Summary.
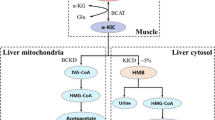
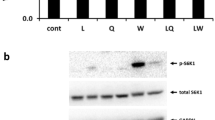
We previously reported that L-leucine suppresses myofibrillar proteolysis in chick skeletal muscles. In the current study, we compared the effects of L- and D-enantiomers of leucine on myofibrillar proteolysis in skeletal muscle of chicks. We also assessed whether leucine itself or its metabolite, α-ketoisocaproate (α-KIC), mediates the effects of leucine. Food-deprived (24 h) chicks were orally administered 225 mg/100 g body weight L-leucine, D-leucine or α-KIC and were sacrificed after 2 h. L-Leucine administration had an obvious inhibitory effect on myofibrillar proteolysis (plasma Nτ-methylhistidine concentration) in chicks while D-leucine and α-KIC were much more effective. We also examined the expression of the proteolytic-related genes (ubiquitin, proteasome, m-calpain and cathepsin B) by real-time PCR of cDNA in chick skeletal muscles. Ubiquitin mRNA expression was decreased by D-leucine and α-KIC but not L-leucine. Proteasome and m-calpain mRNA expressions as well as cathepsin B mRNA expression were likewise decreased by L-leucine, D-leucine and α-KIC. These results indicate that D-leucine and α-KIC suppress proteolytic-related genes, resulting in an decrease in myofibrillar proteolysis while L-leucine is much less effective in skeletal muscle of chicks, may be explain by conversion of D-leucine to α-KIC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JC Anthony F Yoshizawa TG Anthony TC Vary LS Jefferson SR Kimball (2000) ArticleTitleLeucine stimulates translation initiation in skeletal muscle of postabsorptive rats via a rapamycin-sensitive pathway J Nutr 130 2413–2419 Occurrence Handle11015466 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntVShtb0%3D
MG Buse SS Reid (1975) ArticleTitleLeucine. A possible regulator of protein turnover in muscle J Clin Invest 56 1250–1261 Occurrence Handle1237498 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XjvFejsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI108201
S Busquets B Alvarez M Llovera N Agell FJ Lopez-Soriano JM Argiles (2000) ArticleTitleBranched-chain amino acids inhibit proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle: Mechanisms involved J Cell Physiol 184 380–384 Occurrence Handle10911370 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-4652(200009)184:3<380::AID-JCP13>3.0.CO;2-F Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsl2lsrY%3D
O Coux K Tanaka AL Goldberg (1996) ArticleTitleStructure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes Annu Rev Biochem 65 801–847 Occurrence Handle8811196 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.004101 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XktFamurc%3D
RM Fulks JB Li AL Goldberg (1975) ArticleTitleEffects of insulin, glucose, and amino acids on protein turnover in rat diaphragm J Biol Chem 250 290–298 Occurrence Handle1141208 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXhtVKksr4%3D
K Furuno MN Goodman AL Goldberg (1990) ArticleTitleRole of different proteolytic systems in the degradation of muscle proteins during denervation atrophy J Biol Chem 265 8550–8557 Occurrence Handle2187867 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXktlygu7s%3D
DE Goll WR Dayton I Singh RM Robson (1991) ArticleTitleStudies of the alpha-actinin/actin interaction in the z-disk by using calpain J Biol Chem 266 8501–8510 Occurrence Handle2022664 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXktVemsrY%3D
DE Goll VF Thompson RG Taylor JA Christiansen (1992) ArticleTitleRole of the calpain system in muscle growth Biochimie 74 225–237 Occurrence Handle1610936 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0300-9084(92)90121-T Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVGitrg%3D
M Hall-Angeras PO Hasselgren RV Dimlich JE Fischer (1991) ArticleTitleMyofibrillar proteinase, cathepsin B, and protein breakdown rates in skeletal muscle from septic rats Metabolism 40 302–306 Occurrence Handle2000044 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0026-0495(91)90114-C Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M7lsFOmsg%3D%3D
H Hasegawa T Matsukawa Y Shinohara T Hashimoto (2000) ArticleTitleAssessment of the metabolic chiral inversion of D-leucine in rat by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with a stable isotope dilution analysis Drug Metab Dispos 28 920–924 Occurrence Handle10901701 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlt1ahtrk%3D
T Kanazawa I Taneike R Akaishi F Yoshizawa N Furuya S Fujimura M Kadowaki (2004) ArticleTitleAmino acids and insulin control autophagic proteolysis through different signaling pathways in relation to mtor in isolated rat hepatocytes J Biol Chem 279 8452–8459 Occurrence Handle14610086 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M306337200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhsFeis7s%3D
JB Li LS Jefferson (1978) ArticleTitleInfluence of amino acid availability on protein turnover in perfused skeletal muscle Biochim Biophys Acta 544 351–359 Occurrence Handle719005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXltlGjsw%3D%3D
BB Lowell NB Ruderman MN Goodman (1986) ArticleTitleEvidence that lysosomes are not involved in the degradation of myofibrillar proteins in rat skeletal muscle Biochem J 234 237–240 Occurrence Handle3707546 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhtVKqtLo%3D
S Mordier C Deval D Bechet A Tassa M Ferrara (2000) ArticleTitleLeucine limitation induces autophagy and activation of lysosome-dependent proteolysis in C2C12 myotubes through a mammalian target of rapamycin-independent signaling pathway J Biol Chem 275 29900–29906 Occurrence Handle10893413 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M003633200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmvFKjur4%3D
