Abstract
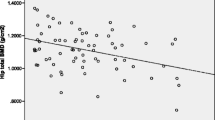
The aim of this study was to evaluate the differences between patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) and phenotypically similar subjects without OSAS in terms of bone mineral density (BMD) and bone turnover markers. The study was conducted on 30 males diagnosed with OSAS and 20 healthy males. All subjects underwent polysomnographic testing. Calcium, phosphorus parathyroid hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, osteocalcin, and beta-CrossLaps (β-CTx) were measured. BMD in the lumbar spine (L1–L4) and femoral neck was measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of demographic data with the exception of bone mass index and waist circumference. (p < 0.05). Analyses showed significantly lower BMD measurements in the femoral neck and T-scores in the femoral neck in patients diagnosed with OSAS. Serum β-CTx levels were found to be statistically significantly higher in the OSAS group (p = 0.017). In multivariate assessments performed for apnea/hypopnea index values, mean saturation O2 levels were found to be significantly associated with osteocalcin levels and neck BMD. OSAS patients might represent a risk group with respect to loss of BMD and bone resorption. It is important to evaluate bone loss in these patients. Further studies should be carried out on larger study populations to evaluate the effects of chronic hypoxia on BMD in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S et al (2001) Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the sleep heart health study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:19–25
Khan F, Walsh C, Lane SJ et al (2014) Sleep apnoea and its relationship with cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic and other morbidities. Ir Med J 107:6–8
Barceló A, Piérola J, de la Peña M et al (2011) Free fatty acids and the metabolic syndrome in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 37:1418–1423. doi:10.1183/09031936.00050410
Nair D, Dayyat EA, Zhang SX et al (2011) Intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits are mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in a murine model of sleep apnea. PLoS ONE 6:e19847. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019847
Destors M, Tamisier R, Baguet JP et al (2014) Cardiovascular morbidity associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rev Mal Respir 31:375–385. doi:10.1016/j.rmr.2013.12.003
Sforza E, Thomas T, Barthélémy JC et al (2013) Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with preserved bone mineral density in healthy elderly subjects. Sleep 36:1509–1515. doi:10.5665/sleep.3046
Uzkeser H, Yildirim K, Aktan B et al (2013) Bone mineral density in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 17:339–342
Tomiyama H, Okazaki R, Inoue D et al (2008) Link between obstructive sleep apnea and increased bone resorption in men. Osteoporos Int 19:1185–1192
Fujimoto H, Fujimoto K, Ueda A, Ohata M (1999) Hypoxemia is a risk factor for bone mass loss. J Bone Miner Metab 17:211–216
Arnett TR (2010) Acidosis, hypoxia and bone. Arch Biochem Biophys 503:103–109
Svensson A, Venge P, Janson C, Lındberg E (2012) Relationship between sleepdisordered breathing and markers of systemic inflammation in women from the general population. J Sleep Res 21:147–154
Almendros I, Carreras A, Montserrat JM et al (2012) Potential role of adult stem cells in obstructive sleep apnea. Front Neurol 3:112
Guven SF, Turkkani MH, Ciftci B et al (2012) The relationship between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and the severity of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 16:217–221. doi:10.1007/s11325-011-0492-2
Yokoe T, Minoguchi K, Matsuo H et al (2003) Elevated levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome are decreased by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Circulation 107:1129–1134
Mariani S, Fiore D, Varone L et al (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea and bone mineral density in obese patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 5:395–401. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S37761
Arnett TR, Gibbons DC, Utting JC et al (2003) Hypoxia is a major stimulator of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J Cell Physiol 196:2–8
Utting JC, Flanagan AM, Brandao-Burch A et al (2010) Hypoxia stimulates osteoclast formation from human peripheral blood. Cell Biochem Funct 28:374–380
Orriss IR, Knight GE, Utting JC et al (2009) Hypoxia stimulates vesicular ATP release from rat osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol 220:155–162
Fink T, Abildtrup L, Fogd K et al (2004) Induction of adipocyte-like phenotype in human mesenchymal stem cells by hypoxia. Stem Cells 22:1346–1355
Utting JC, Robins SP, Brandao-Burch A et al (2006) Hypoxia inhibits the growth, differentiation and bone-forming capacity of rat osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res 312:1693–1702
Song L, Liang X, Zhou Y (2014) Estrogen-mimicking isoflavone genistein prevents bone loss in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:1687–1694 (eCollection 2014)
Lemann J Jr, Litzow JR, Lennon EJ (1966) The effects of chronic acid loads in normal man: further evidence for the participation of bone mineral in the defense against chronic metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest 45:1608–1614
Arnett TR, Spowage M (1996) Modulation of the resorptive activity of rat osteoclasts by small changes in extracellular pH near the physiological range. Bone 18:277–279
Brandao-Burch A, Utting JC, Orriss IR et al (2005) Acidosis inhibits bone formation by osteoblasts in vitro by preventing mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int 77:167–174
Erden ES, Genc S, Motor S et al (2014) Investigation of serum bisphenol A, vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Endocrine 45:311–318. doi:10.1007/s12020-013-0022-z
Wortsman J, Matsuoka LY, Chen TC, Lu Z et al (2000) Decreased bioavailability of vitamin D in obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 72:690–693
Buffington C, Walker B, CowanJr GS et al (1993) Vitamin D deficiency in morbidly obese. Obes Surg 3:421–424
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Terzi, R., Yılmaz, Z. Bone mineral density and changes in bone metabolism in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Bone Miner Metab 34, 475–481 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0691-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0691-1