Abstract
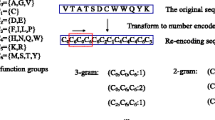
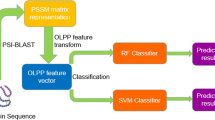
Protein self-interaction, i.e. the interaction between two or more identical proteins expressed by one gene, plays an important role in the regulation of cellular functions. Considering the limitations of experimental self-interaction identification, it is necessary to design specific bioinformatics tools for self-interacting protein (SIP) prediction from protein sequence information. In this study, we proposed an improved computational approach for SIP prediction, termed SPAR (Self-interacting Protein Analysis serveR). Firstly, we developed an improved encoding scheme named critical residues substitution (CRS), in which the fine-grained domain–domain interaction information was taken into account. Then, by employing the Random Forest algorithm, the performance of CRS was evaluated and compared with several other encoding schemes commonly used for sequence-based protein–protein interaction prediction. Through the tenfold cross-validation tests on a balanced training dataset, CRS performed the best, with the average accuracy up to 72.01 %. We further integrated CRS with other encoding schemes and identified the most important features using the mRMR (the minimum redundancy maximum relevance) feature selection method. Our SPAR model with selected features achieved an average accuracy of 92.09 % on the human-independent test set (the ratio of positives to negatives was about 1:11). Besides, we also evaluated the performance of SPAR on an independent yeast test set (the ratio of positives to negatives was about 1:8) and obtained an average accuracy of 76.96 %. The results demonstrate that SPAR is capable of achieving a reasonable performance in cross-species application. The SPAR server is freely available for academic use at http://systbio.cau.edu.cn/zzdlab/spar/.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiva E, Itzhaki Z, Margalit H (2008) Built-in loops allow versatility in domain–domain interactions: lessons from self-interacting domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(36):13292–13297. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801207105
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402
Baisamy L, Jurisch N, Diviani D (2005) Leucine zipper-mediated homo-oligomerization regulates the Rho-GEF activity of AKAP-Lbc. J Biol Chem 280(15):15405–15412. doi:10.1074/jbc.M414440200
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32. doi:10.1023/A:1010933404324
Breuer K, Foroushani AK, Laird MR, Chen C, Sribnaia A, Lo R, Winsor GL, Hancock RE, Brinkman FS, Lynn DJ (2013) InnateDB: systems biology of innate immunity and beyond—recent updates and continuing curation. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D1228–D1233. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1147
Cancherini DV, Franca GS, de Souza SJ (2010) The role of exon shuffling in shaping protein–protein interaction networks. BMC Genom 11(Suppl 5):S11. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-S5-S11
Chatr-Aryamontri A, Breitkreutz BJ, Oughtred R, Boucher L, Heinicke S, Chen D, Stark C, Breitkreutz A, Kolas N, O’Donnell L, Reguly T, Nixon J, Ramage L, Winter A, Sellam A, Chang C, Hirschman J, Theesfeld C, Rust J, Livstone MS, Dolinski K, Tyers M (2015) The BioGRID interaction database: 2015 update. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D470–D478. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1204
Chen Y, Dokholyan NV (2008) Natural selection against protein aggregation on self-interacting and essential proteins in yeast, fly, and worm. Mol Biol Evol 25(8):1530–1533. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn122
Du X, Cheng J, Zheng T, Duan Z, Qian F (2014) A novel feature extraction scheme with ensemble coding for protein–protein interaction prediction. Int J Mol Sci 15(7):12731–12749. doi:10.3390/ijms150712731
Feng ZP, Zhang CT (2000) Prediction of membrane protein types based on the hydrophobic index of amino acids. J Protein Chem 19(4):269–275
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR (2011) HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Web Server issue):W29–W37. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr367
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Heger A, Hetherington K, Holm L, Mistry J, Sonnhammer EL, Tate J, Punta M (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D222–D230. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1223
Gibson TA, Goldberg DS (2009) Questioning the ubiquity of neofunctionalization. PLoS Comput Biol 5(1):e1000252. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000252
Guo Y, Yu L, Wen Z, Li M (2008) Using support vector machine combined with auto covariance to predict protein–protein interactions from protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 36(9):3025–3030. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn159
Hashimoto K, Panchenko AR (2010) Mechanisms of protein oligomerization, the critical role of insertions and deletions in maintaining different oligomeric states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(47):20352–20357. doi:10.1073/pnas.1012999107
Hashimoto K, Nishi H, Bryant S, Panchenko AR (2011) Caught in self-interaction: evolutionary and functional mechanisms of protein homooligomerization. Phys Biol 8(3):035007. doi:10.1088/1478-3975/8/3/035007
Hattori T, Ohoka N, Inoue Y, Hayashi H, Onozaki K (2003) C/EBP family transcription factors are degraded by the proteasome but stabilized by forming dimer. Oncogene 22(9):1273–1280. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206204
Ispolatov I, Yuryev A, Mazo I, Maslov S (2005) Binding properties and evolution of homodimers in protein–protein interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res 33(11):3629–3635. doi:10.1093/nar/gki678
