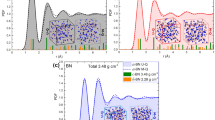
Abstract
Context
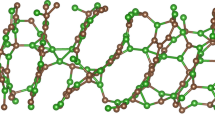
By means of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, possible boron-rich amorphous silicon borides (BnSi1−n, 0.5 ≤ n ≤ 0.95) are generated and their microstructure, electrical properties and mechanical characters are scrutinized in details. As expected, the mean coordination number of each species increases progressively and more closed packed structures form with increasing B concentration. In all amorphous models, pentagonal pyramid-like configurations are observed and some of which lead to the development of B12 and B11Si icosahedrons. It should be noted that the B11Si icosahedron does not form in any crystalline silicon borides. Due to the affinity of B atoms to form cage-like clusters, phase separations (Si:B) are perceived in the most models. All simulated amorphous configurations are a semiconducting material on the basis of GGA+U calculations. The bulk modulus of the computer-generated amorphous compounds is in the range of 90 GPa to 182 GPa. As predictable, the Vickers hardness increases with increasing B content and reaches values of 25-33 GPa at 95% B concentration. Due to their electrical and mechanical properties, these materials might offer some practical applications in semiconductor technologies.
Method
The density functional theory (DFT) based ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations were used to generate B-rich amorphous configurations.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms a part of an ongoing study.
References
Moissan H, Stock A (1990) Preparation and properties of two silicon borides: SiB3 and SiB6. CR Acad Sci 131:139–143
Samsonov GV, Latysheva VP (1995) voprosu o khimicheskikh soedineniyakh bora s kremniem. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 105:499–499
Zhuravlev NN (1956) X-ray determination of the structure of SiB. Kristallografiya 1:666–668
Adamsky RF (1958) Unit cell and space group of orthorhombic SiB6. Acta Crystallogr 11:744–745
Cline CF (1958) Preliminary investigations of the silicon boride, SiB6. Nature 181:476–477
Cline CF (1959) An investigation of the compound silicon boride (SiB6). J Electrochem Soc 106:322–322
Giese R (1970) Polyhedral groups in the phase SiB6. Electron Technol 3:151–157
Vlasse M, Slack GA, Garbauslas M, Kasper JS, Viala JC (1986) The crystal structure of SiB6. J Solid State Chem 63:31–45
Brosset C (1960) Magnusson B. The silicon-boron system. Nature 187:54–55
Cline CF, Sands DE (1960) A new silicon boride, SiB4. Nature 185:456–456
Matkovich VI (1960) A new form of boron silicide, B4Si. Acta Crystallogr 13:679–680
Magnusson B, Brosset C (1962) The crystal structure of В2.8Si. Acta Chem Scand 16:449–455
Dietze W, Miller M, Amberger E (1970) Pyrolitic formation of Si-doped B and silicon borides. Electron Technol 3:73–79
Rizzo HF, Bidwell LR (1960) Formation and structure of SiB4. J Am Ceram Soc 43:550–552
Samsonov GV, Sleptsov VM (1964) Preparation of boron-silicon alloys. Sov Powder Metall Met Ceram 3:488–496
Bairamashvili IA, Kalandadze GI, Eristavi AM, Jobava JS, Chotulidi VV, Saloev YI (1979) An investigation of the physicomechanical properties of B6O and SiB4. J Less Common Met 67:455–459
Tremblay R (1989) Angers R. Preparation of high purity SiB4 by solid-state reaction between Si and B. Ceram Int 15:73–78
Tremblay R, Angers R (1991) Mechanical characterization of dense silicon tetraboride (SiB4). Ceram Int 18:113–117
Emin D (1987) Icosahedral boron-rich solids as refractory semiconductors. MRS OPL Archive 97:3–15
Lundstro T, Andreev YG (1996) Superhard boron-rich borides and studies of the BCN system. Mater Sci Eng A 209:16–22
Slack GA, Morgan KE (2014) Some crystallography, chemistry, physics, and thermodynamics of B12O2, B12P2, B12As2, and related alpha-boron type crystals. J Phys Chem Solid 75:1054–1074
Slack GA, McNelly TF, Taft EA (1983) Melt growth and properties of B6P crystals. J Phys Chem Solid 44:1009–1013
Hubert H, Devouard B, Garvie LA, O'Keeffe M, Buseck PR, Petuskey WT, McMillan PF (1998) Icosahedral packing of B12 icosahedra in boron suboxide (B6O). Nature 391:376–378
Zhang H, Yao S, Widom M (2016) Predicted phase diagram of boron-carbon-nitrogen. Phys Rev B 93:144107
Franz R, Werheit H (1991) Boron—rich solids. AIP Conf Proc 231:29
Emin D (1987) Icosahedral boron-rich solids. Phys Today 40:55–62
Hori A, Takeda M, Yamashita H, Kimura K (1995) Absorption edge spectra of boron-rich amorphous films constructed with icosahedral cluster. J Physical Soc Japan 64:3496–3505
Berezin AA, Golokova OA, Kazanin MM, Khomidov T, Mirlin DN, Petrov AV, Umarov AS, Zaitsev VK (1974) Electrical and optical properties of amorphous boron and amorphous concept for ß-rhombohedral boron. J Non Cryst Solids 16:237–246
Matsuda H, Nakayama T, Kimura K, Murakami Y, Suematsu H, Kobayashi M, Higashi I (1995) Structural and electronic properties of Li-and Cu-doped β-rhombohedral boron constructed from icosahedral and truncated icosahedral clusters. Phys Rev B 52:6102–6110
Motozima S, Sugiyama K, Takahashi Y (1975) Chemical vapor deposition of tetraboron silicide whiskers. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 48:1463–1466
