Abstract
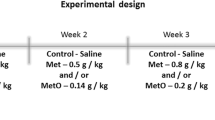
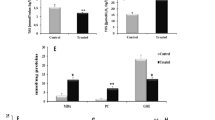
High levels of methionine (Met) and methionine sulfoxide (MetO) are found in several genetic abnormalities. Oxidative stress is involved in the pathophysiology of many inborn errors of metabolism. However, little is known about the role of oxidative damage in hepatic and renal changes in hypermethioninemia. We investigated the effect of chronic treatment with Met and/or MetO on oxidative stress parameters in liver and kidney, as lipid peroxidation (TBARS), total sulfhydryl content (SH), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enzymes activities superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and delta aminolevulinic dehydratase (ALA-D). Serum biochemical parameters were evaluated. Wistar rats were treated daily with two subcutaneous injections of saline (control), Met (0.2–0.4 g/kg), MetO (0.05–0.1 g/kg) and the association between these (Met plus MetO) from the 6th to the 28th day of life. Our data demonstrated an increase of glucose and urea levels in all experimental groups. Cholesterol (MetO and Met plus MetO) were decreased and triglycerides (MetO) were increased. SOD (MetO and Met plus MetO) and CAT (Met, MetO and Met plus MetO) activities were decreased, while GPx was enhanced by MetO and Met plus MetO treatment in liver. In kidney, we observed a reduction of SH levels, SOD and CAT activities and an increase of TBARS levels in all experimental groups. ROS levels in kidney were increased in MetO and Met plus MetO groups. ALA-D activity was enhanced in liver (MetO and Met plus MetO) and kidney (Met plus MetO). These findings help to understand the pathophysiology of hepatic and renal alterations present in hypermethioninemia.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Aksenov MY, Markesbery WR (2001) Changes in thiol content and expression of glutathione redox system genes in the hippocampus and cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 302:141–145. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(01)01636-6
Ali SF, LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13:637–648
Avila MA, Berasain C, Torres L, Martín-Duce A, Corrales FJ, Yang H, Prieto J, Lu SC, Caballería J, Rodés J, Mato JM (2000) Reduced mRNA abundance of the main enzymes involved in methionine metabolism in human liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 33:907–914. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(00)81126-5
Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S (2014) Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:360438. doi:10.1155/2014/360438
Bó CD, Martini D, Porrini M, Klimis-Zacasc D, Riso P (2015) Berries and oxidative stress markers: an overview of human intervention studies. Food Funct 6:2890–2917. doi:10.1039/c5fo00657k
Costa MZ, Silva TM, Flores NP, Schmitz F, Scherer EBS, Viau CM, Saffi J, Barschak AG, Wyse AT, Spanevello RM, Stefanello FM (2013) Methionine and methionine sulfoxide alter parameters of oxidative stress in the liver of young rats: in vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Cell Biochem 384:21–28. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1777-5
Couce ML, Bóveda MD, García-Jimémez C, Balmaseda E, Vives I, Castiñeiras DE, Fernández-Marmiesse A, Fraga JM, Mudd SH, Corrales FJ (2013) Clinical and metabolic findings in patients with methionine adenosyltransferase I/III deficiency detected by newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab 110:218–221. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.08.003
Davies M (2016) Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem J 473:805–825. doi:10.1042/BJ20151227
Enns GM (2008) Neurologic damage and neurocognitive dysfunction in urea cycle disorders. Semin Pediatr Neurol 15:132–139. doi:10.1016/j.spen.2008.05.007
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86134-H
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408:239–247. doi:10.1038/35041687
Finkelstein JD (1990) Methionine metabolism in mammals. J Nutr Biochem 1:228–237. doi:10.1016/0955-2863(90)90070-2
Folmer V, Soares JC, Gabriel D, Rocha JB (2003) A high fat diet inhibits delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase and increases lipid peroxidation in mice (Mus musculus). J Nutr 133:2165–2170. doi:10.1016/j.etp.2010.03.003
França RT, Da Silva AS, Wolkmer P, Oliveira VA, Pereira ME, Leal MLR, Silva CB, Nunes MAG, Dressler V, Mazzanti CM, Monteiro SG, Lopes STA (2011) Delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase activity in red blood cells of rats infected with Trypanosoma evansi. Parasitology 138:1272–1277. doi:10.1017/S0031182011000989
Gonsette RE (2008) Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: the role of oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. J Neurol Sci 274:48–53. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.06.029
Ha HL, Shin HJ, Feitelson MA, Yu DY (2010) Oxidative stress and antioxidants in hepatic pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 16:6035–6043. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6035
Hidiroglou N, Gilani GS, Long L, Zhao X, Madere R, Cockell K, Belonge B, Ratnayake WM, Peace R (2004) The influence of dietary vitamin E, fat, and methionine on blood cholesterol profile, homocysteine levels, and oxidizability of low density lipoprotein in the gerbil. J Nutr Biochem 15:730–740. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2004.04.009
Hirabayashi K, Shiohara M, Yamada K, Sueki A, Ide Y, Takeuchi K, Hagimoto R, Kinoshita T, Yabuhara A, Mudd SH, Koike K (2013) Neurologically normal development of a patient with severe methionine adenosyltransferase I/III deficiency after continuing dietary methionine restriction. Gene 530:104–108. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.025
Kumagai H, Katoh S, Hirosawa K, Kimura M, Hishida A, Ikegaya N (2002) Renal tubulointerstitial injury in weanling rats with hyperhomocysteinemia. Kidney Int 62:1219–1228. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2002.kid558.x
