Abstract
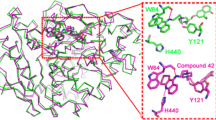
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is a potential target for the development of small molecules as inhibitors for the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To design highly active acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, a three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) approach was performed on a series of N-benzylpyrrolidine derivatives previously evaluated for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. The developed two models, CoMFA and CoMSIA, were statistically validated, and good predictability was achieved for both models. The information generated from 3D-QSAR contour maps may provide a better understanding of the structural features required for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and help to design new potential anti-acetylcholinesterase molecules. Consequently, six novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors were designed, among which compound A1 with the highest predicted activity was subjected to detailed molecular docking and compared to the most active compound. Extra-precision molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of 50 ns and binding free energy calculations using MM-GBSA were performed for the selected compounds to validate the stability. These results may afford important structural insights needed to identify novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and other promising strategies in drug discovery.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All the data are available in the main manuscript.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Sivakumar M, Saravanan K, Saravanan V, Sugarthi S, Madan Kumar SM, Alhaji Isa M, Rajakumar P, Aravindhan S (2020) Discovery of new potential triplet acting inhibitor for Alzheimer’s disease via X-ray crystallography, molecular docking and molecular dynamics. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38:1903–1917. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1620128
Xu M, Peng Y, Zhu L, Wang S, Ji J, Rakesh KP (2019) Triazole derivatives as inhibitors of Alzheimer’s disease: Current developments and structure-activity relationships. Eur J Med Chem 180:656–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.07.059
Scipioni M, Kay G, Megson IL, Kong Thoo Lin P (2019) Synthesis of novel vanillin derivatives: novel multi-targeted scaffold ligands against Alzheimer’s disease. MedChemComm 10:764–777. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00048H
Zhang C, Du Q-Y, Chen L-D, Wu W-H, Liao S-Y, Yu L-H, Liang X-T (2016) Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel tacrine-multialkoxybenzene hybrids as multi-targeted compounds against Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem 116:200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.077
El Khatabi K, Aanouz I, El-Mernissi R, Khaldan A, Ajana MA, Bouachrine M, Lakhlifi T (2020) 3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of p-aminobenzoic acid derivatives to explore the features requirements of Alzheimer inhibitors. Orbital Electron J Chem 12:172–181. https://doi.org/10.17807/orbital.v12i4.1467
Nichols MR, Moss MA, Reed DK, Cratic-McDaniel S, Hoh JH, Rosenberry TL (2004) Amyloid-β protofibrils differ from amyloid-β aggregates induced in dilute hexafluoroisopropanol in stability and morphology. J Biol Chem 280:2471–2480. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M410553200
Wu M, Ma J, Ji L, Wang M, Han J, Li Z (2019) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of rutacecarpine derivatives as multitarget-directed ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem 177:198–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.05.055
Du X, Wang X, Geng M (2018) Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Transl Neurodegener 7:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-018-0107-y
Barai P, Raval N, Acharya S, Borisa A, Bhatt H, Acharya N (2018) Neuroprotective effects of bergenin in Alzheimer’s disease: Investigation through molecular docking, in vitro and in vivo studies. Behav Brain Res 356:18–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.010
Dvir H, Silman I, Harel M, Rosenberry TL, Sussman JL (2010) Acetylcholinesterase: from 3D structure to function. Chem Biol Interact 187:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.042
Choi SS, Lee S-R, Kim SU, Lee HJ (2014) Alzheimer’s disease and stem cell therapy. Exp Neurobiol 23:45–52. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2014.23.1.45
Barakat A, Alshahrani S, Al-Majid AM, Ali M, Altowyan MS, Islam MS, Alamary AS, Ashraf S, Ul-Haq Z (2020) Synthesis of a new class of spirooxindole–benzo[b]thiophene-based molecules as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Molecules 25:4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204671
Sahin Z, Biltekin SN, Bülbül EF, Yurttas L, Berk B, Demirayak S (2020) Design and synthesis of new donepezil analogs derived from arylpiperazine scaffold as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem:1–11.https://doi.org/10.1080/10426507.2020.1830773
Choubey PK, Tripathi A, Sharma P, Shrivastava SK (2020) Design, synthesis, and multitargeted profiling of N-benzylpyrrolidine derivatives for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem 28:115721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115721
El Khatabi̇ K, Aanouz İ, El-Merni̇ssi̇ R, Khaldan A, Ajana MA, Bouachrine M, Lakhlifi T (2020) Designing of novel potential inhibitors of a-amylase by 3D-QSAR modeling and molecular docking studies. J Turk Chem Soc Sect Chem 7:471–480. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.703026
S TRIPOS Associates, Inc. (2012) Sybyl-X molecular modeling software packages., Version X-2.0. Accessed 6 Feb 2020
