Abstract
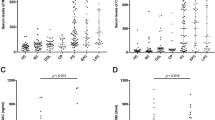
Improvement of diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic cancer in pancreatic disease patients was investigated by examining the combination of three diagnostic methods, i.e., measurements of RCAS1 and CEA levels in pancreatic juice and pancreatic juice cytology. Pancreatic juice was collected from 12 pancreatic cancer (PC) and 26 non-PC patients. RCAS1 and CEA levels were measured by using ELISA. RCAS1 expression on surgically resected tissue was immunohistochemically examined for 2 PC patients. By setting the cutoff level of RCAS1 at 10 U/ml and that of CEA at 18.5 μg/ml, sensitivity of RCAS1 was 42% and that of CEA was 50%. On the other hand, sensitivity and specificity increased from 42% and 85% of RCAS1 alone to 75% and 85% in the examination of RCAS1 + CEA + cytology, and the false-negative rate was also reduced to 25% in this combination. Immunohistochemically, a patient with a high RCAS1 level in pancreatic juice had numerous RCAS1-positive tumor cells in the pancreatic juice. We concluded that RCAS1 and CEA measurements together with cytology in pancreatic juice would be a useful combination method for making a differential diagnosis of PC from non-PC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong JC, Lu DSK (2008) Staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by imaging studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:1301–1308
Strobel K, Heinrich S, Bhure U, Soyka J, Veit-Haibach P, Pestalozzi BC, Clavein PA, Hany TF (2008) Contrast-enhanced 18F-FDG PET/CT: 1-stop-shop imaging for assessing the respectability of pancreatic cancer. J Nucl Med 49:1408–1413
Canto MI, Goggins M, Hruban RH, Petersen GM, Giardiello FM, Yeo C, Fishman EK, Brune K, Axilbund J, Griffin C, Ali S, Richman J, Jagannath S, Kantsevoy SV, Kallon AN (2006) Screening for early pancreatic neoplasm in high-risk individuals: a prospective controlled study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:766–781
Vandervoort J, Soetikno RM, Montes H, Lichtenstein DR, Van Dam J, Ruymann FW, Cibas ES, Carr-Locke DL (1999) Accuracy and complication rate of brush cytology from bile duct versus pancreatic duct. Gastrointest Endosc 49:322–327
Uchida N, Kamada H, Tsutsui K Ono M, Aritomo Y, Masaki T, Kushida Y, Haba R, Nakatsu T, Kuriyama S (2007) Utility of pancreatic duct brushing for diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 42:657–662
Imamura T, Takeshita R, Koyama R, Okuda C, Takeuchi K, Matsuda M, Hashimoto M, Watanabe G, Yoshida H, Imawari M (2006) Effectiveness of cytodiagnosis with pancreatic duct lavage fluid for pancreatic ductal carcinoma: new sampling technique. Dig Endosc 18:303–307
Yan L, McFaul C, Howes N, Leslie J, Lancaster G, Wong T, Threadgold J, Evans J, Glimore I, Smart H, Lombard M, Neoptolemos J, Greenhalf W (2005) Molecular analysis to detect pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in high-risk group. Gastroenterology 128: 2124–2130
Bian Y, Matsubayashi H, Li CP, Abe T, Canto M, Murphy KM, Goggins M (2006) Detecting low-abundance p16 and p53 mutation in pancreatic juice using a novel assay: heteroduplex analysis of limiting dilution PCRs. Cancer Biol Ther 5:1392–1399
Myung SJ, Kim MH, Kim YS Kim HJ, Park ET, Yoo KS, Lim BC, Wan Seo D, Lee SK, Min YI, Kim JY (2000) Telomerase activity in pure pancreatic juice for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer may be complementary to K-ras mutation. Gastrointest Endosc 51: 708–713
Uehara H, Nakaizumi A, Iishi H, Takenaka A, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O (2008) In situ telomerase activity in pancreatic juice may discriminate pancreatic cancer from other pancreatic diseases. Pancreas 36:236–240
Hiraoka K, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, Oshikiri T, Suzuoki M, Nakakubo Y, Shinohara T, Itoh T, Shichinohe T, Kondo S, Kasahara N, Katoh H (2002) High expression of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is an unfavorable prognostic marker. Int J Cancer 99:418–423
