Abstract
Objectives
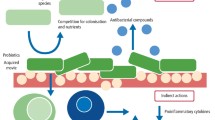
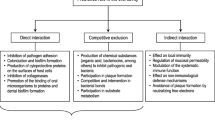
This study was designed to determine the effects of probiotics in prevention and/or treatment of periodontal diseases.
Materials and methods
We performed broad searches in the MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane databases and selected articles that satisfied the description of randomized clinical trials comparing the administration of probiotics versus placebo or another intervention to prevent or treat periodontal diseases in adult patients.
Results
Four randomized clinical trials were analyzed in the final review process. For the primary outcome, probing pocket depth, there would be no clinical beneficial effect of probiotics. For secondary outcomes, probiotics have shown small benefits on plaque index and gingival inflammation.
Conclusions
Based on the results of this review, the effectiveness of probiotics on the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases is questionable. There is currently insufficient evidence demonstrating the benefits of systematic preventative use of probiotics in patients with periodontal diseases.
Clinical relevance
The use of probiotics are described to prevent or treat periodontal diseases in some clinical trials; therefore, a systematic review of the evidence for the effect of periodontal diseases is needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage GC (1995) Clinical evaluation of periodontal diseases. Periodontol 7:39–53
Page RC (1986) Gingivitis. J Clin Periodontol 13(5):345–359
FAO/WHO. (2001) Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live Lactic Acid Bacteria. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf. Accessed 12 October 2012
de Vrese MSJ (2008) Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 111:1–66
Saier MH Jr, Mansour NM (2005) Probiotics and prebiotics in human health. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 10(1):22–25
Stamatova I, Meurman JH (2009) Probiotics and periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000(51):141–151
Caglar E, Sandalli N, Twetman S, Kavaloglu S, Ergeneli S, Selvi S (2005) Effect of yogurt with Bifidobacterium DN-173 010 on salivary mutans streptococci and lactobacilli in young adults. Acta Odontol Scand 63(6):317–320
Marcotte H, Koll-Klais P, Hultberg A, Zhao Y, Gmur R, Mandar R et al (2006) Expression of single-chain antibody against RgpA protease of Porphyromonas gingivalis in Lactobacillus. J Appl Microbiol 100(2):256–263
Higgins JPT, Green S (2009). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org. Accessed 5 January 2012
Shimauchi H, Mayanagi G, Nakaya S, Minamibuchi M, Ito Y, Yamaki K et al (2008) Improvement of periodontal condition by probiotics with Lactobacillus salivariusWB21: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Periodontol 35(10):897–905
Mayanagi G, Kimura M, Nakaya S, Hirata H, Sakamoto M, Benno Y et al (2009) Probiotic effects of orally administered Lactobacillus salivariusWB21-containing tablets on periodontopathic bacteria: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 36(6):506–513
Vivekananda MR, Vandana KL, Bhat KG (2010) Effect of the probiotic Lactobacilli reuteri [Prodentis] in the management of periodontal disease: a preliminary randomized clinical trial. Journal of Oral Microbiology 2:2. doi:10.3402/jom.v2i0.5344
Twetman S, Derawi B, Keller M, Ekstrand K, Yucel-Lindberg T, Stecksen-Blicks C (2009) Short-term effect of chewing gums containing probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri on the levels of inflammatory mediators in gingival crevicular fluid. Acta Odontol Scand 67(1):19–24
Staab B, Eick S, Knöfler G, Jentsch H (2009) The influence of a probiotic milk drink on the development of gingivitis: a pilot study. J Clin Periodontol 36(10):850–856
Armitage GC (2003) Diagnosis of periodontal diseases. J Periodontol 74(8):1237–1247
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D (2010) CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. PLoS Med 7(3):e1000251
Conflicts of interest and source of funding statement
None of the authors of this review declares a conflict of interest or obtained any kind of financing or support from any company related to the production of probiotics. This investigation did not receive any private financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanine, N., Araya, I., Brignardello-Petersen, R. et al. Effects of probiotics in periodontal diseases: a systematic review. Clin Oral Invest 17, 1627–1634 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-0990-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-0990-7