Abstract
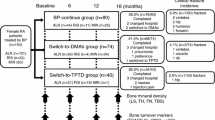
The aim of this 12-month, observational study was to compare the effects of switching daily teriparatide (TPTD) to oral bisphosphonates (BP) therapy or denosumab (DMAb) therapy in patients with primary osteoporosis. Patients [n = 78; 71 postmenopausal women and seven men; mean age 76.3 (64–94) years; mean duration of prior daily TPTD therapy 20.1 (6–24) months] were allocated to either the (1) “switch-to-BP” group [n = 36; weekly alendronate 35 mg (n = 19), weekly risedronate 17.5 mg (n = 12), monthly minodronate 50 mg (n = 5)]; or (2) “switch-to-DMAb” group (n = 42; 60 mg sc every 6 months) based on each physicians’ decision. Changes in bone mineral density (BMD) and serum bone turnover markers were monitored every 6 months. No significant difference was observed in baseline clinical characteristics between the groups. After 12 months, the increase in BMD was significantly greater in the switch-to-DMAb group compared to the switch-to-BP group: lumbar spine (6.2 vs. 2.6 %; P < 0.01), total hip (4.2 vs. 1.1 %; P < 0.05), and femoral neck (3.5 vs. 1.4 %; P < 0.05). In addition, the patients in the switch-to-DMAb group showed a significant decrease compared to those in the switch-to-BP group in TRACP-5b (−55.8 vs. −32.8 %; P < 0.01) and ucOC (−85.5 vs. −65.0 %; P < 0.001), while no significant difference was observed in PINP (−67.5 vs. −62.1 %). Switching daily TPTD to DMAb significantly increased BMD and decreased bone resorption marker compared to switching to oral BP at 12 months, and thus may provide an effective sequential treatment option after daily TPTD treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto T, Taketsuna M, Guo X, Sato M, Sowa H (2014) The safety and effectiveness profile of daily teriparatide in a prospective observational study in Japanese patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: interim report. J Bone Miner Metab 32:699–708
Lee SK, Lorenzo JA (2002) Regulation of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand and osteoprotegerin mRNA expression by parathyroid hormone is predominantly mediated by the protein kinase a pathway in murine bone marrow cultures. Bone 31:252–259
Gallacher SJ, Dixon T (2010) Impact of treatments for postmenopausal osteoporosis (bisphosphonates, parathyroid hormone, strontium ranelate, and denosumab) on bone quality: a systematic review. Calcif Tissue Int 87:469–484
Muschitz C, Kocijan R, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Lung S, Resch H (2013) Antiresorptives overlapping ongoing teriparatide treatment result in additional increases in bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 28:196–205
Obermayer-Pietsch BM, Marin F, McCloskey EV et al (2008) Effects of two years of daily teriparatide treatment on BMD in postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis with and without prior antiresorptive treatment. J Bone Miner Res 23:1591–1600
Brown JP, Prince RL, Deal C et al (2009) Comparison of the effect of denosumab and alendronate on BMD and biochemical markers of bone turnover in postmenopausal women with low bone mass: a randomized, blinded, phase 3 trial. J Bone Miner Res 24:153–161
Recknor C, Czerwinski E, Bone HG et al (2013) Denosumab compared with ibandronate in postmenopausal women previously treated with bisphosphonate therapy: a randomized open-label trial. Obstet Gynecol 121:1291–1299
Roux C, Hofbauer LC, Ho PR et al (2014) Denosumab compared with risedronate in postmenopausal women suboptimally adherent to alendronate therapy: efficacy and safety results from a randomized open-label study. Bone 58:48–54
Kostenuik PJ, Smith SY, Samadfam R, Jolette J, Zhou L, Ominsky MS (2015) Effects of denosumab, alendronate, or denosumab following alendronate on bone turnover, calcium homeostasis, bone mass and bone strength in ovariectomized cynomolgus monkeys. J Bone Miner Res 30:657–669
Zebaze RM, Libanati C, Austin M et al (2014) Differing effects of denosumab and alendronate on cortical and trabecular bone. Bone 59:173–179
Orimo H, Nakamura T, Hosoi T et al (2012) Japanese 2011 guidelines for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis–executive summary. Arch Osteoporos 7:3–20
