Abstract
Objectives
Experimental composite resins with amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) have the potential to regenerate demineralized tooth structures. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of the addition of silanized silica nanofillers to the ACP-based composites on their mechanical properties and the kinetics of calcium and phosphate release.
Materials and methods
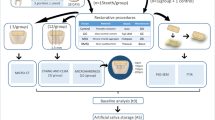
The test materials comprised 5 wt% (5-ACP) or 10 wt% (10-ACP) of silanized silica admixed to the 40 wt% ACP and 50 or 55 wt% resin. The ACP control (0-ACP) contained 40 wt% ACP and 60 wt% resin. Additionally, composite material CeramX (Dentsply, Germany) was included as control. Three-point bending test was performed to calculate flexural strength and modulus of elasticity. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy was used for measurement of ion release. The micromorphology of calcium phosphate depositions on composite samples has been qualitatively evaluated using a scanning electron microscope. The results were analyzed using Mann–Whitney and Wilcoxon rank sum tests (α < 0.05).
Results
Ion release was enhanced by the silica fillers, when compared to the 0-ACP. Although not statistically significant, flexural strength of 10-ACP was improved by 46 % compared to 0-ACP. Flexural modulus of 5-ACP was significantly higher than 0-ACP.
Conclusions
The admixture of silanized fillers seems to be a promising approach for the improvement of mechanical and remineralizing properties of ACP composite resins.
Clinical relevance
ACP-based composite resins with modified composition could serve as an effective remineralizing aid as base materials in restorative dental medicine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skrtic D, Hailer AW, Takagi S, Antonucci JM, Eanes ED (1996) Quantitative assessment of the efficacy of amorphous calcium phosphate/methacrylate composites in remineralizing caries-like lesions artificially produced in bovine enamel. J Dent Res 75:1679–1686
Dorozhkin SV (2010) Amorphous calcium (ortho)phosphates. Acta Biomater 6:4457–4475. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.031
Langhorst SE, O'Donnell JN, Skrtic D (2009) In vitro remineralization of enamel by polymeric amorphous calcium phosphate composite: quantitative microradiographic study. Dent Mater 25:884–891. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2009.01.094
Johns JI, O'Donnell JN, Skrtic D (2010) Selected physicochemical properties of the experimental endodontic sealer. J Mater Sci Mater Med 21:797–805. doi:10.1007/s10856-009-3873-3
O'Donnell JN, Schumacher GE, Antonucci JM, Skrtic D (2009) Structure-composition-property relationships in polymeric amorphous calcium phosphate-based dental composites. Mater(Basel) 2:1929–1959. doi:10.3390/ma2041929
O'Donnell JN, Langhorst SE, Fow MD, Antonucci JM, Skrtic D (2008) Light-cured dimethacrylate-based resins and their composites: comparative study of mechanical strength, water sorption and ion release. J Bioact Compat Polym 23:207–226
O'Donnell JN, Antonucci JM, Skrtic D (2006) Amorphous calcium phosphate composites with improved mechanical properties. J Bioact Compat Polym 21:169–184. doi:10.1177/0883911506064476
Heintze SD, Zimmerli B (2011) Relevance of in vitro tests of adhesive and composite dental materials, a review in 3 parts; part 1: approval requirements and standardized testing of composite materials according to ISO specifications. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed 121:804–816
Rodrigues Junior SA, Zanchi CH, Carvalho RV, Demarco FF (2007) Flexural strength and modulus of elasticity of different types of resin-based composites. Braz Oral Res 21:16–21
Ilie N, Hickel R (2011) Resin composite restorative materials. Aust Dent J 56(Suppl 1):59–66. doi:10.1111/j.1834-7819.2010.01296.x
Ilie N, Hickel R (2009) Investigations on mechanical behaviour of dental composites. Clin Oral Investig 13:427–438. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0258-4
O'Donnell JN, Antonucci JM, Skrtic D (2008) Illuminating the role of agglomerates on critical physicochemical properties of amorphous calcium phosphate composites. J Compos Mater 42:2231–2246. doi:10.1177/0021998308094797
