Abstract
Objectives
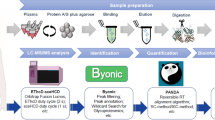
Saliva is a bodily fluid transuded from gingival crevice fluid and blood and contains many proteins. Proteins in saliva have been studied as markers for periodontal diseases. Mass spectrometric analysis is applied to investigate biomarker proteins that are related to periodontitis.
Material and methods
Saliva samples were collected from 207 participants including 36 pairs matched for age, sex, and smoking who joined Yangpyeong health cohort. Periodontitis was defined by 2005 5th European guideline. Shotgun proteomics was applied to detect proteins from saliva samples. Principal component analysis and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis for canonical pathway and protein pathway were applied. Protein-protein interaction was also applied. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to verify the candidate protein markers among another matched participants (n = 80).
Results
Shotgun proteomics indicated that salivary S100A8 and S100A9 were candidate biomarkers for periodontitis. ELISA confirmed that both salivary S100A8 and S100A9 were higher in those with periodontitis compared to those without periodontitis (paired-t test, p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Our proteomics data showed that S100A8 and S100A9 in saliva could be candidate biomarkers for periodontitis. The rapid-test-kit using salivary S100A8 and S100A9 will be a practical tool for reducing the risk of periodontitis and promotion of periodontal health.
Clinical relevance
A rapid-test-kit using salivary biomarkers, S100A8 and S100A9, could be utilized by clinicians and individuals for screening periodontitis, which might reduce the morbidity of periodontitis and promote periodontal health.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu S, Loo JA, Wong DT (2006) Human body fluid proteome analysis. Proteomics 6(23):6326–6353. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200600284
Haigh BJ, Stewart KW, Whelan JRK, Barnett MPG, Smolenski GA, Wheeler TT (2010) Alterations in the salivary proteome associated with periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 37(3):241–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01525.x
Wu Y, Shu R, Luo LJ, Ge LH, Xie YF (2009) Initial comparison of proteomic profiles of whole unstimulated saliva obtained from generalized aggressive periodontitis patients and healthy control subjects. J Periodontal Res 44(5):636–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.2008.01172.x
Salazar MG et al (2013) Identification of periodontitis associated changes in the proteome of whole human saliva by mass spectrometric analysis. J Clin Periodontol 40(9):825–32. 5. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12130
Mertens B, Orti V, Vialaret J, Gibert P, Relaño-Ginés A, Lehmann S, de Périère DD, Hirtz C (2018) Assessing a multiplex-targeted proteomics approach for the clinical diagnosis of periodontitis using saliva samples. Bioanalysis 10(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2017-0218
Orti V, Mertens B, Vialaret J, Gibert P, Relaño-Ginés A, Lehmann S, Deville de Périère D, Hirtz C (2018) Data from a targeted proteomics approach to discover biomarkers in saliva for the clinical diagnosis of periodontitis. Data Brief 18:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.03.036
Danesh J, Collins R, Peto R (1997) Chronic infections and coronary heart disease: is there a link? Lancet 350(9075):430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)03079-1
Seymour GJ, Ford PJ, Cullinan MP, Leishman S, Yamazaki K (2007) Relationship between periodontal infections and systemic disease. Clin Microbiol Infect 13:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01798.x
Ahn YB, Shin MS, Han DH, Sukhbaatar M, Kim MS, Shin HS, Kim HD (2016) Periodontitis is associated with the risk of subclinical atherosclerosis and peripheral arterial disease in Korean adults. Atherosclerosis 251:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.898
Sim SJ, Kim HD, Moon JY, Zavras AI, Zdanowicz J, Jang SJ, Jin BH, Bae KH, Paik DI, Douglass CW (2008) Periodontitis and the risk for non-fatal stroke in Korean adults. J Periodontol 79(9):1652–1658. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080015
Kim JJ, Kim CJ, Camargo PM (2013) Salivary biomarkers in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. J Calif Dent Assoc 41(2):119–124
Ozmeric N (2004) Advances in periodontal disease markers. Clin Chim Acta 343(1–2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cccn.2004.01.022
