Abstract
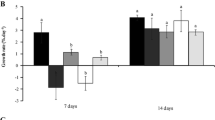
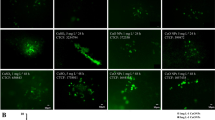
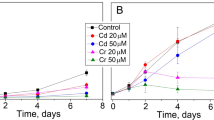
The effects of the heavy metals copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) on Sargassum cymosum were evaluated by determining uptake capacity, growth rates, photosynthetic efficiency, contents of photosynthetic pigments and phenolic compounds, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging capacity, and morphological and cellular changes. S. cymosum was cultivated with Cu and Pb separately and combined at concentrations of 10, 25, and 50 μM for 7 days in laboratory-controlled conditions. Seaweeds under Cu treatment showed the highest biosorption capacity, and growth rates were significantly reduced compared to the control. The photosynthesis/irradiance curves showed alterations in kinetic patterns in the metal-treated samples. Specifically, Cu treatment alone inhibited electron transport rate (ETR) response, while Pb alone induced it. However, samples treated with both Cu and Pb (Cu + Pb) showed inhibition in ETR. The total amount of pigments increased relative to control. Light microscopy showed an increase in phenolic compounds, with physodes migrating towards cortical cells. Scanning electronic microscopy revealed alterations in the typical rough surface of thallus, when compared with control, especially for Pb treatments. Based on these results, it could be concluded that Cu and Pb are stress factors for S. cymosum, promoting alterations in seaweed metabolism and stimulating protective mechanisms against oxidative stress. However, the high bioaccumulation capacity of both heavy metals indicates a possible application for S. cymosum as a biosorbent agent for contaminated wastewater when metals are in low concentrations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alahverdi M, Savabieasfahani M (2012) Metal pollution in seaweed and related sediment of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Environ Contam Toxicol 88(6):939–945
Aman R, Carle R, Conrad J, Beifuss U, Schieber A (2005) Isolation of carotenoids from plant materials and dietary supplements by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1074:99–105
Balboa EM, Conde E, Moure A, Falqué E, Domínguez H (2013) In vitro antioxidant properties of crude extracts and compounds from brown algae. Food Chem 138:1764–1785
Betancor S, Tuya F, Gil-Díaz T, Figueroa FL, Haroun R (2014) Effects of a submarine eruption on the performance of two brown seaweeds. Mar Environ Res 79:37–47
Brinza L, Nygård CA, Dring MJ, Gavrilescu M, Benning LG (2009) Cadmium tolerance and adsorption by the marine brown alga Fucus vesiculosus from the Irish Sea and the Bothnian Sea. Bioresource Technol 100:1727–1733
Collén J, Pinto E, Pedersén M, Colepicolo P (2003) Induction of oxidative stress in the red macroalga Gracilaria tenuistipitata by pollutant metals. Arch Environ Con Tox 45:337–342
Connan S, Stengel DB (2011) Impacts of ambient salinity and copper on brown algae: 1. Interactive effects on photosynthesis, growth, and copper accumulation. Aquat Toxicol 104:94–107
Davis TA, Volesky B, Vieira RHSF (2000) Sargassum seaweed as biosorbent for heavy metals. Water Res 34(17):4270–4278
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37:4311–4330
de Felix MRL, Osorio LKP, Ouriques LC, Farias-Soares FL, Steiner N, Kreusch M, Pereira D, Simioni C, Costa GB, Horta PA, Chow F, Ramlov F, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL, Schmidt EC (2014) The effect of cadmium under different salinity conditions on the cellular architecture and metabolism in the red alga Pterocladiella capillacea (Rhodophyta, Gelidiales). Microsc Microanal (Print) 20:1411–1424
Dummermuth AL, Karsten U, Fisch KM, König GM, Wiencke C (2003) Responses of marine macroalgae to hydrogen-peroxide stress. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 289:103–121
Edwards P (1972) Cultured red alga to measure pollution. Marine Poll Bull 3(12):184–188
Fichet D, Radenac G, Miramand P (1998) Experimental studies of impacts of harbour sediments resuspension to marine invertebrates larvae: bioavailability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn and toxicity. Marine Poll Bull 7–12(36):509–518
