Abstract
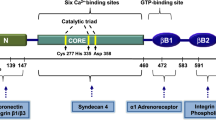
Anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) antibodies are specifically produced in the small-intestinal mucosa of celiac disease (CD) patients. It is now recognized that these antibodies, acting on cell-surface tTG, may play an active role in CD pathogenesis triggering an intracellular response via the activation of different signal transduction pathways. In this study, we report that anti-tTG antibodies, both commercial and from a CD patient, induce a rapid Ca2+ mobilization from intracellular stores in Caco-2 cells. We characterized the mechanism of Ca2+ release using thapsigargin and carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone, which are able to deplete specifically endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of Ca2+, respectively. Our data highlight that both pathways of calcium release were involved, thus indicating that the spectrum of cellular responses downstream can be very wide. In addition, we demonstrate that the increased Ca2+ level in the cells evoked by anti-tTG antibodies was sufficient to activate tTG, which is normally present as a latent protein due to the presence of low Ca2+ and to the inhibitory effect of GTP/GDP. Herein, we discuss the importance of intracellular tTG activation as central in the context of CD pathogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- tTG:
-
Tissue transglutaminase
- CD:
-
Celiac disease
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- Fura-2AM:
-
Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester
- NK:
-
Normal Krebs
- SERCA:
-
Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
- THP:
-
Thapsigargin
- FCCP:
-
Carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
References
Akimov SS, Belkin AM (2001) Cell surface tissue transglutaminase is involved in adhesion and migration of monocytic cells on fibronectin. Blood 98:1567–1576. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.5.1567
Akimov SS, Krylov D, Fleischman LF, Belkin AM (2000) Tissue transglutaminase is an integrin-binding adhesion coreceptor for fibronectin. J Cell Biol 148:825–838. doi:10.1083/jcb.148.4.825
Balklava Z, Verderio E, Collighan R, Gross S, Adams J, Griffin M (2002) Analysis of tissue transglutaminase function in the migration of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: the active-state conformation of the enzyme does not affect cell motility but is important for its secretion. J Biol Chem 277:16567–16575. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109836200
Barone MV, Caputo I, Ribecco MT, Maglio M, Marzari R, Sblattero D, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Esposito C (2007) Humoral immune response to tissue transglutaminase is related to epithelial cell proliferation in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 132(4):1245–1253. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.01.030
Barone MV, Nanayakkara M, Paolella G, Maglio M, Vitale V, Troiano R, Ribecco MT, Lania G, Zanzi D, Santagata S, Auricchio R, Troncone R, Auricchio S (2010) Gliadin peptide P31–43 localises to endocytic vesicles and interferes with their maturation. PLoS One 5(8):e12246. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012246
Briani C, Samaroo D, Alaedini A (2008) Celiac disease: from gluten to autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 7(8):644–650. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2008.05.006
Caja S, Mäki M, Kaukinen K, Lindfors K (2011) Antibodies in celiac disease: implications beyond diagnostics. Cell Mol Immunol 8(2):103–109. doi:10.1038/cmi.2010.65
Caputo I, Barone MV, Martucciello S, Lepretti M, Esposito C (2009) Tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease: role of autoantibodies. Amino Acids 36(4):693–699. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0120-z
Caputo I, Barone MV, Lepretti M, Martucciello S, Nista I, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Sblattero D, Esposito C (2010) Celiac anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies interfere with the uptake of alpha gliadin peptide 31–43 but not of peptide 57–68 by epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(9):717–727. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.010
Daniels I, Cavill D, Murray IA, Longb RG (2005) Elevated expression of iNOS mRNA and protein in celiac disease. Clin Chim Acta 356:134–142. doi:10.1016/j.cccn.2005.01.029
Di Niro R, Ziller F, Florian F, Crovella S, Stebel M, Bestagno M, Burrone O, Bradbury AR, Secco S, Marzari R, Sblattero D (2007) Construction of miniantibodies for the in vivo study of human autoimmune diseases in animal models. BMC Biotechnol 7:46. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-7-46
