Abstract
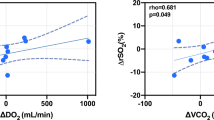
Changes in plasma aromatic amino acids (AAA = phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine) and branched chain amino acids (BCAA = isoleucine, leucine, valine) levels possibly influencing intracranial pressure (ICP) and cerebral oxygen consumption (SjvO2) were investigated in 19 sedated patients up to 14 days following severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). Compared to 44 healthy volunteers, jugular venous plasma BCAA were significantly decreased by 35% (p < 0.001) while AAA were markedly increased in TBI patients by 19% (p < 0.001). The BCAA to AAA ratio was significantly decreased by 55% (p < 0.001) which persisted during the entire study period. Elevated plasma phenylalanine was associated with decreased ICP and increased SjvO2, while higher plasma isoleucine and leucine levels were associated with increased ICP and higher plasma leucine and valine were linked to decreased SjvO2. The amount of enterally administered amino acids was associated with significantly increased plasma levels with the exception of phenylalanine. Contrary to the initial assumption that elevated AAA and decreased BCAA levels are detrimental, increased plasma phenylalanine levels were associated with beneficial signs in terms of decreased ICP and reduced cerebral oxygen consumption reflected by increased SjvO2; concomitantly, elevated plasma isoleucine and leucine levels were associated with increased ICP while leucine and valine were associated with decreased SjvO2 following severe TBI, respectively. The impact of enteral nutrition on this observed pattern must be examined prospectively to determine if higher amounts of phenylalanine should be administered to promote beneficial effects on brain metabolism and if normalization of plasma BCAA levels is without cerebral side effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquilani R, Iadarola P, Contardi A, Boselli M, Verri M, Pastoris O, Boschi F, Arcidiaco P, Viglio S (2005) Branched-chain amino acids enhance the cognitive recovery of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1729–1735
Askanazi J, Furst P, Michelsen CB, Elwyn DH, Vinnars E, Gump FE, Stinchfield FE, Kinney JM (1980a) Muscle and plasma amino acids after injury: hypocaloric glucose vs. amino acid infusion. Ann Surg 191:465–472
Askanazi J, Carpentier YA, Michelsen CB, Elwyn DH, Furst P, Kantrowitz LR, Gump FE, Kinney JM (1980b) Muscle and plasma amino acids following injury. Influence of intercurrent infection. Ann Surg 192:78–85
Avruch J, Long X, Ortiz-Vega S, Rapley J, Papageorgiou A, Dai N (2009) Amino acid regulation of TOR complex 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:592–602
Basler T, Meier-Hellmann A, Bredle D, Reinhart K (2002) Amino acid imbalance early in septic encephalopathy. Intensive Care Med 28:293–298
Blau N, van Spronsen FJ, Levy HL (2010) Phenylketonuria. Lancet 376:1417–1427
Blomstrand E, Møller K, Secher NH, Nybo L (2005) Effect of carbohydrate ingestion on brain exchange of amino acids during sustained exercise in human subjects. Acta Physiol Scand 185:203–209
Bohé J, Low A, Wolfe RR, Rennie MJ (2003) Human muscle protein synthesis is modulated by extracellular, not intramuscular amino acid availability: a dose-response study. J Physiol 552:315–324
Cangiano C, Farber MO, Cardelli-Cangiano P, Rossi-Fanelli F, Cascino A, Capocaccia L, Cockerill EM, Manfredi F (1982) Plasma levels of false neurotransmitters across the brain in portal-systemic encephalopathy. Eur J Clin Invest 12:15–21
Chaplin ER, Goldberg AL, Diamond I (1976) Leucine oxidation in brain slices and nerve endings. J Neurochem 26:701–707
Daubert EA, Condron BG (2010) Serotonin: a regulator of neuronal morphology and circuitry. Trends Neurosci 33:424–434
Dejong CH, van de Poll MC, Soeters PB, Jalan R, Olde Damink SW (2007) Aromatic amino acid metabolism during liver failure. J Nutr 137(6 Suppl 1):1579S–1585S
Feigin RD, Beisel WR, Wannemacher RW Jr (1971) Rhythmicity of plasma amino acids and relation to dietary intake. Am J Clin Nutr 24:329–341
Fernstrom JD (2000) Can nutrient supplements modify brain function? Am J Clin Nutr 71(6 Suppl):1669S–1675S
Fernstrom JD (2005) Branched-chain amino acids and brain function. J Nutr 135(6 Suppl):1539S–1546S
Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH (2007) Tyrosine, phenylalanine, and catecholamine synthesis and function in the brain. J Nutr 137((6 Suppl 1)):1539S–1547S
Fischer JE, Rosen HM, Ebeid AM, James JH, Keane JM, Soeters PB (1976) The effect of normalization of plasma amino acids on hepatic encephalopathy in man. Surgery 80(1):77–91
Freund HR, Ryan JA Jr, Fischer JE (1978) Amino acid derangements in patients with sepsis: treatment with branched chain amino acid rich infusions. Ann Surg 188:423–430
Freund H, Atamian S, Holroyde J, Fischer JE (1979) Plasma amino acids as predictors of the severity and outcome of sepsis. Ann Surg 190:571–576