Figueroa F, Nygard C, Ekelund N, Gómez I (2003) Photobiological characteristics and photosynthetic UV responses in two Ulva species (Chlorophyta) from southern Spain. J Photoch Photobio 72(3):5–44
Fourestand E, Volesky B (1996) Contribution of sulfonate groups and alginate to heavy metal biosorption by the dry biomass of Sargassum fluitans. Environ Sci Technol 30:277–282
Freitas OMM, Martins RJE, Delerue-Matos CM, Boaventura RAR (2008) Removal of Cd(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by brown marine macro algae: kinetic modeling. J Hazard Mater 153:493–501
Fujii MT, Pupo D, Ouriques LC, Guimaraes SMPB, Yokoya NS (2011) Marine benthic algae from Santa Catarina state, Southern Brazil. Boletim do Instituto de Botânica 20, Brazil
Gledhill M, Nimmo M, Hill SJ, Brown MT (1999) The release of copper-complexing ligands by the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus (Phaeophyceae) in response to increasing total copper levels. J Phycol 35:501–509
Gouveia C, Kreusch M, Schmidt EC, Felix MR De L, Osorio LKP, Pereira DT, Santos R, Ouriques LC, Martins RP, Latini A, Ramlov F, Carvalho TJG, Chow F, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL (2013) The effects of lead and copper on the cellular architecture and metabolism of the red alga Gracilaria domingensis. Microsc Microanal 19(3):513–524
Han T, Kang SH, Park JS, Lee HK, Brown MT (2008) Physiological responses of Ulva pertusa and U. armoricana to copper exposure. Aquat Toxicol 86:176–184
Hu JZ, Zheng AZ, Pei DL, Shi GX (2010) Bioaccumulation and chemical forms of cadmium, copper and lead in aquatic plants. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53(1):235–240
Huang D, Ou B, Prior RL (2005) The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J Agr Food Chem 53:1841–1856
Huovinen P, Leal P, Gómez I (2010) Interacting effects of copper, nitrogen and ultraviolet radiation on the physiology of three south Pacific kelps. Mar Freshwater Res 61:330–341
Jacinto MLJAJ, David CPC, Perez TR, Jesus BR (2009) Comparative efficiency of algal biofilters in the removal of chromium and copper from wastewater. Ecol Eng 35:856–860
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol 167:191–194
Jothinayagi N, Anbazhagan C (2009) Heavy metal monitoring of Rameswaram Coast by some Sargassum species. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ 4(2):73–80
Karez CS, Magalhaes VF, Pfeiffer WC (1994) Trace metal accumulation by algae in Sepetiba Bay, Brazil. Environ Pollut 83:351–356
Kim YK, Guo Q, Packer L (2002) Free radical scavenging activity of red ginseng aqueous extracts. Toxicology 172:149–156
Kleinübing SJ, Guibal E, Silva EA, Silva MGC (2012) Copper and nickel competitive biosorption simulation from single and binary systems by Sargassum filipendula. Chem Eng J 184:16–22
Lignell A, Pedersén M (1989) Ágar composition as a function of morphology and growth rate: studies on some morphological strains of Gracilaria secundata and Gracilaria verrucosa (Rhodophyta). Bot Mar 32:219–227
Luna AS, Costa ALH, Costa ACA, Henriques CA (2010) Competitive biosorption of cadmium(II) and zinc(II) ions from binary systems by Sargassum filipendula. Bioresource Technol 101:5104–5111
Mamboya FA, Pratap HB, Mtolera M, Björk M (1999) The effect of copper on the daily growth rate and photosynthetic efficiency of the brown macroalga Padina boergesenii. http://www.oceandocs.org/handle/1834/787. Accessed 17 April 2014
Martins CDL, Arantes N, Faveri C, Batista MB, Oliveira EC, Pagliosa PR, Fonseca AL, Nunes JMC, Chow F, Pereira SB, Horta PA (2012) The impact of coastal urbanization on the structure of phytobenthic communities in southern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 64:772–778
Melville F, Pulkownik A (2007) Investigation of mangrove macroalgae as biomonitors of estuarine metal contamination. Sci Total Environ 387:301–309
Nielsen HD, Nielsen SL (2005) Photosynthetic responses to Cu2+ exposure are independent of light acclimation and uncoupled from growth inhibition in Fucus serratus (Phaeophyceae). Mar Pollut Bull 51:715–721
Nielsen HD, Nielsenb SL (2010) Adaptation to high light irradiances enhances the photosynthetic Cu2+ resistance in Cu2+ tolerant and non-tolerant populations of the brown macroalgae Fucus serratus. Mar Pollut Bull 60:710–717
