Abstract
Objectives
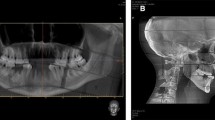
The purpose of this study is to compare the reproducibility of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks on three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) surface rendering using clinical protocols based on low-dose (35-mAs) spiral CT and cone-beam CT (I-CAT). The absorbed dose levels for radiosensitive organs in the maxillofacial region during exposure in both 3D-CT protocols were also assessed.
Materials and methods
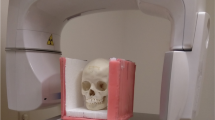
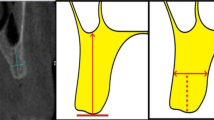
The study population consisted of ten human dry skulls examined with low-dose CT and cone-beam CT. Two independent observers identified 24 cephalometric anatomic landmarks at 13 sites on the 3D-CT surface renderings using both protocols, with each observer repeating the identification 1 month later. A total of 1,920 imaging measurements were performed. Thermoluminescent dosimeters were placed at six sites around the thyroid gland, the submandibular glands, and the eyes in an Alderson phantom to measure the absorbed dose levels.
Results
When comparing low-dose CT and cone-beam CT protocols, the cone-beam CT protocol proved to be significantly more reproducible for four of the 13 anatomical sites. There was no significant difference between the protocols for the other nine anatomical sites. Both low-dose and cone-beam CT protocols were equivalent in dose absorption to the eyes and submandibular glands. However, thyroid glands were more irradiated with low-dose CT.
Conclusions
Cone-beam CT was more reproducible and procured less irradiation to the thyroid gland than low-dose CT.
Clinical relevance
Cone-beam CT should be preferred over low-dose CT for developing three-dimensional bony cephalometric analyses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grayson B, Cutting C, Bookstein FL, Kim H, McCarthy JG (1988) The three-dimensional cephalogram: theory, technique, and clinical application. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 94:327–337
Adams GL, Gansky SA, Miller AJ, Harrell WE Jr, Hatcher DC (2004) Comparison between traditional 2-dimensional cephalometry and a 3-dimensional approach on human dry skulls. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 126:397–409
Swennen GR, Schutyser F, Barth EL, De Groeve P, De Mey A (2006) A new method of 3-D cephalometry Part I: the anatomic Cartesian 3-D reference system. J Craniofac Surg 17:314–325
Richtsmeier JT, Paik CH, Elfert PC, Cole TM 3rd, Dahlman HR (1995) Precision, repeatability, and validation of the localization of cranial landmarks using computed tomography scans. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 32:217–227
Donatsky O, Hillerup S, Bjorn-Jorgensen J, Jacobsen PU (1992) Computerized cephalometric orthognathic surgical simulation, prediction and postoperative evaluation of precision. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 21:199–203
Cavalcanti MG, Haller JW, Vannier MW (1999) Three-dimensional computed tomography landmark measurement in craniofacial surgical planning: experimental validation in vitro. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:690–694
Cavalcanti MG, Rocha SS, Vannier MW (2004) Craniofacial measurements based on 3D-CT volume rendering: implications for clinical applications. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 33:170–176
Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Forrest CR, Alt KW, Bagic I, Baltadjiev G, Cunha E, Cvicelova M, Davies S, Erasmus I, Gillet-Netting R, Hajnis K, Kemkes-Grottenthaler A, Khomyakova I, Kumi A, Kgamphe JS, Kayo-Daigo N, Le T, Malinowski A, Negasheva M, Manolis S, Ogeturk M, Parvizrad R, Rosing F, Sahu P, Sforza C, Sivkov S, Sultanova N, Tomazo-Ravnik T, Toth G, Uzun A, Yahia E (2005) International anthropometric study of facial morphology in various ethnic groups/races. J Craniofac Surg 16:615–646
Delaire J, Schendel SA, Tulasne JF (1981) An architectural and structural craniofacial analysis: a new lateral cephalometric analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 52:226–238
Olszewski R, Zech F, Cosnard G, Nicolas N, Macq B, Reychler H (2007) 3D CT cephalometric craniofacial analysis: experimental validation in vitro. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 36:828–834
