Abstract
Introduction
Postmenopausal osteoporosis and dyslipidemia are well-known skeletal and metabolic changes in middle-aged women. We investigated the effects of combined treatments with a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and exercise on bone and fat parameters in ovariectomized (OVX) rats.
Materials and Methods
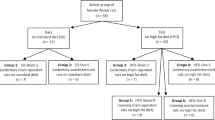
Sixteen-week-old female Sprague–Dawley rats underwent bilateral ovariectomy, and rats were randomized to BZA (bazedoxifene at 0.3 mg/kg/day), Exe (treadmill exercise at 12–15 m/min, 60 min/day, 5 days/week), Comb (BZA and Exe), and Cont (control treated with vehicle and no exercise) groups 8 weeks after ovariectomy. After 4 or 8 weeks of treatment, bone mineral density (BMD) of the total femur and lumbar spine and whole-body percentage fat mass were determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and mechanical testing of the femoral shaft, and bone and fat histomorphometric analyses of the proximal tibia were performed.
Results
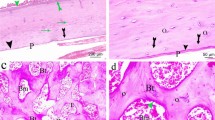
Treadmill exercise had decreased bone marrow adipocytes from 4 weeks of treatment and whole-body percentage fat mass at 8 weeks. BZA increased BMD at the lumbar spine and decreased the whole-body percentage fat mass from 4 weeks and bone marrow adipocytes at 8 weeks. Combination therapy increased BMD for the lumbar spine and decreased bone marrow adipocytes and whole-body percentage fat mass from 4 weeks.
Conclusion
Combination therapy with BZA and exercise appears effective to improve bone and fat parameters in OVX rats.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sari UA, Tobias J, Clark E (2016) Health-related quality of life in older people with osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 27:2891–2900
Nguyen ND, Center JR, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV (2007) Bone loss, weight loss, and weight fluctuation predict mortality risk in elderly men and women. J Bone Miner Res 22:1147–1154
Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Ensrud KC, Scott JC, Black D (2000) Risk of mortality following clinical fractures. Osteoporos Int 11:556–561
Windler EE, Kovanen PT, Chao YS, Brown MS, Havel RJ, Goldstein JL (1980) The estradiol-stimulated lipoprotein receptor of rat liver. A binding site that membrane mediates the uptake of rat lipoproteins containing apoproteins B and E. J Biol Chem 255:10464–10471
Ikenoue N, Wakatsuki A, Okatani Y (1999) Small low-density lipoprotein particles in women with natural or surgically induced menopause. Obstet Gynecol 93:566–570
Parhami F, Jackson SM, Tintut Y, Le V, Balucan JP, Territo M, Demer LL (1999) Atherogenic diet and minimally oxidized low density lipoprotein inhibit osteogenic and promote adipogenic differentiation of marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 14:2067–2078
Yamaguchi M, Kotani K, Tsuzaki K, Takagi A, Motokubota N, Komai N, Sakane N, Moritani T, Nagai N (2015) Circadian rhythm genes CLOCK and PER3 polymorphisms and morning gastric motility in humans. PLoS One 10:e0120009
Itabashi A, Yoh K, Chines AA, Miki T, Takada M, Sato H, Gorai I, Sugimoto T, Mizunuma H, Ochi H, Constantine GD, Ohta H (2011) Effects of bazedoxifene on bone mineral density, bone turnover, and safety in postmenopausal Japanese women with osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 26:519–529
Saito M, Kida Y, Nishizawa T, Arakawa S, Okabe H, Seki A, Marumo K (2015) Effects of 18-month treatment with bazedoxifene on enzymatic immature and mature cross-links and non-enzymatic advanced glycation end products, mineralization, and trabecular microarchitecture of vertebra in ovariectomized monkeys. Bone 81:573–580
Kim JH, Meyers MS, Khuder SS, Abdallah SL, Muturi HT, Russo L, Tate CR, Hevener AL, Najjar SM, Leloup C, Mauvais-Jarvis F (2014) Tissue-selective estrogen complexes with bazedoxifene prevent metabolic dysfunction in female mice. Mol Metab 3:177–190