Park MS, Eanes ED, Antonucci JM, Skrtic D (1998) Mechanical properties of bioactive amorphous calcium phosphate/methacrylate composites. Dent Mater 14:137–141
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM (2007) Effect of chemical structure and composition of the resin phase on vinyl conversion of amorphous calcium phosphate-filled composites. Polym Int 56:497–505. doi:10.1002/pi.2129
Antonucci JM, Fowler BO, Stansbury JW, Weir MD, Skrtic D (2008) Bioactive polymeric ACP composites utilizing ethyl-alpha-hydroxymethylacrylate. Polym Prepr 49:820–821
Antonucci JM, Fowler BO, Weir MD, Skrtic D, Stansbury JW (2008) Effect of ethyl-alpha-hydroxymethylacrylate on selected properties of copolymers and ACP resin composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:3263–3271. doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3463-9
Antonucci JM, Icenogle TB, Regnault WF, Liu DW, O'Donnell JN, Skrtic D (2006) Polymerization shrinkage and stress development in bioactive urethane acrylic resin composites. Polym Prepr 47:498–499
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM, Eanes ED, Brunworth RT (2002) Silica- and zirconia-hybridized amorphous calcium phosphate: effect on transformation to hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res 59:597–604. doi:10.1002/jbm.10017
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM, Eanes ED, Eldelman N (2004) Dental composites based on hybrid and surface-modified amorphous calcium phosphates. Biomaterials 25:1141–1150. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.001
Bowen RL (1956) Use of epoxy resins in restorative materials. J Dent Res 35:360–369
Bowen RL (1963) Properties of a silica-reinforced polymer for dental restorations. J Am Dent Assoc 66:57–64
Chen MH (2010) Update on dental nanocomposites. J Dent Res 89:549–560. doi:10.1177/0022034510363765
Wilson KS, Zhang K, Antonucci JM (2005) Systematic variation of interfacial phase reactivity in dental nanocomposites. Biomaterials 26:5095–5103. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.01.008
Yoshida Y, Shirai K, Nakayama Y, Itoh M, Okazaki M, Shintani H, Inoue S, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G, Van Meerbeek B (2002) Improved filler-matrix coupling in resin composites. J Dent Res 81:270–273
Calais JG, Soderholm KJ (1988) Influence of filler type and water exposure on flexural strength of experimental composite resins. J Dent Res 67:836–840
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM, Eanes ED, Eidelman N (2004) Dental composites based on hybrid and surface-modified amorphous calcium phosphates. Biomaterials 25:1141–1150
Xu HH, Weir MD, Sun L, Takagi S, Chow LC (2007) Effects of calcium phosphate nanoparticles on Ca-PO4 composite. J Dent Res 86:378–383
Tjandrawinata R, Irie M, Suzuki K (2005) Effect of 10 wt% spherical silica filler addition on the various properties of conventional and resin-modified glass-ionomer cements. Acta Odontol Scand 63:371–375
Xu HH, Sun L, Weir MD, Takagi S, Chow LC, Hockey B (2007) Effects of incorporating nanosized calcium phosphate particles on properties of whisker-reinforced dental composites. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 81:116–125. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.30644
Tjandrawinata R, Irie M, Suzuki K (2004) Marginal gap formation and fluoride release of resin-modified glass-ionomer cement: effect of silanized spherical silica filler addition. Dent Mater J 23:305–313
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM, Liu DW (2006) Ethoxylated bisphenol dimethacrylate-based amorphous calcium phosphate composites. Acta Biomater 2:85–94. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2005.10.004
Skrtic D, Antonucci JM, Eanes ED (2003) Amorphous calcium phosphate-based bioactive polymeric composites for mineralized tissue regeneration. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol 108:167–182
Hatanaka K, Irie M, Tjandrawinata R, Suzuki K (2006) Effect of spherical silica filler addition on immediate interfacial gap-formation in Class V cavity and mechanical properties of resin-modified glass-ionomer cement. Dent Mater J 25:415–422
