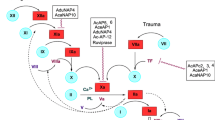
Abstract
Factor VIII, a human blood plasma protein, plays an important role during the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation cascade after its activation by thrombin. The activated form of FVIII acts as cofactor to the serine protease Factor IXa, in the conversion of the zymogen Factor X to the active enzyme Factor Xa. The Ser558–Gln565 region of the A2 subunit of Factor VIII has been shown to be crucial for FVIIIa–FIXa interaction. Based on this, a series of linear peptides, analogs of the 558–565 loop of the A2 subunit of the heavy chain of Factor VIII were synthesized using the acid labile 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin and biologically evaluated in vitro by measuring the chronic delay of activated partial thromboplastin time and the inhibition of Factor VIII activity, as potential anticoagulants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AcOH:
-
Acetic acid
- aPTT:
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time
- Boc:
-
Tert-butoxycarbonyl
- Bzl:
-
Benzyl group
- CLTR-Cl:
-
2-chlorotrityl chloride
- DCM:
-
Dichloromethane
- DIC:
-
N,N′-diisopropylcarbodiimide
- DIPEA:
-
Diisopropylethylamine
- DMF:
-
N,N′-dimethylformamide
- dPPP:
-
Deficient platelet poor plasma
- ESI-MS:
-
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- Fmoc:
-
9-Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group
- FVIII:
-
Factor VIII
- FIX:
-
Factor IX
- HOBt:
-
1-hydroxybenzotriazole
- i-PrOH:
-
2-propanol
- Me:
-
Methyl group
- MeCN:
-
Acetonitrile
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- MBHA:
-
4-methylbenzhydrylamine
- PPP:
-
Platelet poor plasma
- PyBOP:
-
(Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)-tris(pyrrolidino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- rFVIII:
-
Recombinant Factor VIII
- tBu:
-
Tert-butyl group
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography
- TES:
-
Triethylsilane
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- TFE:
-
2,2,2-trifluoroethanol
- TLC:
-
Thin layer chromatography
- Tol:
-
Toluene
- Trt:
-
Trityl group
References
Bajaj P, Schmidt A, Mathur A, Padmanabhan K, Zhong D, Mastrii M, Fay P (2001) Factor IXa:Factor VIIIa interaction. J Biol Chem 276:16302–16309
Barlos K, Chantzi O, Gatos D, Stavropoulos G (1991) 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin: studies on anchoring of Fmoc-amino acids and peptide cleavage. Int J Pept Protein Res 37:513–520
Barrowcliffe T, Raut S, Sands D, Hubbard A (2002) Coagulation and chromogenic assays of factor VIII activity: general aspects, standardization, and recommendations. Semin Thromb Hemostasis 28:247–255
Brunnee T, La Porta C, Reddigari S, Salerno V, Kaplan A, Silverberg M (1993) Activation of factor XI in plasma is dependent on factor XII. Blood 81:580–586
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2008) One stage prothrombin time (PT) test and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) test: approved guide line, document H47-A2, 2nd edn
Fang H, Wang L, Wang H (2007) The protein structure and effect of factor VIII. Thromb Res 119:1–13
Fay P (2004) Activation of factor VIII and mechanisms of cofactor action. Blood Rev 18:1–15
Fay P, Beattie T, Huggins C, Regan L (1994) Factor VIIIa A2 subunit residues 558-565 represent a factor IXa interactive site. J Biol Chem 269:20522–20527
Fay P, Jenkins P (2005) Mutating Factor VIII: lessons from structure to function. Blood Rev 19:15–27
Franchini M, Mannucci P (2011) Inhibitors of propagation of coagulation (factors VIII, IX and XI): a review of current therapeutic practice. British J Clin Pharmacol 72:553–562
Gailani D, Renne T (2007) The intrinsic pathway of coagulation: a target for treating thromboembolic disease. J Thromb Haemostasis 5:1106–1112
Howard E, Becker K, Rusconi C, Becker R (2007) Factor IXa Inhibitors as Novel Anticoagulants. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:722–727
Jenkins PV, Freas J, Schmidt KM, Zhou Q, Fay PJ (2002) Mutations associated with hemophilia A in the 558–565 loop of the factor VIIIa A2 subunit alter the catalytic activity of the factor Xase complex. Blood 100:501–508
Lenting P, Christophe O, Gueguen P (2010) The disappearing act of factor VIII. Haemophilia 16:6–15
Lin J et al (2006) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of peptidomimetic inhibitors of factor XIa as novel anticoagulants. J Med Chem 49:7781–7791
Mahan C, Fanikos J (2011) New antithrombotics: the impact on global health care. Thromb Res 127:518–524
Minors D (2007) Haemostasis, blood platelets and coagulation. Anaesth Intensive Care Med 8:214–216
Ngo J, Huang M, Roth D, Furie B, Furie BR (2008) Crystal structure of human factor VIII: implications for the formation of the factor IXa–factor VIIIa complex. Structure 16:597–606
O’Brien L, Medved L, Fay P (1995) Localization of factor IXa and factor VIIIa interactive sites. J Biol Chem 270:27087–27092
Sarigiannis Y, Anastasopoulos C, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M, Stavropoulos G (2006) Peptides 2006. In: Proceedings of the 29th EPS Gdansk, Poland 0344:694–695
Shen B, Spiegel P, Chang Ch, Huh J, Lee J, Kim J, Kim Y, Stoddard B (2008) The tertiary structure and domain organization of coagulation factor VIII. Blood 111:1240–1247
Terraube V, O’ Donnell J, Jenkins P (2010) Factor VIII and von Willebrand factor interaction: biological, clinical and therapeutic importance. Haemophilia 16:3–13
Vehar G, Keyt B, Eaton D et al (1984) Structure of human factor VIII. Nature 312:337–342
Woodruff B, Sullenger B, Becker R (2010) Antithrombotic therapy in acute coronary syndrome: how far up the coagulation cascade will we go. Curr Cardiol Rep 12:315–320
Acknowledgments
Anticoagulant assays were performed under the supervision of Professor of Haematology, Dr Pantelis Makris, School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece. This Research Project is co-financed: 80 % by European Union—European Social Fund and 20 % by General Secretary of Research & Technology (PENED 03ED569). We also thank SANOFI S.A., Athens, Greece for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abbreviations of common amino acids are in accordance with the recommendations of IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature: Arch Biochem Biophys 206 (1988) v–xxii, J Biol Chem 264 (1989) 668–673, J Peptide Sci 12 (2006) 1–8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anastasopoulos, C., Sarigiannis, Y. & Stavropoulos, G. A novel approach in potential anticoagulants from peptides epitope 558–565 of A2 subunit of factor VIII. Amino Acids 44, 1159–1165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1448-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1448-y