Abstract
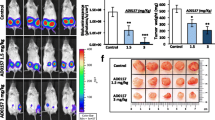
Metastasis contributes significantly to cancer mortality, and the most common pathway of initial dissemination is via the afferent ducts of the lymphatics. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C has been associated with lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in a multitude of human neoplasms, including breast cancers. We recently reported that both VEGF-C siRNA and endogenous soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (esVEGFR-2, a new splicing variant) inhibit VEGF-C function and metastasis in a mouse model of metastatic mammary cancer. Here we briefly review our previous experimental work, specifically targeting tumor lymphangiogenesis, in which metastatic mouse mammary cancers received direct intratumoral injections of either expression vectors VEGF-C siRNA or esVEGFR-2, or the empty plasmid vector, once a week for 6 or 8 weeks, followed by in vivo gene electrotransfer of the injected tumors. Throughout our study, both tumor lymphangiogenesis and the multiplicity of lymph node metastasis were significantly inhibited, with an overall reduction in tumor growth, by both VEGF-C siRNA and esVEGFR-2; further, a significant reduction in the number of dilated lymphatic vessels containing intraluminal cancer cells was observed with both treatments. Thus, therapeutic strategies targeting lymphangiogenesis may have great clinical significance for the treatment of metastatic human breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guarneri V, Conte PF (2004) The curability of breast cancer and the treatment of advanced disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31(suppl 1):S149–S161
Kuroishi T, Tominaga S (2001) Epidemiology of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Chemother 28:168–173
Agarwal G, Pradeep PV, Aggarwal V, Yip CH, Cheung PS (2007) Spectrum of breast cancer in Asian women. World J Surg 31: 1031–1040
Brinton LA, Sherman ME, Carreon JD, Anderson WF (2008) Recent trends in breast cancer among younger women in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:1643–1648
Bouchardy C, Fioretta G, Verkooijen HM, Vlastos G, Schaefer P, Delaloye JF, Neyroud-Caspar I, Balmer Majno S, Wespi Y, Forni M, Chappuis P, Sappino AP, Rapiti E (2007) Recent increase of breast cancer incidence among women under the age of forty. Br J Cancer 96:1743–1746
Nguyen DX, Massague J (2007) Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Genet 8:341–352
Joory KD, Levick JR, Mortimer PS, Bates DO (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) expression in normal human tissues. Lymphat Res Biol 4:73–82
Salven P, Lymboussaki A, Heikkila P, Jaaskela-Saari H, Enholm B, Aase K, von Euler G, Eriksson U, Alitalo K, Joensuu H (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF-B and VEGF-C are expressed in human tumors. Am J Pathol 153:103–108
Mylona E, Alexandrou P, Mpakali A, Giannopoulou I, Liapis G, Markaki S, Keramopoulos A, Nakopoulou L (2007) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF)-C and -D and VEGF receptor 3 in invasive breast carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 33:294–300
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Imabun S, Nakahara M, Nakao K, Nakamura M, Mori I, Kakudo K (2005) Lymph vessel density correlates with nodal status, VEGF-C expression, and prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 91:125–132
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Janes L, Velasco P, Riccardi L, Alitalo K, Claffey K, Detmar M (2001) Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 7:192–198
Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo H, Yla-Herttuala S, Jaattela M, Alitalo K (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res 61:1786–1790
He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K, Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T, Alitalo K (2002) Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:819–825
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M, Compagni A, Baetens D, Prevo R, Banerji S, Huarte J, Montesano R, Jackson DG, Orci L, Alitalo K, Christofori G, Pepper MS (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J 20:672–682
Albuquerque RJ, Hayashi T, Cho WG, Kleinman ME, Dridi S, Takeda A, Baffi JZ, Yamada K, Kaneko H, Green MG, Chappell J, Wilting J, Weich HA, Yamagami S, Amano S, Mizuki N, Alexander JS, Peterson ML, Brekken RA, Hirashima M, Capoor S, Usui T, Ambati BK, Ambati J (2009) Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth. Nat Med 15:1023–1030
Shibata MA, Morimoto J, Shibata E, Otsuki Y (2008) Combination therapy with short interfering RNA vectors against VEGF-C and VEGF-A suppresses lymph node and lung metastasis in a mouse immunocompetent mammary cancer model. Cancer Gene Ther 15:776–786
Shibata MA, Ambati J, Shibata E, Albuquerque RJ, Morimoto J, Ito Y, Otsuki Y (2010) The endogenous soluble VEGF receptor-2 isoform suppresses lymph node metastasis in a mouse immunocompetent mammary cancer model. BMC Med 8:69
Morimoto J, Imai S, Haga S, Iwai Y, Iwai M, Hiroishi S, Miyashita N, Moriwaki K, Hosick HL (1991) New murine mammary tumor cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 27A:349–351
Shibata MA, Morimoto J, Otsuki Y (2002) Suppression of murine mammary carcinoma growth and metastasis by HSVtk/GCV gene therapy using in vivo electroporation. Cancer Gene Ther 9:16–27