Lee BC, Gladyshev VN (2011) The biological significance of methionine sulfoxide stereochemistry. Free Radic Biol Med 50:221–227. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.11.008
Li S, Tan H, Wang N, Zhang Z, Lao L, Wong C, Feng Y (2015) The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26087–26124. doi:10.3390/ijms161125942
Ljubisavljevic S (2016) Oxidative stress and neurobiology of demyelination. Mol Neurobiol 53:744–758. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9041-x
Lowe F (2014) Biomarkers of oxidative stress. In: Laher I (ed) Systems biology of free radicals and antioxidants, 1st edn, vol 2, chap 3. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–87
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.46.27489
Lushchak VI (2015) Radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stresses and their classifications. Ukr Biochem 87:11–18. doi:10.15407/ubj87.06.011
Martinov MV, Vitvitsky VM, Banerjee R, Ataullakhanov FI (2010) The logic of hepatic methionine metabolic cycle. Biochim Biophys Act 1804:86–96. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.10.004
Mato JM, Lu SC (2007) Role of S-adenosyl-l-methionine in liver health and injury. Hepatology 45:1306–1312. doi:10.1002/hep.21650
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Moskovitz J (2014) Detection and localization of methionine sulfoxide residues of specific proteins in brain tissue. Protein Pept Lett 21:52–55. doi:10.2174/09298665113209990068
Mudd SH (2011) Hypermethioninemias of genetic and non-genetic origin: a review. Am J Med Genet Part C (seminars in medical genetics) 157:3–32. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30293
Nair J, Srivatanakul P, Haas C, Jedpiyawongse A, Khuhaprema T, Seitz HK, Bartsch H (2010) High urinary excretion of lipid peroxidation-derived DNA damage in patients with cancer-prone liver diseases. Mutat Res 683:23–28. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6035
Polachini CRN, Spanevello RM, Zanini D, Baldissarelli J, Pereira LB, Schetinger MRC, Cruz IBM, Assmann CE, Bagatini MD, Morsch VM (2016) Evaluation of delta-aminolevulinic dehydratase activity, oxidative stress biomarkers, and vitamin D levels in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurotox Res 29:230–242. doi:10.1007/s12640-015-9584-2
Sanchez-Roman I, Barja G (2013) Regulation of longevity and oxidative stress by nutritional interventions: role of methionine restriction. Exp Gerontol 48:1030–1042. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.021
Sassa S (1982) Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase assay. Enzyme 28:133–145
Stadtman ER, Moskovitz J, Levine RL (2003) Oxidation of methionine residues of proteins: biological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 5:577–582
Stefanello FM, Matté C, Scherer EB, Wannmacher CMD, Wajner M, Wyse ATS (2007a) Chemically induced model of hypermethioninemia in rats. J Neurosci Methods 160:1–4. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.07.029
Stefanello FM, Kreutz F, Scherer EB, Breier AC, Vianna LP, Trindade VM, Wyse AT (2007b) Reduction of gangliosides, phospholipids and cholesterol content in cerebral cortex of rats caused by chronic hypermethioninemia. Int J Dev Neurosci 25:473–477
Stefanello FM, Matté C, Pederzolli CD, Kolling J, Mescka CP, Lamers ML, Assis AM, Perry ML, Santos MF, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS (2009) Hypermethioninemia provokes oxidative damage and histological changes in liver of rats. Biochimie 91:961–968. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2009.04.018
Stefanello FM, Ferreira AG, Pereira TC, da Cunha MJ, Bonan CD, Bogo MR, Wyse AT (2011) Acute and chronic hypermethioninemia alter Na+ K+-ATPase activity in rat hippocampus: prevention by antioxidants. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:483–488. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.02.001
Troen AM, Lutgens E, Smith DE, Rosenberg IH, Selhub J (2003) The atherogenic effect of excess methionine intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15089–15094. doi:10.1073/pnas.2436385100
Valentini J, Grotto D, Paniz C, Roehrs M, Burg G, Garcia SC (2008) The influence of the hemodialysis treatment time under oxidative stress biomarkers in chronic renal failure patients. Biomed Pharmacother 62:378–382. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2007.10.017
Yu T, Jhun BS, Yoon Y (2011) High-glucose stimulation increases reactive oxygen species production through the calcium and mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated activation of mitochondrial fission. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(3):425–437. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3284
Zanini D, Pelinson LP, Schmatz R, Belmonte PL, Curry MC, Baldissareli J, Pires AG, Antunes SFA, Brenner RLG, Arau´jo MC, Chiesa J, Morsch VM, Bitencourt RLD, Schetinger MR (2014) d-Aminolevulinate dehydratase activity in lung cancer patients and its relationship with oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 68:603–609. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2014.04.005
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hedy L. Hofmann for english revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported in part by grants for Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) and Universidade Federal de Pelotas.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Committee of Ethics and Animal Experimentation of the Federal University of Pelotas, Brazil under protocol number: CEEA 3527.
Additional information
Handling Editor: H. Jakubowski.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, M.S.P., Oliveira, P.S., Debom, G.N. et al. Chronic administration of methionine and/or methionine sulfoxide alters oxidative stress parameters and ALA-D activity in liver and kidney of young rats. Amino Acids 49, 129–138 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2340-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2340-y