Tjandrawinata R, Irie M, Yoshida Y, Suzuki K (2004) Effect of adding spherical silica filler on physico-mechanical properties of resin modified glass-ionomer cement. Dent Mater J 23:146–154
Tarle Z, Knezevic A, Matosevic D, Skrtic D, Ristic M, Prskalo K, Music S (2009) Degree of vinyl conversion in experimental amorphous calcium phosphate composites. J Mol Struc 924–926:161–165
Marovic D, Tarle Z, Ristic M, Music S, Skrtic D, Hiller K, Schmalz G (2011) Influence of different types of fillers on the degree of conversion of ACP composite resins. Acta Stomal Croat 45:231–238
E L, Irie M, Nagaoka N, Yamashiro T, Suzuki K (2010) Mechanical properties of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement for luting: effect of adding spherical silica filler. Dent Mater J 29:253–261
Hosseinalipour M, Javadpour J, Rezaie H, Dadras T, Hayati AN (2010) Investigation of mechanical properties of experimental Bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composite resins containing various mass fractions of silica nanoparticles. J Prosthodont 19:112–117. doi:10.1111/j.1532-849X.2009.00530.x
Chung KH, Greener EH (1990) Correlation between degree of conversion, filler concentration and mechanical properties of posterior composite resins. J Oral Rehabil 17:487–494
Debnath S, Ranade R, Wunder SL, McCool J, Boberick K, Baran G (2004) Interface effects on mechanical properties of particle-reinforced composites. Dent Mater 20:677–686. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2003.12.001
Karmaker A, Prasad A, Sarkar NK (2007) Characterization of adsorbed silane on fillers used in dental composite restoratives and its effect on composite properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18:1157–1162. doi:10.1007/s10856-007-0145-y
Sideridou ID, Karabela MM (2009) Effect of the amount of 3-methacyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane coupling agent on physical properties of dental resin nanocomposites. Dent Mater 25:1315–1324. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2009.03.016
Ilie N, Rencz A, Hickel R (2013) Investigations towards nano-hybrid resin-based composites. Clin Oral Investig 17:185–193. doi:10.1007/s00784-012-0689-1
Soderholm KJ, Yang MC, Garcea I (2000) Filler particle leachability of experimental dental composites. Eur J Oral Sci 108:555–560
Damen JJ, ten Cate JM (1989) The effect of silicic acid on calcium phosphate precipitation. J Dent Res 68:1355–1359
Damen JJ, Ten Cate JM (1992) Silica-induced precipitation of calcium phosphate in the presence of inhibitors of hydroxyapatite formation. J Dent Res 71:453–457
Gajjeraman S, Narayanan K, Hao J, Qin C, George A (2007) Matrix macromolecules in hard tissues control the nucleation and hierarchical assembly of hydroxyapatite. J Biol Chem 282:1193–1204. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604732200
Barnes DH, Jugdaosingh R, Kiamil S, SM B (2011) Shelf life and chemical stability of calcium phosphate coatings applied to poly carbonate urethane substrates. J Biotechnol Biomaterial 1. doi:10.4172/2155- 952X.1000112
Kokubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27:2907–2915. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.017
Arifuzzaman SM, Rohani S (2004) Experimental study of brushite precipitation. J Cryst Growth 267:624–634. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2004.04.024
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Ministry of Science, Education and Sports, Republic of Croatia (065-0352851-0410 and 098-0982904-2952), Croatian Science Foundation, Forschungsgemeinschaft Dental, University Hospital Regensburg, University of Regensburg and NIDCR (DE13169). Generous contribution of the fillers from Evonik Degussa (Essen, Germany) and the monomers from Esstech (Essington, PA, USA) and Sigma Aldrich (Milwaukee, WI, USA) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marovic, D., Tarle, Z., Hiller, K.A. et al. Effect of silanized nanosilica addition on remineralizing and mechanical properties of experimental composite materials with amorphous calcium phosphate. Clin Oral Invest 18, 783–792 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1044-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1044-x