Olszewski R, Reychler H, Cosnard G, Denis JM, Vynckier S, Zech F (2008) Accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) craniofacial cephalometric landmarks on low-dose 3D computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37:261–267
Connnor SEJ, Arscott T, Berry J, Greene L, O’Gorman R (2007) Precision and accuracy of low-dose CT protocols in the evaluation of skull landmarks. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 36:270–276
De Vos W, Casselman J, Swennen GR (2009) Cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:609–625
Olszewski R, Tanesy O, Cosnard G, Zech F, Reychler H (2010) Reproducibility of osseous landmarks used for computed tomography based three-dimensional cephalometric analyses. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38:214–221
Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Comp Graph 21:163–169
McCullagh P (1983) Quasi-likelihood functions. Ann Stat 11:59–67
Chaganty NR, Shults J (1999) On eliminating the asymptotic bias in the quasi-least squares estimate of the correlation parameter. J Stat Plan Inf 76:145–161
Morel JG, Bokossa MC, Neerchal NK (2003) Small sample correction for the variance of GEE estimators. Biometric J 45:395–409
Larzelere RE, Mulaik SA (1977) Single-sample tests for many correlations. Psychol Bull 84:557–569
Van Cauter S, Okkerse W, Brijs G, De Beule M, Braem M, Verhegghe B (2010) A new method for improved standardisation in three-dimensional computed tomography cephalometry. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 13:59–69
Enlow DH (1975) Handbook of facial growth. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Ludlow JB, Davies-Ludlow LE, Brooks SL (2003) Dosimetry of two extraoral direct digital imaging devices: NewTom cone beam CT and Orthophos Plus DS panoramic unit. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 32:229–234
Van Vlijmen OJ, Maal TJ, Berge SJ, Bronkhorst EM, Katsaros C, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM (2009) A comparison between two-dimensional and three-dimensional cephalometry on frontal radiographs and on cone beam computed tomography scans of human skulls. Eur J Oral Sci 117:300–305
Schulze D, Heiland M, Thurmann H, Adam G (2004) Radiation exposure during midfacial imaging using 4- and 16-slice computed tomography, cone beam computed tomography systems and conventional radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 33:83–86
Ludlow JB, Davies-Ludlow LE, Brooks SL, Howerton WB (2006) Dosimetry of 3 CBCT devices for oral and maxillofacial radiology: CB Mercuray, NewTom 3 G and i-CAT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35:219–226
Van Vlijmen OJC, Rangel FA, Bergé SJ, Bronkhorst EM, Becking AG, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM (2010) Measurements on 3D models of human skulls derived from two different cone beam CT scanners. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-010-0440-80
Boetticher H, Lachmund J, Looe HK, Hoffmann W, Poppe B (2008) 2007 recommendations of the ICRP change basis for estimation of the effective dose: what is the impact on radiation dose assessment of patient and personnel? Rofo 180:391–395
Mah JK, Hunag JC, Choo H (2010) Practical applications of cone-beam computed tomography in orthodontics. J Am Dent Assoc 141:7S–13S
Cevidanes L, Baccetti T, Franchi L, McNamara JA Jr, De Clerck H (2010) Comparison of two protocols for maxillary protraction: bone anchors versus face mask with rapid maxillary expansion. Angle Orthod 80:799–806
Cevidanes LH, Heymann G, Cornelis MA, De Clerck HJ, Tulloch JF (2009) Superimposition of 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography models of growing patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 136:94–99
Garib DG, Yatabe MS, Ozawa TO, da Silva Filho OG (2011) Alveolar bone morphology in patients with bilateral complete cleft lip and palate in the mixed dentition: CBCT evaluation. Cleft Palate Craniofac J (in press)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Disclosure
There was no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1556 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olszewski, R., Frison, L., Wisniewski, M. et al. Reproducibility of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks in cone-beam and low-dose computed tomography. Clin Oral Invest 17, 285–292 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-012-0688-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-012-0688-2