Abstract
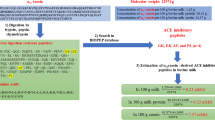
The capacity of buffalo milk proteins to release bioactive peptides was evaluated and novel bioactive peptides were identified. The sequential similarity between buffalo milk proteins and their cow counterparts was analysed. Buffalo milk proteins were simulated to yield theoretical peptides via in silico proteolysis. The potential of selected proteins to release specific bioactive peptides was evaluated by the A value obtained from the BIOPEP–UWM database (Minkiewicz et al. in Int J Mol Sci 20(23):5978, 2019). Buffalo milk protein is a suitable precursor to produce bioactive peptides, particularly dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Two novel ACE inhibitory peptides (KPW and RGP) and four potential DPP-IV inhibitory peptides (RGP, KPW, FPK and KFTW) derived from in silico proteolysis of buffalo milk proteins were screened using different integrated bioinformatic approaches (PeptideRanker, Innovagen, peptide-cutter and molecular docking). The Lineweaver–Burk plots showed that KPW (IC50 = 136.28 ± 10.77 μM) and RGP (104.72 ± 8.37 μM) acted as a competitive inhibitor against ACE. Similarly, KFTW (IC50 = 873.92 ± 32.89 μM) was also a competitive inhibitor of DPP-IV, while KPW and FPK (82.52 ± 10.37 and 126.57 ± 8.45 μM, respectively) were mixed-type inhibitors. It should be emphasized that this study does not involve any clinical trial.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hamid M, Otte J, De Gobba C, Osman A, Hamad E (2017) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and antioxidant capacity of bioactive peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of buffalo milk proteins. Int Dairy J 66:91–98
Ahmad S, Gaucher I, Rousseau F, Beaucher E, Piot M, Grongnet JF, Gaucheron F (2008) Effects of acidification on physico-chemical characteristics of buffalo milk: a comparison with cow’s milk. Food Chem 106(1):11–17
Basilicata MG, Pepe G, Sommella E, Ostacolo C, Manfra M, Sosto G, Pagano G, Novellino E, Campiglia P (2018) Peptidome profiles and bioactivity elucidation of buffalo-milk dairy products after gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res Int 105:1003–1010
Bonfatti V, Giantin M, Rostellato R, Dacasto M, Carnier P (2013) Separation and quantification of water buffalo milk protein fractions and genetic variants by RP-HPLC. Food Chem 136(2):364–367
Brijesha N, Aparna H (2017) Comprehensive characterization of bioactive peptides from Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) colostrum and milk fat globule membrane proteins. Food Res Int 97:95–103
Chen H, Qi X, Guan K, Gu Y, Wang R, Li Q, Ma Y (2021) Peptides released from bovine α-lactalbumin by simulated digestion alleviated free fatty acids-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. J Funct Foods 85:104618
Dalgleish DG, Corredig M (2012) The structure of the casein micelle of milk and its changes during processing. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 3:449–467
Dave LA, Montoya CA, Rutherfurd SM, Moughan PJ (2014) Gastrointestinal endogenous proteins as a source of bioactive peptides-an in silico study. PLoS One 9(6):e98922
Dziuba M, Dziuba B (2010) In silico analysis of bioactive peptides. In: Mine Y, Li-Chan E, Jiang B (eds) Bioactive proteins and peptides as functional foods and nutraceuticals. Wiley-Blackwell and IFT Press, Ames, pp 325–340
El-Salam MHA, El-Shibiny S (2013) Bioactive peptides of buffalo, camel, goat, sheep, mare, and yak milks and milk products. Food Rev Int 29(1):1–23
Fan F, Shi P, Chen H, Tu M, Wang Z, Lu W, Du M (2019) Identification and availability of peptides from lactoferrin in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Food Funct 10(2):879
Fekete AA, Givens DI, Lovegrove JA (2015) Casein-derived lactotripeptides reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Nutrients 7(1):659–681
Ghasemi JB, Abdolmaleki A, Shiri F (2017) Molecular docking challenges and limitations. In: Association IRM (ed) Pharmaceutical sciences: breakthroughs in research and practice. IGI Global, Hershey, pp 770–794
Gong H, Gao J, Wang Y, Luo Q, Guo K, Ren F, Mao X (2020) Identification of novel peptides from goat milk casein that ameliorate high-glucose-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. J Dairy Sci 103(6):4907–4918
Gu Y, Li X, Liu H, Li Q, Xiao R, Dudu OE, Yang L, Ma Y (2020) The impact of multiple-species starters on the peptide profiles of yoghurts. Int Dairy J 106:104684
Han B-Z, Meng Y, Li M, Yang Y-X, Ren F-Z, Zeng Q-K, Nout MR (2007) A survey on the microbiological and chemical composition of buffalo milk in China. Food Control 18(6):742–746
Han R, Maycock J, Murray BS, Boesch C (2018) Identification of angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides derived from oilseed proteins using two integrated bioinformatic approaches. Food Res Int 115:283–291
Hatanaka T, Inoue Y, Arima J, Kumagai Y, Usuki H, Kawakami K, Kimura M, Mukaihara T (2012) Production of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from defatted rice bran. Food Chem 134(2):797–802
Ichimura T, Hu J, Aita D, Maruyama S (2003) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and insulin secretion stimulative activity of fermented fish sauce. J Biosci Bioeng 96:496–499
Joost S, Jesper B, Francois S, Robby N, Frederic R, Luis S (2005) The FoldX web server: an online force field. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Web Server issue):W382-388
Kapila R, Kavadi PK, Kapila S (2013) Comparative evaluation of allergic sensitization to milk proteins of cow, buffalo and goat. Small Rumin Res 112(1–3):191–198
Korhonen H, Pihlanto A (2003) Food-derived bioactive peptides-opportunities for designing future foods. Curr Pharm Des 9:1297–1308
Lan VTT, Ito K, Ohno M, Motoyama T, Kawarasaki Y (2015) Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem 175:66–73