Bragger U (2005) Radiographic parameters: biological significance and clinical use. Periodontol 39:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2005.00128.x
Loos BG, Tjoa S (2005) Host-derived diagnostic markers for periodontitis: do they exist in gingival crevice fluid. Periodontol 39:53–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2005.00129.x
Offenbacher S, Barros SP, Beck JD (2008) Rethinking periodontal inflammation. J Periodontol 79(8):1577–1584. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080220
Good DM, Thongboonkerd V, Novak J, Bascands JL, Schanstra JP, Coon JJ, Dominiczak A, Mischak H (2007) Body fluid proteomics for biomarker discovery: lessons from the past hold the key to success in the future. J Proteome Res 6(12):4549–4555. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr070529w
Zhang L et al (2009) The clinical value of salivary biomarkers for periodontal disease. Periodontol 51:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2009.00315.x
Goncalves LD et al (2010) Comparative proteomic analysis of whole saliva from chronic periodontitis patients. J Proteome 73(7):1334–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2010.02.018
Li Y, St John MA, Zhou X, Kim Y, Sinha U, Jordan RC, Eisele D, Abemayor E, Elashoff D, Park NH, Wong DT (2004) Salivary transcriptome diagnostics for oral cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res 10(24):8442–8450. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-04-1167
Ambatipudi KS, Swatkoski S, Moresco JJ, Tu PG, Coca A, Anolik JH, Gucek M, Sanz I, Yates JR III, Melvin JE (2012) Quantitative proteomics of parotid saliva in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Proteomics 12(19–20):3113–3120. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201200208
Caseiro A, Ferreira R, Padrão A, Quintaneiro C, Pereira A, Marinheiro R, Vitorino R, Amado F (2013) Salivary proteome and peptidome profiling in type 1 diabetes mellitus using a quantitative approach. J Proteome Res 12(4):1700–1709. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr3010343
Rao PV, Reddy AP, Lu X, Dasari S, Krishnaprasad A, Biggs E, Roberts CT, Nagalla SR (2009) Proteomic identification of salivary biomarkers of Type-2 diabetes. J Proteome Res 8(1):239–245. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr8003776
Streckfus CF, Mayorga-Wark O, Arreola D, Edwards C, Bigler L, Dubinsky WP (2008) Breast cancer related proteins are present in saliva and are modulated secondary to ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Investig 26(2):159–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357900701783883
Wulfkuhle JD, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF (2003) Proteomic applications for the early detection of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3(4):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.1043
Bandhakavi S, Stone MD, Onsongo G, van Riper SK, Griffin TJ (2009) A dynamic range compression and three-dimensional peptide fractionation analysis platform expands proteome coverage and the diagnostic potential of whole saliva. J Proteome Res 8(12):5590–5600. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr900675w
Xie H, Rhodus NL, Griffin RJ, Carlis JV, Griffin TJ (2005) A catalogue of human saliva proteins identified by free flow electrophoresis-based peptide separation and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 4(11):1826–1830. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.D500008-MCP200
Zia A, Khan S, Bey A, Gupta ND, Mukhtar-Un-Nisar S (2011) Oral biomarkers in the diagnosis and progression of periodontal diseases. Biol Med 3:45–52
Range H et al (2012) Salivary proteome modifications associated with periodontitis in obese patients. J Clin Periodontol 39(9):799–806. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01913.x
Tonetti MS, Claffey N, European Workshop in Periodontology group C (2005) Advances in the progression of periodontitis and proposal of definitions of a periodontitis case and disease progression for use in risk factor research - Group C Consensus report of the 5th European workshop in periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 32:210–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00822.x
Foster LJ, De Hoog CL, Mann M (2003) Unbiased quantitative proteomics of lipid rafts reveals high specificity for signaling factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(10):5813–5818. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0631608100
