Abstract
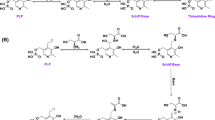
l-Thioproline (l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylate, l-T4C) is a cyclic sulfur-containing analog of l-proline found in multiple kingdoms of life. The oxidation of l-T4C leads to l-cysteine formation in bacteria, plants, mammals, and protozoa. The conversion of l-T4C to l-Cys in bacterial cell lysates has been attributed to proline dehydrogenase and l-Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) reductase (PYCR) enzymes but detailed kinetic studies have not been conducted. Here, we characterize the dehydrogenase activity of human PYCR isozymes 1 and 2 with l-T4C using NAD(P)+ as the hydride acceptor. Both PYCRs exhibit significant l-T4C dehydrogenase activity; however, PYCR2 displays nearly tenfold higher catalytic efficiency (136 M−1 s−1) than PYCR1 (13.7 M−1 s−1). Interestingly, no activity was observed with either l-Pro or the analog dl-thiazolidine-2-carboxylate, indicating that the sulfur at the 4-position is critical for PYCRs to utilize l-T4C as a substrate. Inhibition kinetics show that l-Pro is a competitive inhibitor of PYCR1 \(\left({K_{IC}^{app}}=15.7 \,{\rm mM} \right)\) with respect to l-T4C, consistent with these ligands occupying the same binding site. We also confirm by mass spectrometry that l-T4C oxidation by PYCRs leads to cysteine product formation. Our results suggest a new enzyme function for human PYCRs in the metabolism of l-T4C.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study for the figures and tables are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- l-T4C:
-
l-Thiazolidine-4-carboxylate
- l-Pro:
-
l-Proline
- l-Cys:
-
l-Cysteine
- dl--T2C:
-
dl--Thiazolidine-2-carboxylate
- l-GSAL:
-
l-Glutamate γ-semialdehyde
- GSALDH:
-
l-GSAL dehydrogenase
- IAM:
-
Iodoacetamide
- NADH:
-
Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NAD+ :
-
Oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NAD(P)H:
-
Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate)
- NAD(P)+ :
-
Oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate)
- l-P5C:
-
l-∆1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate
- PYCR:
-
∆1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase
References
Cavallini D, De Marco C, Mondovi B, Trasarti F (1956) Studies of the metabolism of thiazolidine carboxylic acid by rat liver homogenate. Biochim Biophys Acta 22(3):558–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3002(56)90068-3
Christensen EM, Patel SM, Korasick DA, Campbell AC, Krause KL, Becker DF, Tanner JJ (2017) Resolving the cofactor-binding site in the proline biosynthetic enzyme human pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1. J Biol Chem 292(17):7233–7243. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.780288
Christensen EM, Bogner AN, Vandekeere A, Tam GS, Patel SM, Becker DF, Fendt SM, Tanner JJ (2020) In crystallo screening for proline analog inhibitors of the proline cycle enzyme PYCR1. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.016106
De Ingeniis J, Ratnikov B, Richardson AD, Scott DA, Aza-Blanc P, De SK, Kazanov M, Pellecchia M, Ze R, Osterman AL, Smith JW (2012) Functional specialization in proline biosynthesis of melanoma. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045190
Deichmann U, Schuster S, Mazat J-P, Cornish-Bowden A (2014) Commemorating the 1913 Michaelis-Menten paper Die kinetik der invertinwirkung: three perspectives. FEBS J 281(2):435–463
Deutch CE (1992) Oxidation of l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylate by l-proline dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol 138(Pt 8):1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-138-8-1593
Deutch CE, Klarstrom JL, Link CL, Ricciardi DL (2001) Oxidation of l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylate by Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase in Escherichia coli. Curr Microbiol 42:442–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010245
Elthon TE, Stewart CR (1984) Effects of the proline analog l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid on proline metabolism. Plant Physiol 74(2):213–218
Fleming GA, Hagedorn CH, Granger AS, Phang JM (1984) Pyrroline-5-carboxylate in human plasma. Metabolism 33(8):739–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0495(84)90215-4
Furlan AL, Bianucci E, Giordano W, Castro S, Becker DF (2020) Proline metabolic dynamics and implications in drought tolerance of peanut plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 151:566–578
Garnier R, Conso F, Efthymiou ML, Fournier E (1980) Thioproline. Lancet 1(8164):365
Howard-Lock H, Lock C, Martins M, Smalley P, Bell R (1986) Amino-acid zwitterion equilibria: vibrational and nuclear magnetic resonance studies of methyl-substituted thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acids. Can J Chem 64(6):1215–1219
Jeelani G, Sato D, Soga T, Watanabe H, Nozaki T (2014) Mass spectrometric analysis of l-cysteine metabolism: physiological role and fate of l-cysteine in the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Mbio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01995-14
Johnson AB, Strecker HJ (1962) The interconversion of glutamic acid and proline. IV. The oxidation of proline by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem 237:1876–1882
Kumagai H, Mukaisho K, Sugihara H, Miwa K, Yamamoto G, Hattori T (2004) Thioproline inhibits development of esophageal adenocarcinoma induced by gastroduodenal reflux in rats. Carcinogenesis 25(5):723–727. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgh067