Katsamba P, Carroll K, Ahlsen G, Bahna F, Vendome J, Posy S, Rajebhosale M, Price S, Jessell TM, Ben-Shaul A, Shapiro L, Honig BH (2009) Linking molecular affinity and cellular specificity in cadherin-mediated adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(28):11594–11599. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905349106
Koike R, Kidera A, Ota M (2009) Alteration of oligomeric state and domain architecture is essential for functional transformation between transferase and hydrolase with the same scaffold. Protein Sci 18(10):2060–2066. doi:10.1002/pro.218
Launay G, Salza R, Multedo D, Thierry-Mieg N, Ricard-Blum S (2015) MatrixDB, the extracellular matrix interaction database: updated content, a new navigator and expanded functionalities. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D321–D327. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1091
Liu Z, Guo F, Zhang J, Wang J, Lu L, Li D, He F (2013) Proteome-wide prediction of self-interacting proteins based on multiple properties. Mol Cell Proteomics 12(6):1689–1700. doi:10.1074/mcp.M112.021790
Marianayagam NJ, Sunde M, Matthews JM (2004) The power of two: protein dimerization in biology. Trends Biochem Sci 29(11):618–625. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.09.006
Miller S, Lesk AM, Janin J, Chothia C (1987) The accessible surface area and stability of oligomeric proteins. Nature 328(6133):834–836. doi:10.1038/328834a0
Mosca R, Ceol A, Stein A, Olivella R, Aloy P (2014) 3did: a catalog of domain-based interactions of known three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D374–D379. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt887
Orchard S, Ammari M, Aranda B, Breuza L, Briganti L, Broackes-Carter F, Campbell NH, Chavali G, Chen C, del-Toro N, Duesbury M, Dumousseau M, Galeota E, Hinz U, Iannuccelli M, Jagannathan S, Jimenez R, Khadake J, Lagreid A, Licata L, Lovering RC, Meldal B, Melidoni AN, Milagros M, Peluso D, Perfetto L, Porras P, Raghunath A, Ricard-Blum S, Roechert B, Stutz A, Tognolli M, van Roey K, Cesareni G, Hermjakob H (2014) The MIntAct project—IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D358–D363. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1115
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Perez-Bercoff A, Makino T, McLysaght A (2010) Duplicability of self-interacting human genes. BMC Evol Biol 10:160. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-160
Rao HB, Zhu F, Yang GB, Li ZR, Chen YZ (2011) Update of PROFEAT: a web server for computing structural and physicochemical features of proteins and peptides from amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Web Server issue):W385–w390. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr284
Salwinski L, Miller CS, Smith AJ, Pettit FK, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (2004) The database of interacting proteins: 2004 update. Nucleic Acids Res 32(Database issue):D449–D451. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh086
Shatnawi M, Zaki NM (2015) Novel domain identification approach for protein–protein interaction prediction. In: Computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology (CIBCB), 2015 IEEE (conference on, 12–15 Aug 2015), pp 1–8. doi:10.1109/CIBCB.2015.7300340
Shen J, Zhang J, Luo X, Zhu W, Yu K, Chen K, Li Y, Jiang H (2007) Predicting protein–protein interactions based only on sequences information. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(11):4337–4341. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607879104
UniProt C (2015) UniProt: a hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D204–D212. doi:10.1093/nar/gku989
Woodcock JM, Murphy J, Stomski FC, Berndt MC, Lopez AF (2003) The dimeric versus monomeric status of 14-3-3zeta is controlled by phosphorylation of Ser58 at the dimer interface. J Biol Chem 278(38):36323–36327. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304689200
Xia JF, Han K, Huang DS (2010) Sequence-based prediction of protein–protein interactions by means of rotation forest and autocorrelation descriptor. Protein Pept Lett 17(1):137–145
Yang L, Xia JF, Gui J (2010) Prediction of protein–protein interactions from protein sequence using local descriptors. Protein Pept Lett 17(9):1085–1090
You ZH, Lei YK, Zhu L, Xia J, Wang B (2013) Prediction of protein–protein interactions from amino acid sequences with ensemble extreme learning machines and principal component analysis. BMC Bioinform 14(Suppl 8):S10. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-S8-S10
Zahiri J, Yaghoubi O, Mohammad-Noori M, Ebrahimpour R, Masoudi-Nejad A (2013) PPIevo: protein–protein interaction prediction from PSSM based evolutionary information. Genomics 102(4):237–242. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.05.006
Zahiri J, Mohammad-Noori M, Ebrahimpour R, Saadat S, Bozorgmehr JH, Goldberg T, Masoudi-Nejad A (2014) LocFuse: human protein–protein interaction prediction via classifier fusion using protein localization information. Genomics 104(6 Pt B):496–503. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.10.006
Zaki N, Lazarova-Molnar S, El-Hajj W, Campbell P (2009) Protein–protein interaction based on pairwise similarity. BMC Bioinform 10:150. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-150
Zhou Y, Zhou YS, He F, Song J, Zhang Z (2012) Can simple codon pair usage predict protein–protein interaction? Mol BioSyst 8(5):1396–1404. doi:10.1039/c2mb05427b
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yuan Zhou at China Agricultural University for helpful discussions on this work. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31271414, 31471249, 61202167, 61303169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: L. Taher.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Yang, S., Li, C. et al. SPAR: a random forest-based predictor for self-interacting proteins with fine-grained domain information. Amino Acids 48, 1655–1665 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2226-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2226-z