Lin K, Zhang LW, Han X, Cheng DY (2017) Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hydrolysates of Qula casein: quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J Funct Foods 32:266–277
Lin K, Zhang LW, Han X, Xin L, Meng ZX, Gong PM, Cheng DY (2018) Yak milk casein as potential precursor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides based on in silico proteolysis. Food Chem 254:340–347
Maruyama S, Ohmori T, Nakagami T (1996) Prolylendopeptidase inhibitory activity of a glial fibrillary acidic protein fragment and other proline-rich peptides. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60(2):358–359
Minervini F, Algaron F, Rizzello CG, Fox PF, Monnet V, Gobbetti M (2003) Angiotensin I-converting-enzyme-inhibitory and antibacterial peptides from Lactobacillus helveticus PR4 proteinase-hydrolyzed caseins of milk from six species. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(9):5297
Minkiewicz P, Iwaniak A, Darewicz M (2019) BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: current opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):5978
Mullally MM, Meisel H, FitzGerald RJ (1997) Identification of a novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide corresponding to a tryptic fragment of bovine β-lactoglobulin. FEBS Lett 402(2–3):99–101
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto N, Sakai K, Okubo A, Yamazaki S, Takano T (1995) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J Dairy Sci 78(4):777–783
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2013a) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidative properties of milk protein-derived dipeptides and hydrolysates. Peptides 39(Complete):157–163
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2013b) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) by proline containing peptides. J Funct Foods 5(4):1909–1917
Nongonierma AB, FitzGerald RJ (2014) Susceptibility of milk protein-derived peptides to dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) hydrolysis. Food Chem 145:845–852
Nongonierma AB, Mooney C, Shields DC, Fitzgerald RJ (2013) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and xanthine oxidase by amino acids and dipeptides. Food Chem 141(1):644–653
Norris R, Poyarkov A, O’Keeffe MB, FitzGerald RJ (2014) Characterisation of the hydrolytic specificity of Aspergillus niger derived prolyl endoproteinase on bovine β-casein and determination of ACE inhibitory activity. Food Chem 156:29–36
Pepe G, Basilicata MG, Carrizzo A, Adesso S, Ostacolo C, Sala M, Sommella E, Ruocco M, Cascioferro S, Ambrosio M, Pisanti S, Di Sarno V, Bertamino A, Marzocco S, Vecchione C, Campiglia P (2019) β-Lactoglobulin heptapeptide reduces oxidative stress in intestinal epithelial cells and angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction on mouse mesenteric arteries by induction of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) translocation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1–13
Rafiq S, Huma N, Pasha I, Sameen A, Mukhtar O, Khan MI (2016) Chemical composition, nitrogen fractions and amino acids profile of milk from different animal species. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 29(7):1022–1028
Reddi S, Shanmugam VP, Kapila S, Kapila R (2016) Identification of buffalo casein-derived bioactive peptides with osteoblast proliferation activity. Eur Food Res Technol 242(12):2139–2146
Reddi S, Shanmugam VP, Tanedjeu KS, Kapila S, Kapila R (2018) Effect of buffalo casein-derived novel bioactive peptides on osteoblast differentiation. Eur J Nutr 57(2):593–605
Richter B, Bandeira-Echtler E, Bergerhoff K, Lerch C (2008) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 32(2):193–203
Shanmugam VP, Kapila S, Sonfack TK, Kapila R (2015) Antioxidative peptide derived from enzymatic digestion of buffalo casein. Int Dairy J 42:1–5
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461
Tu M, Cheng S, Lu W, Du M (2018a) Advancement and prospects of bioinformatics analysis for studying bioactive peptides from food-derived protein: sequence, structure, and functions. Trends Analyt Chem 105:7–17
Tu M, Wang C, Chen C, Zhang R, Liu H, Lu W, Jiang L, Du M (2018b) Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem 256(Aug. 1):98–104
Udenigwe CC (2014) Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci Technol 36(2):137–143
Uenishi H, Kabuki T, Seto Y, Serizawa A, Nakajima H (2012) Isolation and identification of casein-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4)-inhibitory peptide LPQNIPPL from gouda-type cheese and its effect on plasma glucose in rats. Int Dairy J 22(1):24–30
Vercruysse L, Smagghe G, van der Bent A, van Amerongen A, Ongenaert M, Van Camp J (2009) Critical evaluation of the use of bioinformatics as a theoretical tool to find high-potential sources of ACE inhibitory peptides. Peptides 30(3):575–582
Zafar SK, Iqbal S, Mumtaz M, Ali SK, Ali ST (2018) Inhibitory mechanism exhibited by phenol-based natural products against DNA polymerase [alpha] from Psoralea corylifolia by molecular docking. J Chem Soc Pak 40(6):1089–1092
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Xiuxiu Zhang for valuable discussion and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation and writing—original draft: YG. Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation and writing—review and editing: XL. Writing—review and editing: XQ. Resources and supervision: YM. Writing—review and editing: ECYC.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
No informed consent is required for this study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Alexandre de Brevern.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Li, X., Qi, X. et al. In silico identification of novel ACE and DPP-IV inhibitory peptides derived from buffalo milk proteins and evaluation of their inhibitory mechanisms. Amino Acids 55, 161–171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03202-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03202-z