Summary.
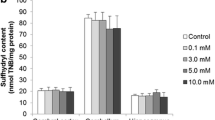
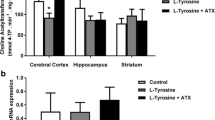
We observed here that acute proline (Pro) administration provoked a decrease (32%) of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in cerebral cortex and an increase (22%) of butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) activity in the serum of 29-day-old rats. In contrast, chronic administration of Pro did not alter AChE or BuChE activities. Furthermore, pretreatment of rats with vitamins E and C combined or alone, Nϖ-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester or melatonin prevented the reduction of AChE activity caused by acute Pro administration, suggesting the participation of oxidative stress in such effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delwing, D., Chiarani, F., Wannmacher, C. et al. Effect of hyperprolinemia on acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities in rat. Amino Acids 28, 305–308 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-005-0186-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-005-0186-9