Abstract
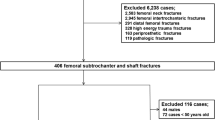
The long-term treatment with anti-resorptive drugs for osteoporotic patients is suggested to be associated with an increase in atypical femoral fractures (AFFs). However, their incidence, patient characteristics, and risk factors have not been fully elucidated especially in Asian countries. This retrospective observational cohort study found fourteen AFFs in ten patients (four bilateral fractures) among 2,238 hip and femoral shaft fractures treated in our associated hospitals between 2005 and 2010; this incidence (0.63 %) was similar to Caucasians. Of the ten patients with AFFs, nine (90 %) and six (60 %) were using bisphosphonates (BPs) and glucocorticoids (GCs), respectively, compared to 14.3 and 8.6 % for patients with typical femoral fractures who were using these agents. As comorbid conditions, five patients had collagen disease (CD) and two had diabetes. A fracture location-, age- and gender-matched (1:3) case–control study revealed that administration of BPs, GCs, and suffering from collagen disease (CD) were significant risk factors for developing AFFs [odds ratios 36.0 (95 % confidence intervals 3.8–342.2), 13.0 (2.3–74.1) and 9.0 (1.6–50.3), respectively]. Interestingly, all of the patients with atypical subtrochanteric femoral fractures, defined as those within 5 cm of the lesser trochanter, were taking GCs due to CD, and the age of these patients (average of 54.8 years) was significantly younger than those with atypical diaphyseal femoral fractures (average of 77.2 years, p < 0.05). In conclusion, the incidence of AFFs in the Japanese population was similar to that of Caucasians, and taking BPs and GCs and suffering from CD were risk factors for developing AFFs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ioannidis G, Papaioannou A, Hopman WM, Akhtar-Danesh N, Anastassiades T, Pickard L, Kennedy CC, Prior JC, Olszynski WP, Davison KS, Goltzman D, Thabane L, Gafni A, Papadimitropoulos EA, Brown JP, Josse RG, Hanley DA, Adachi JD (2009) Relation between fractures and mortality: results from the Canadian Multicentre Osteoporosis Study. CMAJ 181:265–271
Papaioannou A, Kennedy CC, Ioannidis G, Sawka A, Hopman WM, Pickard L, Brown JP, Josse RG, Kaiser S, Anastassiades T, Goltzman D, Papadimitropoulos M, Tenenhouse A, Prior JC, Olszynski WP, Adachi JD (2009) The impact of incident fractures on health-related quality of life: 5 years of data from the Canadian Multicentre Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos Int 20:703–714
Wells GA, Cranney A, Peterson J, Boucher M, Shea B, Robinson V, Coyle D, Tugwell P (2008) Alendronate for the primary and secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev :CD001155
Wells G, Cranney A, Peterson J, Boucher M, Shea B, Robinson V, Coyle D, Tugwell P (2008) Risedronate for the primary and secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev :CD004523
Recker R, Masarachia P, Santora A, Howard T, Chavassieux P, Arlot M, Rodan G, Wehren L, Kimmel D (2005) Trabecular bone microarchitecture after alendronate treatment of osteoporotic women. Curr Med Res Opin 21:185–194
Nakatsuka K, Miki T, Naka H, Inaba M, Nishizawa Y (2004) Long-term effect of intermittent cyclical etidronate on microarchitecture and quality of trabecular bone in an elderly woman with severe osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 22:153–158
Mashiba T, Hirano T, Turner CH, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB (2000) Suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates increases microdamage accumulation and reduces some biomechanical properties in dog rib. J Bone Miner Res 15:613–620
Saito M, Mori S, Mashiba T, Komatsubara S, Marumo K (2008) Collagen maturity, glycation induced-pentosidine, and mineralization are increased following 3-year treatment with incadronate in dogs. Osteoporos Int 19:1343–1354
Yoneda T, Hagino H, Sugimoto T, Ohta H, Takahashi S, Soen S, Taguchi A, Toyosawa S, Nagata T, Urade M (2010) Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: position paper from the Allied Task Force Committee of Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research, Japan Osteoporosis Society, Japanese Society of Periodontology, Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, and Japanese Society of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. J Bone Miner Metab 28:365–383
Shane E, Burr D, Ebeling PR, Abrahamsen B, Adler RA et al (2010) Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 25:2267–2294
Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY (2005) Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:1294–1301
Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS, Wong MK, Chua SY, Chua DT, Howe TS (2007) Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Jt Surg Br 89:349–353
Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Papapoulos SE (2010) Atypical fractures of the femur and bisphosphonate therapy: a systematic review of case/case series studies. Bone 47:169–180
Neviaser AS, Lane JM, Lenart BA, Edobor-Osula F, Lorich DG (2008) Low-energy femoral shaft fractures associated with alendronate use. J Orthop Trauma 22:346–350
Lenart BA, Neviaser AS, Lyman S, Chang CC, Edobor-Osula F, Steele B, van der Meulen MC, Lorich DG, Lane JM (2009) Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case control study. Osteoporos Int 20:1353–1362
Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, Adler RA, Brown TD et al (2014) Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 29:1–23
Black DM, Kelly MP, Genant HK, Palermo L, Eastell R, Bucci-Rechtweg C, Cauley J, Leung PC, Boonen S, Santora A, de Papp A, Bauer DC (2010) Bisphosphonates and fractures of the subtrochanteric or diaphyseal femur. N Engl J Med 362:1761–1771
Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, Hawker GA, Gunraj N, Austin PC, Whelan DB, Weiler PJ, Laupacis A (2011) Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 305:783–789
Rizzoli R, Akesson K, Bouxsein M, Kanis JA, Napoli N, Papapoulos S, Reginster JY, Cooper C (2011) Subtrochanteric fractures after long-term treatment with bisphosphonates: a European Society on Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis, and International Osteoporosis Foundation Working Group Report. Osteoporos Int 22:373–390
Schilcher J, Michaelsson K, Aspenberg P (2011) Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med 364:1728–1737
Orimo H, Hayashi Y, Fukunaga M, Sone T, Fujiwara S, Shiraki M, Kushida K, Miyamoto S, Soen S, Nishimura J, Oh-Hashi Y, Hosoi T, Gorai I, Tanaka H, Igai T, Kishimoto H (2001) Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: year 2000 revision. J Bone Miner Metab 19:331–337
Nieves JW, Bilezikian JP, Lane JM, Einhorn TA, Wang Y, Steinbuch M, Cosman F (2010) Fragility fractures of the hip and femur: incidence and patient characteristics. Osteoporos Int 21:399–408
ACR ad hoc Committee on Neuropsychiatric Lupus Nomenclature (1999) The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum 42:599–608
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:344–347
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:403–407
Nutter J (1922) On delayed union and non-union of fractures. J Bone Jt Surg Am 4:25
Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R (2009) Subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures in patients treated with alendronate: a register-based national cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 24:1095–1102
Schilcher J, Aspenberg P (2009) Incidence of stress fractures of the femoral shaft in women treated with bisphosphonate. Acta Orthop 80:413–415
Thompson RN, Phillips JR, McCauley SH, Elliott JR, Moran CG (2012) Atypical femoral fractures and bisphosphonate treatment: experience in two large United Kingdom teaching hospitals. J Bone Jt Surg Br 94:385–390
Bottai V, Giannotti S, Dell’osso G, De Paola G, Menconi A, Falossi F, Raffaeta G, Guido G (2013) Atypical femoral fractures: retrospective radiological study of 319 femoral fractures and presentation of clinical cases. Osteoporos Int 25:993–997
Meier RP, Perneger TV, Stern R, Rizzoli R, Peter RE (2012) Increasing occurrence of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use. Arch Intern Med 172:930–936
Ishijima M, Sakamoto Y, Yamanaka M, Tokita A, Kitahara K, Kaneko H, Kurosawa H (2009) Minimum required vitamin D level for optimal increase in bone mineral density with alendronate treatment in osteoporotic women. Calcif Tissue Int 85:398–404
Girgis CM, Sher D, Seibel MJ (2010) Atypical femoral fractures and bisphosphonate use. N Engl J Med 362:1848–1849
Stevenson JC (2011) Bisphosphonates and atypical femoral shaft fractures. N Engl J Med 365:377
Weinstein RS (2000) True strength. J Bone Miner Res 15:621–625
Frost HM (1963) Introduction to biomechanics. Charles C Thomas, Springfield
Acknowledgments
We thank all orthopedic surgeons working at Juntendo University Hospital, Juntendo Urayasu Hospital, Juntendo Shizuoka Hospital, Juntendo Nerima Hospital, Koto Hospital and Chiba Central Medical Center for providing the clinical data and information about the treatment courses of patients.
This work was not funded by any research or training grants. The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Saita, Y., Ishijima, M., Mogami, A. et al. The incidence of and risk factors for developing atypical femoral fractures in Japan. J Bone Miner Metab 33, 311–318 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-014-0591-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-014-0591-9