Freund H, Dienstag J, Lehrich J, Yoshimura N, Bradford RR, Rosen H, Atamian S, Slemmer E, Holroyde J, Fischer JE (1982) Infusion of branched-chain enriched amino acid solution in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Surg 196:209–220
Holecek M (2010) Three targets of branched-chain amino acid supplementation in the treatment of liver disease. Nutrition 26:482–490
Lieberman HR (2003) Nutrition, brain function and cognitive performance. Appetite 40:245–254
Meier C, Ristic Z, Klauser S, Verrey F (2002) Activation of system L heterodimeric amino acid exchangers by intracellular substrates. EMBO J 21:580–589
Miyazaki T, Matsuzaki Y, Karube M, Bouscarel B, Miyakawa S, Tanaka N (2003) Amino acid ratios in plasma and tissues in a rat model of liver cirrhosis before and after exercise. Hepatol Res 27:230–237
Oertel MF, Hauenschild A, Gruenschlaeger J, Mueller B, Scharbrodt W, Boeker DK (2009) Parenteral and enteral nutrition in the management of neurosurgical patients in the intensive care unit. J Clin Neurosci 16:1161–1167
Petersen SR, Jeevanandam M, Holaday NJ, Lubhan CL (1996) Arterial–jugular vein free amino acid levels in patients with head injuries: important role of glutamine in cerebral nitrogen metabolism. J Trauma 41:687–694
Riggio O, Merli M, Pièche U, Romiti A, Pasqualetti P, Coppola A, Danese D, Cugini P, Capocaccia L (1989) Circadian rhythmicity of plasma amino acid variations in healthy subjects. Recenti Prog Med 80(11):591–593
Roberts LM, Black DS, Raman C, Woodford K, Zhou M, Haggerty JE, Yan AT, Cwirla SE, Grindstaff KK (2008) Subcellular localization of transporters along the rat blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebral-spinal fluid barrier by in vivo biotinylation. Neuroscience 155:423–438
Robertson CS, Gopinath SP, Goodman JC, Contant CF, Valadka AB, Narayan RK (1995) SjvO2 monitoring in head-injured patients. J Neurotrauma 12:891–896
Rossetti P, Porcellati F, Busciantella Ricci N, Candeloro P, Cioli P, Nair KS, Santeusanio F, Bolli GB, Fanelli CG (2008) Effect of oral amino acids on counterregulatory responses and cognitive function during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in nondiabetic and type 1 diabetic people. Diabetes 57:1905–1917
Scarnà A, McTavish SF, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM, Rogers RD (2005) The effects of a branched chain amino acid mixture supplemented with tryptophan on biochemical indices of neurotransmitter function and decision-making. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:761–768
Shikata N, Maki Y, Nakatsui M, Mori M, Noguchi Y, Yoshida S, Takahashi M, Kondo N, Okamoto M (2010) Determining important regulatory relations of amino acids from dynamic network analysis of plasma amino acids. Amino Acids 38:179–187
Stinnett JD, Alexander JW, Watanabe C, MacMillan BG, Fischer JE, Morris MJ, Trocki O, Miskell P, Edwards L, James H (1982) Plasma and skeletal muscle amino acids following severe burn injury in patients and experimental animals. Ann Surg 195(1):75–89
Stover JF (2011) Actual evidence for neuromonitoring-guided intensive care following severe traumatic brain injury. Swiss Med Wkly 141:w13245
Stover JF, Steiger P, Stocker R (2005) Treating intracranial hypertension in patients with severe traumatic brain injury during neurointensive care. Eur J Trauma 4:308–330
Suzuki M, Kudo A, Sugawara A, Yoshida K, Kubo Y, Suzuki T, Ogasawara K, Doi M, Ogawa A (2002) Amino acid concentrations in the blood of the jugular vein and peripheral artery after traumatic brain injury: decreased release of glutamate into the jugular vein in the early phase. J Neurotrauma 19:285–292
Valerio A, D’Antona G, Nisoli E (2011) Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: an evolutionary perspective. Aging (Albany NY) 3:464–478
Vente JP, von Meyenfeldt MF, van Eijk HM, van Berlo CL, Gouma DJ, van der Linden CJ, Soeters PB (1989) Plasma-amino acid profiles in sepsis and stress. Ann Surg 209:57–62
Verrey F (2003) System L: heteromeric exchangers of large, neutral amino acids involved in directional transport. Pflugers Arch 445:529–533
Vuille-Dit-Bille RN, Ha-Huy R, Tanner M, Stover JF (2011) Changes in calculated arterio-jugular venous glutamate difference and SjvO2 in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Minerva Anestesiol 77:870–876
Acknowledgments
The help of the nursing staff in collecting plasma samples is gratefully acknowledged. The study was supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF) and the SUVA Fonds to JFS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuille-Dit-Bille, R.N., Ha-Huy, R. & Stover, J.F. Changes in plasma phenylalanine, isoleucine, leucine, and valine are associated with significant changes in intracranial pressure and jugular venous oxygen saturation in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Amino Acids 43, 1287–1296 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1202-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1202-x