Barengolts EI, Lathon PV, Curry DJ, Kukreja SC (1994) Effects of endurance exercise on bone histomorphometric parameters in intact and ovariectomized rats. Bone Miner 26:133–140
McNerny EMB, Gardinier JD, Kohn DH (2015) Exercise increases pyridinoline cross-linking and counters the mechanical effects of concurrent lathyrogenic treatment. Bone 81:327–337
Ginsburg GS, Agil A, O’Toole M, Rimm E, Douglas PS, Rifai N (1996) Effects of a single bout of ultraendurance exercise on lipid levels and susceptibility of lipids to peroxidation in triathletes. JAMA 276:221–225
Styner M, Pagnotti GM, McGrath C, Wu X, Sen B, Uzer G, Xie Z, Zong X, Styner MA, Rubin CT, Rubin J (2017) Exercise decreases marrow adipose tissue through ß-oxidation in obese running mice. J Bone Miner Res 32:1692–1702
Kharode Y, Bodine PV, Miller CP, Lyttle CR, Komm BS (2008) The pairing of a selective estrogen receptor modulator, bazedoxifene, with conjugated estrogens as a new paradigm for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis prevention. Endocrinology 149:6084–6091
Komm BS, Vlasseros F, Samadfam R, Chouinard L, Smith SY (2011) Skeletal effects of bazedoxifene paired with conjugated estrogens in ovariectomized rats. Bone 49:376–386
Miyakoshi N, Fujii M, Kasukawa Y, Shimada Y (2018) Impact of vitamin C on teriparatide treatment in the improvement of bone mineral density, strength, and quality in vitamin C-deficient rats. J Bone Miner Metab 37:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-018-0941-0
Segawa T, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Aonuma H, Tsuchie H, Shimada Y (2016) Combined treatment with minodronate and vitamin C increases bone mineral density and strength in vitamin C-deficient rats. Osteoporos Sarcopenia 2:30–37
Miyakoshi N, Sato K, Yoshida S, Abe T (1997) Bone-loss pattern of corticosteroid-induced osteopenia in rats: a node-strut analysis of the tibia. J Bone Miner Metab 15:94–99
Kawano T, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Hongo M, Tsuchie H, Sato C, Fujii M, Suzuki M, Akagawa M, Ono Y, Yuasa Y, Nagahata I, Shimada Y (2017) Effects of combined therapy of alendronate and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on metaphyseal bone repair after osteotomy in the proximal tibia of glucocorticoid-induced osteopenia rats. Osteoporos Sarcopenia 3:185–191
Nozaka K, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Maekawa S, Noguchi H, Shimada Y (2008) Intermittent administration of human parathyroid hormone enhances bone formation and union at the site of cancellous bone osteotomy in normal and ovariectomized rats. Bone 42:90–97
Murata K, Yano E (2002) Medical statistics for evidence-based medicine with SPBS user’s guide. Nankodo, Tokyo
Benayahu D, Shur I, Ben-Eliyahu S (2000) Hormonal changes affect the bone and bone marrow cells in a rat model. J Cell Biochem 79:407–415
Syed FA, Oursler MJ, Hefferanm TE, Peterson JM, Riggs BL, Khosla S (2008) Effects of estrogen therapy on bone marrow adipocytes in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Osteoporos Int 19:1323–1330
Cohen A, Dempster DW, Stein EM, Nickolas TL, Zhou H, McMahon DJ, Müller R, Kohler T, Zwahlen A, Lappe JM, Young P, Recker RR, Shane E (2012) Increased marrow adiposity in premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:2782–2791
Devlin MJ (2011) Why does starvation make bones fat? Am J Hum Biol 23:577–585
Styner M, Thompson WR, Galior K, Uzer G, Wu X, Kadari S, Case N, Xie Z, Sen B, Romaine A, Pagnotti GM, Rubin CT, Styner MA, Horowitz MC, Rubin J (2014) Bone marrow fat accumulation accelerated by high fat diet is suppressed by exercise. Bone 64:39–46