Lankelma J, Penders PGM, Leyva A, Pinedo HM (1981) Determination of thioproline in plasma using high-performance liquid-chromatography. Cancer Lett 12(1–2):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3835(81)90048-3
Lebreton S, Cabassa-Hourton C, Savoure A, Funck D, Forlani G (2020) Appropriate activity assays are crucial for the specific determination of proline dehydrogenase and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase activities. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.602939
Liang S, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Xie H, Ma J, Wu X, Liang D (2015) Determination of proline in human serum by a robust LC-MS/MS method: application to identification of human metabolites as candidate biomarkers for esophageal cancer early detection and risk stratification. Biomed Chromatogr 29(4):570–577. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3315
Lyu M, Liu H, Ye Y, Yin Z (2020) Inhibition effect of thiol-type antioxidants on protein oxidative aggregation caused by free radicals. Biophys Chem 260:106367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2020.106367
Mackenzie CG, Harris J (1957) N-formylcysteine synthesis in mitochondria from formaldehyde and l-cysteine via thiazolidinecarboxylic acid. J Biol Chem 227(1):393–406
Magdaleno A, Ahn IY, Paes LS, Silber AM (2009) Actions of a proline analogue, l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (T4C), on Trypanosoma cruzi. PLoS ONE 4(2):e4534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004534
Mayerhofer TG, Pahlow S, Popp J (2020) The Bouguer-Beer-Lambert law: shining light on the obscure. Chem Phys Chem 21(18):2029–2046. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202000464
Navarro A, Sánchez-Pino MJ, Gómez C, Bández MJ, Cadenas E, Boveris A (2007) Dietary thioproline decreases spontaneous food intake and increases survival and neurological function in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 9(1):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.9.131
Papas TS, Mehler AH (1970) Analysis of the amino acid binding to the proline transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 245(7):1588–1595
Parthasarathy R, Paul B, Korytnyk W (1976) X-ray and NMR studies on thiazolidines: crystal structure and conformational equilibriums of N-acetyl-2-(p-tolyl) thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid ad related thiazolidine derivatives. J Am Chem Soc 98(21):6634–6643
Patel SM, Smith TG, Morton M, Stiers KM, Seravalli J, Mayclin SJ, Edwards TE, Tanner JJ, Becker DF (2020) Cautionary tale of using tris(alkyl)phosphine reducing agents with NAD(+)-dependent enzymes. Biochemistry 59(36):3285–3289. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00490
Patel SM, Seravalli J, Liang XW, Tanner JJ, Becker DF (2021) Disease variants of human A1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 2 (PYCR2). Arch Biochem Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2021.108852
Ratner S, Clarke H (1937) The action of formaldehyde upon cysteine. J Am Chem Soc 59(1):200–206
Unger L, DeMoss R (1966) Metabolism of a proline analogue, l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 91(4):1564–1569
Walsh R (2018) Comparing enzyme activity modifier equations through the development of global data fitting templates in excel. PeerJ. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6082
Weber HU, Fleming JF, Miquel J (1982) Thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, a physiologic sulfhydryl antioxidant with potential value in geriatric medicine. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 1(4):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4943(82)90030-9
Yadav GD, Magadum DB (2017) Kinetic modeling of enzyme catalyzed biotransformation involving activations and inhibitions. In: Senturk M (ed) Enzyme inhibitors and activators. IntechOpen, pp 73–124
Yang X, Du Z, Pu J, Zhao H, Chen H, Liu Y, Li Z, Cheng Z, Zhong H, Liao F (2013) Classification of difference between inhibition constants of an inhibitor to facilitate identifying the inhibition type. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 28(1):205–213. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2011.645240
Yarlett N, Wu G, Waters WR, Harp JA, Wannemuehler MJ, Morada M, Athanasopoulos D, Martinez MP, Upton SJ, Marton LJ (2007) Cryptosporidium parvum spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase exhibits different characteristics from the host enzyme. Mol Biochem Parasitol 152(2):170–180
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Thomas Clemente, Daniel Schachtman, Jaekwon Lee, Paul Black, and Concetta C. DiRusso (all from University of Nebraska-Lincoln) for providing access equipment in their laboratories for this study.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported in part by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under award numbers R01GM065546 (J.J.T.) and R01GM132640 (J.J.T. and D.F. B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMP and DFB designed the experiments. SMP conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. JS performed and analyzed the data of the LC-ESI tandem mass spectrometry of l-T4C reaction mixtures with and without PYCR1 and PYCR2 enzymes. KMS purified PYCR1. All authors contributed to data analysis, interpretation, and writing of the manuscript; all have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, S.M., Seravalli, J., Stiers, K.M. et al. Kinetics of human pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase in l-thioproline metabolism. Amino Acids 53, 1863–1874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03095-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03095-4