HE Morgan DC Earl A Broadus EB Wolpert KE Giger LS Jefferson (1971) ArticleTitleRegulation of protein synthesis in heart muscle. I. Effect of amino acid levels on protein synthesis J Biol Chem 246 2152–2162 Occurrence Handle5555564 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3MXht1agu7k%3D
T Nagasawa J Hirano F Yoshizawa N Nishizawa (1998) ArticleTitleMyofibrillar protein catabolism is rapidly suppressed following protein feeding Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62 1932–1937 Occurrence Handle9836429 Occurrence Handle10.1271/bbb.62.1932 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntlegt7Y%3D
T Nagasawa T Kido F Yoshizawa Y Ito N Nishizawa (2002) ArticleTitleRapid suppression of protein degradation in skeletal muscle after oral feeding of leucine in rats J Nutr Biochem 13 121–127 Occurrence Handle11834228 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0955-2863(01)00209-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovFChsg%3D%3D
T Nagasawa F Yoshizawa N Nishizawa (1996) ArticleTitlePlasma Nτ-methylhistidine concentration is a sensitive index of myofibrillar protein degradation during starvation in rats Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60 501–502 Occurrence Handle8901113 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhvFygtLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1271/bbb.60.501
K Nakashima A Ishida M Yamazaki H Abe (2005) ArticleTitleLeucine suppresses myofibrillar proteolysis by down-regulating ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in chick skeletal muscles Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336 660–666 Occurrence Handle16153608 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.138 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtVWnsL7F
K Peyrollier E Hajduch AS Blair R Hyde HS Hundal (2000) ArticleTitleL-leucine availability regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p70 S6 kinase and glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity in L6 muscle cells: evidence for the involvement of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway in the L-leucine-induced up-regulation of system a amino acid transport Biochem J 350 361–368 Occurrence Handle10947949 Occurrence Handle10.1042/0264-6021:3500361 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmvVGksLg%3D
V Solomon AL Goldberg (1996) ArticleTitleImportance of the ATP-ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in the degradation of soluble and myofibrillar proteins in rabbit muscle extracts J Biol Chem 271 26690–26697 Occurrence Handle8900146 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.41.25240 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmsV2rtbo%3D
S Tesseraud K Bigot M Taouis (2003) ArticleTitleAmino acid availability regulates S6K1 and protein synthesis in avian insulin-insensitive QM7 myoblasts FEBS Lett 540 176–180 Occurrence Handle12681504 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00260-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXislCiu7o%3D
MG Thompson RM Palmer A Thom SC Mackie KS Morrison CI Harris (1996) ArticleTitleMeasurement of protein degradation by release of labelled 3-methylhistidine from skeletal muscle and non-muscle cells J Cell Physiol 166 506–511 Occurrence Handle8600154 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199603)166:3<506::AID-JCP5>3.0.CO;2-T Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhsVegt7k%3D
ME Tischler M Desautels AL Goldberg (1982) ArticleTitleDoes leucine, leucyl-tRNA, or some metabolite of leucine regulate protein synthesis and degradation in skeletal and cardiac muscle? J Biol Chem 257 1613–1621 Occurrence Handle6915936 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XhtF2ktLc%3D
SJ Wassner JL Schlitzer JB Li (1980) ArticleTitleA rapid, sensitive method for the determination of 3-methylhistidine levels in urine and plasma using high-pressure liquid chromatography Anal Biochem 104 284–289 Occurrence Handle7446954 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(80)90076-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXkt1Wrt7w%3D
F Yoshizawa (2004) ArticleTitleRegulation of protein synthesis by branched-chain amino acids in vivo Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313 417–422 Occurrence Handle14684178 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.07.013 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvVWmtbY%3D
F Yoshizawa S Hirayama H Sekizawa T Nagasawa K Sugahara (2002) ArticleTitleOral administration of leucine stimulates phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and S6K1 in skeletal muscle but not in liver of diabetic rats J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 48 59–64 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xis1Wntbk%3D
F Yoshizawa H Sekizawa S Hirayama Y Yamazaki T Nagasawa K Sugahara (2004) ArticleTitleTissue-specific regulation of 4E-BP1 and S6K1 phosphorylation by α-ketoisocaproate J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 50 56–60 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXitV2ntr4%3D
VR Young SD Alexis BS Baliga HN Munro W Muecke (1972) ArticleTitleMetabolism of administered 3-methylhistidine. Lack of muscle transfer ribonucleic acid charging and quantitative excretion as 3-methylhistidine and its n-acetyl derivative J Biol Chem 247 3592–3600 Occurrence Handle5030632 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE38XksF2gu7o%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, K., Yakabe, Y., Ishida, A. et al. Suppression of myofibrillar proteolysis in chick skeletal muscles by α-ketoisocaproate. Amino Acids 33, 499–503 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-006-0404-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-006-0404-0