Abstract.
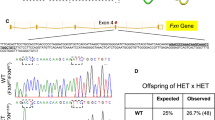
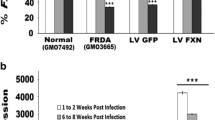
We have generated and characterised transgenic mice that contain the entire Friedreich's ataxia gene (FRDA) within a human YAC clone of 370 kb. In an effort to overcome the embryonic lethality of homozygous Frda knockout mice and to study the behaviour of human frataxin in a mouse cellular environment, we bred the FRDA YAC transgene onto the null mouse background. Phenotypically normal offspring that express only YAC-derived human frataxin were identified. The human frataxin was expressed in the appropriate tissues at levels comparable to the endogenous mouse frataxin, and it was correctly processed and localised to mitochondria. Biochemical analysis of heart tissue demonstrated preservation of mitochondrial respiratory chain function, together with some increase in citrate synthase and aconitase activities. Thus, we have demonstrated that human frataxin can effectively substitute for endogenous murine frataxin in the null mutant. Our studies are of immediate consequence for the generation of Friedreich's ataxia transgenic mouse models, and further contribute to the accumulating knowledge of human-mouse functional gene replacement systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pook, M.A., Al-Mahdawi, S., Carroll, C.J. et al. Rescue of the Friedreich's ataxia knockout mouse by human YAC transgenesis. Neurogenetics 3, 185–193 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100480100118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100480100118