Shibata MA, Ito Y, Morimoto J, Kusakabe K, Yoshinaka R, Otsuki Y (2006) In vivo electrogene transfer of interleukin-12 inhibits tumor growth and lymph node and lung metastases in mouse mammary carcinomas. J Gene Med 8:335–352
Shibata MA, Akao Y, Shibata E, Nozawa Y, Ito T, Mishima S, Morimoto J, Otsuki Y (2007) Vaticanol C, a novel resveratrol tetramer, reduces lymph node and lung metastases of mouse mammary carcinoma carrying p53 mutation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 60:681–691
Shibata MA, Morimoto J, Shibata E, Akamatsu K, Kurose H, Li Z-L, Kusakabe M, Ohmichi M, Otsuki Y (2010) Raloxifene inhibits tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in a xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer. BMC Cancer 10:566
Shibata MA, Iinuma M, Morimoto J, Kurose H, Akamatsu K, Okuno Y, Akao Y, Otsuki Y (2011) a-Manogstin extracted from the pericarp of the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn.) reduces tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in an immunocompetent xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer carrying a p53 mutation. BMC Med 9:69
Shibata MA, Liu M-L, Knudson MC, Shibata E, Yoshidome K, Bandy T, Korsmeyer SJ, Green JE (1999) Haploid loss of bax leads to accelerated mammary tumor development in C3(1)/SV40-TAg transgenic mice: reduction in protective apoptotic response at the preneoplastic stage. EMBO J 18:2692–2701
Gorrin-Rivas MJ, Arii S, Furutani M, Mizumoto M, Mori A, Hanaki K, Maeda M, Furuyama H, Kondo Y, Imamura M (2000) Mouse macrophage metalloelastase gene transfer into a murine melanoma suppresses primary tumor growth by halting angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 6:1647–1654
Shibata MA, Shibata E, Morimoto J, Eid NAS, Tanaka Y, Watanabe M, Otsuki Y (2009) An immunocompetent murine model of metastatic mammary cancer accessible to bioluminescence imaging. Anticancer Res 29:4389–4396
Sleeman JP (2000) The lymph node as a bridgehead in the metastatic dissemination of tumors. Recent Results Cancer Res 157: 55–81
Valtola R, Salven P, Heikkila P, Taipale J, Joensuu H, Rehn M, Pihlajaniemi T, Weich H, deWaal R, Alitalo K (1999) VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 154:1381–1390
Achen MG, Mann GB, Stacker SA (2006) Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. Br J Cancer 94:1355–1360
Chen Z, Varney ML, Backora MW, Cowan K, Solheim JC, Talmadge JE, Singh RK (2005) Down-regulation of vascular endothelial cell growth factor-C expression using small interfering RNA vectors in mammary tumors inhibits tumor lymphangiogenesis and spontaneous metastasis and enhances survival. Cancer Res 65: 9004–9011
Kaipainen A, Korhonen J, Mustonen T, van Hinsbergh VW, Fang GH, Dumont D, Breitman M, Alitalo K (1995) Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3566–3570
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N, Alitalo K (1996) A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 15:290–298
Shimizu K, Kubo H, Yamaguchi K, Kawashima K, Ueda Y, Matsuo K, Awane M, Shimahara Y, Takabayashi A, Yamaoka Y, Satoh S (2004) Suppression of VEGFR-3 signaling inhibits lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 95:328–333
Lin J, Lalani AS, Harding TC, Gonzalez M, Wu WW, Luan B, Tu GH, Koprivnikar K, VanRoey MJ, He Y, Alitalo K, Jooss K (2005) Inhibition of lymphogenous metastasis using adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer of a soluble VEGFR-3 decoy receptor. Cancer Res 65:6901–6909
Laakkonen P, Waltari M, Holopainen T, Takahashi T, Pytowski B, Steiner P, Hicklin D, Persaud K, Tonra JR, Witte L, Alitalo K (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 is involved in tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res 67:593–599
Burton JB, Priceman SJ, Sung JL, Brakenhielm E, An DS, Pytowski B, Alitalo K, Wu L (2008) Suppression of prostate cancer nodal and systemic metastasis by blockade of the lymphangiogenic axis. Cancer Res 68:7828–7837
Hasebe T, Okada N, Iwasaki M, Akashi-Tanaka S, Hojo T, Shibata T, Sasajima Y, Tsuda H, Kinoshita T (2010) Grading system for lymph vessel tumor emboli: significant outcome predictor for invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Hum Pathol 41:706–715
Hasebe T, Sasaki S, Imoto S, Ochiai A (2002) Characteristics of tumors in lymph vessels play an important role in the tumor progression of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: a prospective study. Mod Pathol 15:904–913
Tuomela J, Valta M, Seppanen J, Tarkkonen K, Vaananen HK, Harkonen P (2009) Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor C increases growth and alters the metastatic pattern of orthotopic PC-3 prostate tumors. BMC Cancer 9:362
Kodama M, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M, Kuwai T, Tanaka S, Oue N, Yasui W, Chayama K (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor C stimulates progression of human gastric cancer via both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 14:7205–7214
Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE (1989) Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24 740 breast cancer cases. Cancer (Phila) 63:181–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibata, MA., Ambati, J., Shibata, E. et al. Mammary cancer gene therapy targeting lymphangiogenesis: VEGF-C siRNA and soluble VEGF receptor-2, a splicing variant. Med Mol Morphol 45, 179–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-012-0576-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-012-0576-5