Dieterich W, Ehnis T, Bauer M, Donner P, Volta U, Riecken EO, Schuppan D (1997) Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med 3:797–801. doi:10.1038/nm0797-797
Dong Z, Saikumar P, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA (2006) Calcium in cell injury and death. Annu Rev Pathol 1:405–434. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100218
Esposito C, Caputo I, Auricchio S, Troncone R (2005) Tissue transglutaminase and celiac disease. Prog Exp Tumor Res 38:158–173. doi:10.1159/000084239
Esposito G, Cirillo C, Sarnelli G, De Filippis D, D’Armiento FP, Rocco A, Tardone G, Petruzzelli R, Grosso M, Izzo P, Iuvone T, Cuomo R (2007) Enteric glial-derived s100b protein stimulates nitric oxide production in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 133(3):918–925. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.009
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature’s biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396. doi:10.1042/BJ20021234
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260(6):3440–3450
Halttunen T, Mäki M (1999) Serum Immunoglobulin A from patients with celiac disease inhibits human T84 intestinal crypt epithelial cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 116:566–572. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70178-2
Hasegawa G, Suwa M, Ichikawa Y, Ohtsuka T, Kumagai S, Kikuchi M, Sato Y, Saito Y (2003) A novel function of tissue-type transglutaminase: protein disulphide isomerase. Biochem J 373:793–803. doi:10.1042/BJ20021084
Hodrea J, Demény MA, Majai G, Sarang Z, Korponay-Szabó IR, Fésüs L (2010) Transglutaminase 2 is expressed and active on the surface of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and macrophages. Immunol Lett 130(1–2):74–81. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2009.12.010
Iismaa SE, Mearns BM, Lorand L, Graham RM (2009) Transglutaminases and disease: lessons from genetically engineered mouse models and inherited disorders. Physiol Rev 89(3):991–1023
Jabri B, Sollid LM (2009) Tissue-mediated control of immunopathology in coeliac disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9(12):858–870. doi:10.1038/nri2670
Janiak A, Zemskov EA, Belkin AM (2006) Cell surface transglutaminase promotes RhoA activation via integrin clustering and suppression of the Src–p190RhoGAP signaling pathway. Mol Biol Cell 17:1606–1619. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-06-0549
Jeitner TM, Muma NA, Battaile KP, Cooper AJ (2009) Transglutaminase activation in neurodegenerative diseases. Future Neurol 4(4):449–467. doi:10.2217/fnl.09.17
Kaukinen K, Peräaho M, Collin P, Partanen J, Woolley N, Kaartinen T, Nuutinen T, Halttunen T, Mäki M, Korponay-Szabo I (2005) Small-bowel mucosal transglutaminase 2-specific IgA deposits in coeliac disease without villous atrophy: a prospective and randomized clinical study. Scand J Gastroenterol 40:564–572. doi:10.1080/00365520510023422
Korponay-Szabo IR, Halttunen T, Szalai Z, Laurila K, Kiraly R, Kovacs JB, Fesus L, Maki M (2004) In vivo targeting of intestinal and extraintestinal transglutaminase 2 by coeliac autoantibodies. Gut 53:641–648. doi:10.1136/gut.41.6.851
Lee J, Kim YS, Choi DH, Bang MS, Han TR, Joh TH, Kim SY (2004) Transglutaminase 2 induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a novel pathway in BV-2 microglia. J Biol Chem. 279(51):53725–53735. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407627200
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:140–156. doi:10.1038/nrm1014
Luciani A, Villella VR, Vasaturo A, Giardino I, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Guido S, Cexus ON, Peake N, Londei M, Quaratino S, Maiuri L (2010) Lysosomal accumulation of gliadin p31–43 peptide induces oxidative stress and tissue transglutaminase-mediated PPARgamma downregulation in intestinal epithelial cells and coeliac mucosa. Gut 59(3):311–319
Maiuri L, Luciani A, Giardino I, Raia V, Villella VR, D’Apolito M, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Guido S, Ciacci C, Cimmino M, Cexus ON, Londei M, Quaratino S (2008) Tissue transglutaminase activation modulates inflammation in cystic fibrosis via PPARgamma down-regulation. J Immunol 180(11):7697–7705
Marzari R, Sblattero D, Florian F, Tongiorgi E, Not T, Tommasini A, Ventura A, Bradbury A (2001) Molecular dissection of the tissue transglutaminase autoantibody response in celiac in celiac disease. J Immunol 166:4170–4176