Ebina K, Hashimoto J, Shi K, Kashii M, Hirao M, Yoshikawa H (2014) Comparison of the effect of 18-month daily teriparatide administration on patients with rheumatoid arthritis and postmenopausal osteoporosis patients. Osteoporos Int 25:2755–2765
Ebina K, Noguchi T, Hirao M, Kaneshiro S, Tsukamoto Y, Yoshikawa H (2015) Comparison of the effects of 12 months of monthly minodronate monotherapy and monthly minodronate combination therapy with vitamin K2 or eldecalcitol in patients with primary osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. doi:10.1007/s00774-015-0710-2
Ebina K, Shi K, Hirao M, Kaneshiro S, Morimoto T, Koizumi K, Yoshikawa H, Hashimoto J (2013) Vitamin K2 administration is associated with decreased disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 23:1001–1007
Ebina K, Hashimoto J, Shi K, Kashii M, Hirao M, Yoshikawa H (2015) Undercarboxylated osteocalcin may be an attractive marker of teriparatide treatment in RA patients: response to Mokuda. Osteoporos Int 26:1445
Booth SL, Centi A, Smith SR, Gundberg C (2013) The role of osteocalcin in human glucose metabolism: marker or mediator? Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:43–55
Ominsky MS, Libanati C, Niu QT, Boyce RW, Kostenuik PJ, Wagman RB, Baron R, Dempster DW (2015) Sustained modeling-based bone formation during adulthood in cynomolgus monkeys may contribute to continuous BMD gains with denosumab. J Bone Miner Res 30:1280–1289
Russell RG, Watts NB, Ebetino FH, Rogers MJ (2008) Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy. Osteoporos Int 19:733–759
Joo NS, Dawson-Hughes B, Kim YS, Oh K, Yeum KJ (2013) Impact of calcium and vitamin D insufficiencies on serum parathyroid hormone and bone mineral density: analysis of the fourth and fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3, 2009 and KNHANES V-1, 2010). J Bone Miner Res 28:764–770
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR et al (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Lambert C, Oury C, Dejardin E, Chariot A, Piette J, Malaise M, Merville MP, Franchimont N (2007) Further insights in the mechanisms of interleukin-1beta stimulation of osteoprotegerin in osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Res 22:1350–1361
Samadfam R, Xia Q, Goltzman D (2007) Co-treatment of PTH with osteoprotegerin or alendronate increases its anabolic effect on the skeleton of oophorectomized mice. J Bone Miner Res 22:55–63
Inage K, Orita S, Yamauchi K et al (2015) The time course changes in bone metabolic markers after administering the anti-receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand antibody and drug compliance among patients with osteoporosis. Asian Spine J 9:338–343
Eastell R, Christiansen C, Grauer A et al (2011) Effects of denosumab on bone turnover markers in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 26:530–537
Nakamura T, Matsumoto T, Sugimoto T et al (2014) Clinical trials express: fracture risk reduction with denosumab in Japanese postmenopausal women and men with osteoporosis: denosumab fracture intervention randomized placebo controlled trial (DIRECT). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:2599–2607
Sugimoto T, Matsumoto T, Hosoi T et al (2015) Three-year denosumab treatment in postmenopausal Japanese women and men with osteoporosis: results from a 1-year open-label extension of the Denosumab Fracture Intervention Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial (DIRECT). Osteoporos Int 26:765–774
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Eiji Sogo, Dr. Hirokazu Iwata, and Dr. Hirotaka Tsuji for their excellent cooperation in conducting the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K Ebina has received payments for lectures from Daiichi Sankyo. J Hashimoto, M Kashii, M Hirao, S Kaneshiro, T Noguchi, Y Tsukamoto, and H Yoshikawa declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Ebina, K., Hashimoto, J., Kashii, M. et al. The effects of switching daily teriparatide to oral bisphosphonates or denosumab in patients with primary osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 35, 91–98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0731-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0731-x