Tsai CC (1979) Characterization of amorphous semiconducting silicon-boron alloys prepared by plasma decomposition. Phys Rev B 19:2041–2055
Murase K, Ogino T, Mizushima Y (1983) Thermal oxidation of amorphous silicon-germanium-boron alloy. Jpn J Appl Phys 22:1771–1777
Ong CW, Chik KP, Wong HK (1993) Effects of Si incorporation on the structural change of a-BxSi1−x alloy films. J Appl Phys 74:6094–6099
Yang GR, Zhao YP, Tong BY (1996) FTIR and UV study of amorphous silicon-boron alloys deposited by LPCVD. MRS OPL Archive 426:83–88
Yang GR, Zhao YP, Abburi M, Dabral S, Tong BY (1997) Comparison of low-temperature oxidation of crystalline Si and B with a-Si:B alloy: an x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. J Vac Sci Technol A 15:279–283
Chen L, Goto T, Li J, Hirai T (1996) Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of boron-rich silicon borides. Mater Trans JIM 37:1182–1185
Takeda M, Ichimura M, Yamaguchi H, Sakairi Y, Kimura K (2000) Preparation of boron–silicon thin film by pulsed laser deposition and its properties. J Solid State Chem 154:141–144
Ordejón P, Artacho E, Soler JM (1996) Self-consistent order-N density-functional calculations for very large systems. Phys Rev B 53:R10441–R10444
Troullier N, Martins JL (1991) Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys Rev B 43:1993–2006
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190
Mostafa A, Medraj M (2017) Binary phase diagrams and thermodynamic properties of silicon and essential doping elements (Al, As, B, Bi, Ga, In, N, P, Sb and Tl). Materials 10(6):676
Eklöf D, Fischer A, Ektarawong A et al (2019) Mysterious SiB3: identifying the relation between α-and β-SiB3. ACS Omega 4:18741–18759
Salvador JR, Bilc D, Mahanti SD, Kanatzidis MG (2003) Stabilization of β-SiB3 from liquid Ga: a boron-rich binary semiconductor resistant to high-temperature air oxidation. Angew Chem 42:1973–1976
Gali A, Miro J, Deák P, Ewels CP, Jones R (1996) Theoretical studies on nitrogen-oxygen complexes in silicon. J Phys Condens Matter 8:7711–7722
Voronoi G (1908) Recherches sur les paralléloèdres primitives. J Reine Angew Math 134:198–287
Brostow W et al (1998) Voronoi polyhedra and Delaunay simplexes in the structural analysis of molecular-dynamics-simulated materials. Physical Review B 57:13448
Momma K, Izumi F (2011) VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J Appl Cryst 44:1272–1276
Nelmes RJ, Loveday JS, Allan DR, Besson JM, Hamel G, Grima P, Hull S (1993) Neutron-and x-ray-diffraction measurements of the bulk modulus of boron. Phys Rev B 47:7668–7673
Zhang B, Wu L, Li Z (2017) Predicted structural evolution and detailed insight into configuration correlation, mechanical properties of silicon–boron binary compounds. RSC Adv 7:16109–16118
Zarechnaya EY, Dubrovinsky L, Dubrovinskaia N et al (2009) Superhard semiconducting optically transparent high pressure phase of boron. Phys Rev Lett 102:185501
Jiang C, Lin Z, Zhang J, Zhao Y (2009) First-principles prediction of mechanical properties of gamma-boron. Appl Phys Lett 94:191906
Aydin S, Simsek M (2011) First-principles calculations of elemental crystalline boron phases under high pressure: Orthorhombic B28 and tetragonal B48. J Alloys Compd 509:5219–5229
Getmanskii IV, Minyaev RM, Koval VV, Minkin VI (2018) Quantum chemical modeling of solid-state B4X structures containing tetrahedral B4 units with X= B, C, Al, Si. Mendeleev Comm 28:173–175
Qin J, Nishiyama N, Ohfuji H, Shinmei T, Lei L, He D, Irifune T (2012) Polycrystalline γ-boron: as hard as polycrystalline cubic boron nitride. Scr Mater 67:257–260
Teter DM (1998) Computational alchemy: the search for new superhard materials. MRS Bull 23:22–27
Chen XQ, Niu H, Li D, Li Y (2011) Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 19:1275–1281
Tian Y, Xu B, Zhao Z (2012) Microscopic theory of hardness and design of novel superhard crystals. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 33:93–106
Oganov AR, Chen J, Gatti C et al (2012) Ionic high-pressure form of elemental boron. Nature 457:863–867
Solozhenko VL, Kurakevych OO, Oganov AR (2008) On the hardness of a new boron phase, orthorhombic γ-B28. J Superhard Mater 30:428–429
Vaitheeswaran G, Kanchana V, Svane A, Delin A (2007) Elastic properties of MgCNi3—a superconducting perovskite. J Phys Condens Matter 19:326214
Frantsevich IN (1982) Elastic moduli of metals and ınsulators handbook. Naukova Dumka, Kiev
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) under MAG award 117M372. AÖK acknowledges partial financial support from YÖK 100/2000 and TÜBİTAK BİDEB 2211-C programs. We acknowledge the computing time provided by the TÜBİTAK High Performance and Grid Computing Center (TRUBA resources).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ayşegül Özlem Çetin Karacaoğlan: investigation, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft, and visualization. Murat Durandurdu: conceptualization, methodology, resources, supervision, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no known competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karacaoğlan, A.Ö.Ç., Durandurdu, M. Possible boron-rich amorphous silicon borides from ab initio simulations. J Mol Model 29, 92 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05491-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05491-x