Clark M, Cramer RD, Van Opdenbosch N (1989) Validation of the general purpose tripos 5.2 force field. J Comput Chem 10:982–1012. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.540100804
Purcell WP, Singer JA (1967) A brief review and table of semiempirical parameters used in the Hueckel molecular orbital method. J Chem Eng Data 12:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1021/je60033a020
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988) Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37:785–789. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.37.785
AbdulHameed MDM, Hamza A, Liu J, Zhan C-G (2008) Combined 3D-QSAR modeling and molecular docking study on indolinone derivatives as inhibitors of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. J Chem Inf Model 48:1760–1772. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci800147v
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00226a005
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00050a010
Ståhle L, Wold S (1988) 6 Multivariate Data Analysis and Experimental Design in Biomedical Research. Prog Med Chem:291–338.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70281-9
Bush AI (2012) The metal theory of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33:S277–S281. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2012-129011
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2! J Mol Graph Model 20:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-3263(01)00123-1
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar V (2003) The Importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb Sci 22:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/qsar.200390007
Baroni M, Clementi S, Cruciani G, Costantino G, Riganelli D (1992) Predictive ability of regression models. Part II: selection of the best predictive PLS model. J Chemom 6:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.1180060605
Rücker C, Rücker G, Meringer M (2007) y-Randomization and its variants in QSPR/QSAR. J Chem Inf Model 47:2345–2357. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci700157b
Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA (2016), Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 2017. San Diego: Dassault Systèmes
DeLano WL (2002) Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl Protein Crystallogr 40:82–92
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-987x(19981115)19:14%3c1639::aid-jcc10%3e3.0.co;2-b
Salomon-Ferrer R, Case DA, Walker RC (2013) An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package: Amber biomolecular simulation package. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 3:198–210. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1121
Price DJ, Brooks CL (2004) A modified TIP3P water potential for simulation with Ewald summation. J Chem Phys 121:10096–10103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1808117
Meza JC (2010) Steepest descent. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat 2:719–722. https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.117
Salomon-Ferrer R, Götz AW, Poole D, Le Grand S, Walker RC (2013) Routine microsecond molecular dynamics simulations with AMBER on GPUs. 2. Explicit solvent particle mesh Ewald. J Chem Theory Comput 9:3878–3888. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct400314y
Kräutler V, Gunsteren WFV, Hünenberger PH (2013) A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 22:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1002/1096-987x(20010415)22:5%3c501::aid-jcc1021%3e3.0.co;2-v
Roe DR, Cheatham TE (2013) PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Chem Theory Comput 9:3084–3095. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct400341p
Khan A, Ali SS, Khan MT, Saleem S, Ali A, Suleman M, Babar Z, Shafiq A, Khan M, Wei D-Q (2020) Combined drug repurposing and virtual screening strategies with molecular dynamics simulation identified potent inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro). J Biomol Struct Dyn:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1779128
Ali A, Khan A, Kaushik AC, Wang Y, Ali SS, Junaid M, Saleem S, Cho WCS, Mao X, Wei D-Q (2019) Immunoinformatic and systems biology approaches to predict and validate peptide vaccines against Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Sci Rep 9:720. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37070-z
Khan A, Ashfaq-Ur-Rehman JM, Li C-D, Saleem S, Humayun F, Shamas S, Ali SS, Babar Z, Wei D-Q (2020) Dynamics insights into the gain of flexibility by Helix-12 in ESR1 as a mechanism of resistance to drugs in breast cancer cell lines. Front Mol Biosci 6:159. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00159
Hou T, Wang J, Li Y, Wang W (2011) Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 1. The accuracy of binding free energy calculations based on molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 51:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci100275a
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the “Association Marocaine des Chimistes Théoriciens” (AMCT) for its technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KE: draft preparation, data handling, data analysis, writing, and reviewing. RE: conceptualization and data handling. IA: data handling and reviewing. MAA: data analysis, study justification, and supervision. TL: supervision and project administration. AK: data analysis and writing. DQW: writing and reviewing. MB: study justification and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Khatabi, K., El-Mernissi, R., Aanouz, I. et al. Identification of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors through 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation targeting Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Model 27, 302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-021-04928-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-021-04928-5