Mehta K, Kumar A, Kim HI (2010) Transglutaminase 2: A multi-tasking protein in the complex circuitry of inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1921–1929. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.029
Mishra S, Murphy LJ (2004) Tissue transglutaminase has intrinsic kinase activity: identification of transglutaminase 2 as an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 kinase. J Biol Chem 279:23863–23868. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311919200
Myrsky E, Caja S, Simon-Vecsei Z, Korponay-Szabo IR, Nadalutti C, Collighan R, Mongeot A, Griffin M, Mäki M, Kaukinen K, Lindfors K (2009) Celiac disease IgA modulates vascular permeability in vitro through the activity of transglutaminase 2 and RhoA. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(20):3375–3385. doi:10.1007/s00018-009-0116-1
Nakaoka H, Perez DM, Baek KJ, Das T, Husain A, Misono K et al (1994) Gh: a GTP binding protein with transglutaminase activity and receptor signaling function. Science 264:1593–1596. doi:10.1126/science.7911253
Orrù S, Caputo I, D’Amato A, Ruoppolo M, Esposito C (2003) Proteomics identification of acyl-acceptor and acyl-donor substrates for transglutaminase in a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Implications for celiac disease. J Biol Chem 278(34):31766–31773. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305080200
Reif S, Lerner A (2004) Tissue transglutaminase-the key player in celiac disease: a review. Autoimmun Rev 3:40–45. doi:10.1016/S1568-9972(03)00065-X
Robitaille K, Daviau A, Tucholski J, Johnson GV, Rancourt C, Blouin R (2004) Tissue transglutaminase triggers oligomerization and activation of dual leucine zipper-bearing kinase in calphostin C-treated cells to facilitate apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 11:542–549. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401392
Salmi TT, Collin P, Korponay-Szabó IR, Laurila K, Partanen J, Huhtala H, Király R, Lorand L, Reunala T, Mäki M, Kaukinen K (2006) Endomysial antibody-negative coeliac disease: clinical characteristics and intestinal autoantibody deposits. Gut 55:1746–1753. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.071514
Secondo A, Staiano RI, Scorziello A, Sirabella R, Boscia F, Adornetto A, Valsecchi V, Molinaro P, Canzoniero LM, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2007) BHK cells transfected with NCX3 are more resistant to hypoxia followed by reoxygenation than those transfected with NCX1 and NCX2: Possible relationship with mitochondrial membrane potential. Cell Calcium 42(6):521–535. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2007.01.006
Sollid LM (2002) Coelic disease: dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat Rev Immunol 2:647–655. doi:10.1038/nri885
Sollid LM, Molberg O, McAdam S, Lundin KE (1997) Autoantibodies in coeliac disease: Tissue transglutaminase-guilt by association? Gut 41:851–852. doi:10.1136/gut.41.6.851
Zanoni G, Navone R, Lunardi C, Tridente G, Bason C, Sivori S, Beri R, Dolcino M, Valletta E, Corrocher R, Puccetti A (2006) In celiac disease, a subset of autoantibodies against transglutaminase binds toll-like receptor 4 and induces activation of monocytes. PLoS Med 3(9):e358. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030358
Zemskov EA, Janiak A, Hang J, Waghray A, Belkin AM (2006) The role of tissue transglutaminase in cell-matrix interactions. Front Biosci 11:1057–1076. doi:10.2741/1863
Zemskov EA, Loukinova E, Mikhailenko I, Coleman RA, Strickland DK, Belkin AM (2009) Regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor function by integrin-associated cell surface transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 284:16693–16703. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.010769
Zemskov EA, Mikhailenko I, Hsia RC, Zaritskaya L, Belkin AM (2011) Unconventional secretion of tissue transglutaminase involves phospholipid-dependent delivery into recycling endosomes. PLoS ONE 6(4):e19414. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019414
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from Fondi di Ateneo per la Ricerca di Base (FARB-ex 60%) and EC Marie Curie Research Training Network (contract n. MRTN-CT-20010-289964).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
I. Caputo and M. Lepretti contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caputo, I., Lepretti, M., Secondo, A. et al. Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies activate intracellular tissue transglutaminase by modulating cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis. Amino Acids 44, 251–260 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1120-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1120-y