David V, Martin A, Lafage-Proust MH, Malaval L, Peyroche S, Jones DB, Vico L, Guignandon A (2007) Mechanical loading down-regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bone marrow stromal cells and favors osteoblastogenesis at the expense of adipogenesis. Endocrinology 148:2553–2562
Menuki K, Mori T, Sakai A, Sakuma M, Okimoto N, Shimizu Y, Kunugita N, Nakamura T (2008) Climbing exercise enhances osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation with high expression of PTH/PTHrP receptor in bone marrow cells. Bone 43:613–620
Case N, Thomas J, Xie Z, Sen B, Styner M, Rowe D, Rubin J (2013) Mechanical input restrains PPARγ2 expression and action to preserve mesenchymal stem cell multipotentiality. Bone 52:454–464
Marędziak M, Śmieszek A, Chrząstek K, Basinska K, Marycz K (2015) Physical activity increases the total number of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, enhances their osteogenic potential, and inhibits their adipogenic properties. Stem Cells Int 2015:379093
Imai Y, Youn MY, Inoue K, Takada I, Kouzmenko A, Kato S (2013) Nuclear receptors in bone physiology and diseases. Physiol Rev 93:481–523
Lama A, Santoro A, Corrado B, Pirozzi C, Paciello O, Pagano TB, Russo S, Calignano A, Mattace Raso G, Meli R (2017) Extracorporeal shock waves alone or combined with raloxifene promote bone formation and suppress resorption in ovariectomized rats. PLoS One 12:e0171276
Heine PA, Taylor JA, Iwamoto GA, Lubahn DB, Cooke PS (2000) Increased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12729–12734
Bonavera JJ, Dube MG, Kalra PS, Kalra SP (1994) Anorectic effects of estrogen may be mediated by decreased neuropeptide-Y release in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Endocrinology 134:2367–2370
Misso ML, Jang C, Adams J, Tran J, Murata Y, Bell R, Boon WC, Simpson ER, Davis SR (2005) Differential expression of factors involved in fat metabolism with age and the menopause transition. Maturitas 51:299–306
Meli R, Pacilio M, Raso GM, Esposito E, Coppola A, Nasti A, Di Carlo C, Nappi C, Di Carlo R (2004) Estrogen and raloxifene modulate leptin and its receptor in hypothalamus and adipose tissue from ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 145:3115–3121
Barrera J, Chambliss KL, Ahmed M, Tanigaki K, Thompson B, McDonald JG, Mineo C, Shaul PW (2014) Bazedoxifene and conjugated estrogen prevent diet-induced obesity, hepatic steatosis, and type 2 diabetes in mice without impacting the reproductive tract. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 307:E345–E354
Stringhetta-Garcia CT, Singulani MP, Santos LF, Louzada MJ, Nakamune AC, Chaves-Neto AH, Rossi AC, Ervolino E, Dornelles RC (2016) The effects of strength training and raloxifene on bone health in aging ovariectomized rats. Bone 85:45–54
Zhao C, Hou H, Chen Y, Lv K (2016) Effect of aerobic exercise and raloxifene combination therapy on senile osteoporosis. J Phys Ther Sci 28:1791–1794
Barengolts EI, Curry DJ, Bapna MS, Kukreja SC (1993) Effects of endurance exercise on bone mass and mechanical properties in intact and ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 8:937–942
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Matsuzawa and Ms. Kudo for their support in performing the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The protocols for all animal experiments were approved in advance by the Animal Research Committee of our institute, and all subsequent animal experiments adhered to the “Guidelines for Animal Experimentation” of our university (approval number: a-1-2827).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuasa, Y., Miyakoshi, N., Kasukawa, Y. et al. Effects of bazedoxifene and low-intensity aerobic exercise on bone and fat parameters in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab 38, 179–187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-019-01045-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-019-01045-5