Choi CW, Park EC, Yun SH, Lee SY, Lee YG, Hong Y, Park KR, Kim SH, Kim GH, Kim SI (2014) Proteomic characterization of the outer membrane vesicle of Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Proteome Res 13(10):4298–4309. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr500411d
Tsuchida S, Satoh M, Umemura H, Sogawa K, Kawashima Y, Kado S, Sawai S, Nishimura M, Kodera Y, Matsushita K, Nomura F (2012) Proteomic analysis of gingival crevicular fluid for discovery of novel periodontal disease markers. Proteomics 12(13):2190–2202. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201100655
Topoll HH, Zwadlo G, Lange DE, Sorg C (1989) Phenotypic dynamics of macrophage subpopulations during human experimental gingivitis. J Periodontal Res 24(2):106–112
Kido J et al (2005) Calprotectin expression in human monocytes: induction by porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1beta. J Periodontol 76(3):437–442. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2005.76.3.437
Kojima T, Andersen E, Sanchez JC, Wilkins MR, Hochstrasser DF, Pralong WF, Cimasoni G (2000) Human gingival crevicular fluid contains MRP8 (S100A8) and MRP14 (S100A9), two calcium-binding proteins of the S100 family. J Dent Res 79(2):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345000790020701
Gursoy UK, Könönen E, Huumonen S, Tervahartiala T, Pussinen PJ, Suominen AL, Sorsa T (2013) Salivary type I collagen degradation end-products and related matrix metalloproteinases in periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 40(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12020
Sorsa T, Tjaderhane L, Salo T (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in oral diseases. Oral Dis 10(6):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-0825.2004.01038.x
Burt BS, Research, Science and Therapy Committee of the American Academy of Periodontology (2005) Therapy Committee of the American Academy of, position paper: epidemiology of periodontal diseases. J Periodontol 76(8):1406–1419. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2005.76.8.1406
Baliban RC, Sakellari D, Li Z, DiMaggio PA, Garcia BA, Floudas CA (2012) Novel protein identification methods for biomarker discovery via a proteomic analysis of periodontally healthy and diseased gingival crevicular fluid samples. J Clin Periodontol 39(3):203–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01805.x
Lamster IB, Ahlo JK (2007) Analysis of gingival crevicular fluid as applied to the diagnosis of oral and systemic diseases. Oral-Based Diagn 1098:216–229. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1384.027
Ramseier CA, Kinney JS, Herr AE, Braun T, Sugai JV, Shelburne CA, Rayburn LA, Tran HM, Singh AK, Giannobile WV (2009) Identification of pathogen and host-response markers correlated with periodontal disease. J Periodontol 80(3):436–446. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080480
Siqueira WL, Dawes C (2011) The salivary proteome: challenges and perspectives. Proteomics Clin Appl 5(11–12):575–579. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201100046
Giannobile WV et al (2009) Saliva as a diagnostic tool for periodontal disease: current state and future directions. Periodontol 50:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2008.00288.x
Kinney JS, Ramseier CA, Giannobile WV (2007) Oral fluid-based biomarkers of alveolar bone loss in periodontitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1098:230–251. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1384.028
Scannapieco FA et al (2007) Salivary biomarkers associated with alveolar bone loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1098:496–497. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1384.034
Taba M Jr, Kinney J, Kim AS, Giannobile WV (2005) Diagnostic biomarkers for oral and periodontal diseases. Dent Clin N Am 49(3):551–571, vi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2005.03.009
Buduneli N, Kinane DF (2011) Host-derived diagnostic markers related to soft tissue destruction and bone degradation in periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 38(Suppl 11):85–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01670.x
Funding
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017M3A9B6062984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This cross-sectional study was approved by institutional review board (SNU SOD N0: S-D20170045).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, MS., Kim, YG., Shin, Y.J. et al. Deep sequencing salivary proteins for periodontitis using proteomics. Clin Oral Invest 23, 3571–3580 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2779-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2779-1