Kaku T, Sonoda K, Kamura T, Hirakawa T, Sakai K, Amada S, Ogawa S, Kobayashi H, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H (1999) The prognostic significance of tumor-associated antigen 22-1-1 expression in adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix. Clin Cancer Res 5:1449–1453
Sonoda K, Kaku T, Hirakawa T, Kobayashi H, Amada S, Sakai K, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H (2000) The clinical significance of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 expression in the normal, hyperplastic, and malignant uterine endometrium. Gynecol Oncol 79:424–429
Takahashi H, Iizuka H, Nakashima M, Wada T, Asano K, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Watanabe T (2001) RCAS1 antigen is highly expressed in extramammary Paget’s disease and in advanced stage squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. J Dermatol Sci 26:140–144
Suzuki T, Inoue S, Kawabata W, Akahira J, Moriya T, Tsuchiya F, Ogawa S, Marumatsu M, Sasano H (2001) EBAG9/RCAS1 in human breast carcinoma: a possible factor in endocrine-immune interactions. Br J Cancer 85:1731–1737
Tsuneizumi M, Nagai H, Harada H, Kazui T, Emi M (2002) A highly polymorphic CA repeat marker at the EBAG9/RCAS1 locus on 8q23 that detected frequent multiplication in breast cancer. Ann Hum Biol 29:457–460
Noguchi K, Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Nakashima M, Nishi H, Choi I, Taguchi K, Kotoh K, Shimada M, Sugimachi K, Tsuneyoshi M, Nawata H, Watanabe T (2001) Expression of a tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 168: 197–202
Oshikiri T, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, Hashida H, Katoh K, Suzuoki M, Nakakubo Y, Hiraoka K, Shinohara T, Itoh T, Kondo S, Katoh H (2001) RCAS1 as a tumour progression marker: an independent negative prognostic factor in gallbladder cancer. Br J Cancer 85:1922–1927
Kubokawa M, Nakashima M, Yao T, Ito KI, Harada N, Nawata H, Watanabe T (2001) Aberrant intracellular localization of RCAS1 is associated with tumor progression of gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 19:695–700
Ohshima K, Muta K, Nakashima M, Haraoka S, Tutiya T, Suzumiya J, Kawasaki C, Watanabe T, Kikuchi M (2001) Expression of human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 in Reed-Sternberg cells in association with Epstein-Barr virus infection: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Int J Cancer 93:91–96
Izumi M, Nakanishi Y, Yoshino I, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Hara N (2001) Expression of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 correlates significantly with poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer (Phila) 92:446–451
Nakashima M, Sonoda K, Watanabe T (1999) Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptotic cell death by the human tumorassociated antigen RCAS1. Nat Med 5:938–942
Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Noguchi K, Sugimoto R, Kotoh K, Nawata H, Nakashima M, Watanabe T (2002) RCAS1 expression in immune-mediated liver diseases. J Clin Gastroenterol 34:286–287
Yamaguchi K, Enjoji M, Nakashima M, Nakamuta M, Watanabe T, Tanaka M (2005) Novel serum tumor marker, RCAS1, in pancreatic diseases. World J Gastroenterol 11:5199–5202
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K, Matsuno S; International Association of Pancreatology (2006) International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 6:17–32
Matsushima T, Nakashima M, Ohshima K, Abe Y, Nishimura J, Nawata H, Watanabe T, Muta K (2001) Receptor binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells, a novel regulator of apoptosis of erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 98:313–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naito, Y., Okabe, Y., Nagayama, M. et al. Accuracy of differential diagnosis for pancreatic cancer is improved in the combination of RCAS1 and CEA measurements and cytology in pancreatic juice. Med Mol Morphol 44, 86–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0511-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0511-6