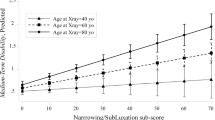
This study aims to examine the long-term articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients according to rheumatoid arthritis articular damage (RAAD) score and to evaluate the parameters correlated with this score. The RAAD score was assessed in 85 RA patients who had the disease for more than 10 years. Patients were divided into three groups according to duration of the disease: group 1, 10–14 years; group 2, 15–19 years; and group 3, more than 20 years. Patients were also divided into three groups according to the time of initiation of treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: group A, within the first 2 years, group B, between 2 and 5 years; and group C, after 5 years. We investigated the RAAD score relationship between groups 1, 2, 3; groups A, B, C; sex; drug compliance; age of onset of the disease; and Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ). We observed significant differences in RAAD scores according to groups 1, 2, 3 (p<0.01), but not to groups A, B, C; sex; or drug compliance (p>0.05). While the RAAD score correlated well with the HAQ (r=0.560, p<0.001), it did not correlate with the age at onset of the disease (p>0.05). As RA is not a benign disease and articular damage progresses over time, the goal of RA therapy must be to maintain a response before the onset of irreversible damage and loss of function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott DL, Pugner K, Kaarela K et al (2000) The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 39:122–132
Zijlstra TR, Moens HJ, Bukhari MAS (2002) The rheumatoid arthritis articular damage score: first steps in developing a clinical index of long term damage in RA. Ann Rheum Dis 61:20–23
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1998) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SAJ et al (1983) Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum 26:1346–1353
Ritchie DM, Boyle JA, McInnes JM et al (1968) Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 37:393–406
Lubeck DP (2004) Patient reported outcomes and their role in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 22(suppl 1):13–26
Harris ED Jr (1989) The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB (eds) Textbook of rheumatology. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, pp 943–981
Drossaers-Bakker KW, Kroon HM, Zwinderman AH et al (2000) Radiographic damage of large joints in long-term rheumatoid arthritis and its relation to function. Rheumatology 39:998–1003
Scott DL, Smith C, Kingsley G (2003) Joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis: an updated systematic review. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21:20–27
Li C, Scott DL, Deodhar A et al (1999) Radiological gradients and predicting the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 58(suppl):97
Larsen A, Thoen J (1987) Hand radiography of 200 patients with rheumatoid arthritis repeated after an interval of one year. Scand J Rheumatol 16:395–401
Wolfe F, Sharp JT (1998) Radiologic outcome of recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41:1571–1582
van Riel PLCM, Wijnands MJH, van de Putte LBA (1998) Evaluation and management of active inflammatory disease. In: Klippel JH, Dieppe PA (eds) Rheumatology, 2nd edn. Mosby, London, pp 14.1–14.12
Thompson PW, Pegley FS (1991) A comparison of disability measured by the Standford Health Assessment Questionnaire disability scales (HAQ) in male and female rheumatoid outpatients. Br J Rheumatol 30:298–300
Egsmose C, Lund B, Borg G et al (1995) Patients with rheumatoid arthritis benefit from early 2nd line therapy: 5 year follow up of a prospective double blind placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol 22:2208–2213
Van der Heide A, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW et al (1996) The effectiveness of early treatment with “second line” antirheumatic drugs. A randomised, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 124:699–707
Scott DL (2004) Pursuit of optimal outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 22:13–26
Lee P, Tan WP (1979) Drug compliance in outpatients with rheumatoid arthritis. Aust N Z J Med 9:274–277
Gradual N (2004) The natural history and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis: association of radiographic outcome with process variables, joint motion and immune proteins. Scand J Rheumatol 33:1–37
Skoumal M, Wottawa A (2002) Long term observation study of Austrian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Med Austriaca 29:52–56
Welsing PM, Van Gestel AM, Swýnkels HL et al (2001) The relationship between disease activity, joint destruction and functional capacity over the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44:2009–2017
Bakker KW, Amesz E, van Zeben D et al (1998) Long term outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: destruction versus disability. Br J Rheumatol 37:85
Pollard Z, Choy EH, Scott DL (2005) The consequences of rheumatoid arthritis: Quality of life measures in the individual patient. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(suppl 9):S43–S52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eksioglu, E., Tuncay, R., Gurcay, E. et al. Articular damage in late rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 26, 314–318 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0293-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0293-3