Pagliosa PR, Fonseca A, Barbosa FA (2006) Evidence of systemic changes in trace metal concentrations in subtropical estuarine sediments as a result of urbanization. J Coastal Res 39:1078–1083
Pinto E, Sigaud-Kutner TCS, Leitão MAS, Okamoto OK, Morse D, Colepicolo P (2003) Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress in algae. J Phycol 39:1008–1018
Platt T, Gallegos C, Harrison W (1980) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38(68):7–701
Polo LK, Felix MRL, Kreusch M, Pereira DT, Costa GB, Simioni C, Ouriques LC, Chow F, Ramlov F, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL, Schmidt EC (2014) Photoacclimation responses of the brown macroalga Sargassum cymosum to the combined influence of UV radiation and salinity: cytochemical and ultrastructural organization and photosynthetic performance. J Photoch Photobiol
Ragan MA, Glombitza KW (1986) Phlorotannins, brown algal polyphenols. Progr Phycologic Research 4:129–241
Ramus J, Rosenberg G (1980) Diurnal photosynthetic performance of seaweeds measured under natural conditions. Mar Biol 56:21–28
Randhir R, Shetty P, Shetty K (2002) L-DOPA and total phenolic stimulation in dark germinated fava bean in response to peptide and phytochemical elicitors. Process Biochem 37:1247–1256
Romera E, González F, Ballester A, Blázquez ML, Muñoz JA (2007) Comparative study of biosorption of heavy metals using different types of algae. Bioresour Technol 98(17):3344–3353
Rovai AS, Barufi JB, Pagliosa PR, Scherner F, Torres MA, Horta PA, Simonassi JC, Quadros DPC, Borges DLG, Soriano-Sierra EJ (2013) Photosynthetic performance of restored and natural mangroves under different environmental constraints. Environ Pollut 181:233–241
Santos RW, Schmidt EC, Martins RP, Latini A, Maraschin M, Horta PA, Bouzon ZL (2012) Effects of cadmium on growth, photosynthetic pigments, photosynthetic performance, biochemical parameters and structure of chloroplasts in the agarophyte Gracilaria domingensis (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales). Am J Plant Sci 3:1077–1084
Santos RW, Schmidt EC, Felix MRL, Polo LK, Kreusch M, Pereira DT, Costa GB, Simioni C, Chow F, Ramlov F, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL (2014) Bioabsorption of cadmium, copper and lead by the red macroalga Gelidium floridanum: physiological responses and ultrastructure features. Ecotox Environ Safe 105:80–89
Scherner F, Ventura R, Barufi JB, Horta PA (2012a) Salinity critical threshold values for photosynthesis of two cosmopolitan seaweed species: providing baselines for potential shifts on seaweed assemblages. Mar Environ Res 79:1–12
Scherner F, Barufi JB, Horta PA (2012b) Photosynthetic response of two seaweed species along an urban pollution gradient: evidence of selection of pollution-tolerant species. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2380–2390
Scherner F, Horta PA, Oliveira EC, Simonassi JC, Hall-Spencer JM, Chow F, Nunes JMC, Pereira SMB (2013) Coastal urbanization leads to remarkable seaweed species loss and community shifts along the SW Atlantic. Mar Pollut Bull 76:106–115
Schmidt EC, Scariot LA, Rover T, Bouzon ZL (2009) Changes in ultrastructure and histochemistry of two red macroalgae strains of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales), as a consequence of ultraviolet B radiation exposure. Micron 40:860–869
Schmidt EC, Pereira B, Pontes CLM, Santos R, Scherner F, Horta PA, Martins RP, Latini A, Maraschin M, Bouzon ZL (2012) Alterations in architecture and metabolism induced by ultraviolet radiation-B in the carragenophyte Chondracanthus teedei (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). Protoplasma 249:353–367
Schreiber U, Schliwa U, Bilger W (1986) Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynth Res 10:51–62
Sheng PX, Ting YP, Chen JP, Hong L (2004) Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:131–141
Shoenwaelder M (2002) The occurrence and cellular significance of physodes in the brown algae. Phycologia 41(2):125–139
Shoenwaelder M (2008) The biology of phenolic containing vesicles. Algae 23:163–75
Széchy MTM, Paula EJ (2000) Padrões estruturais quantitativos de bancos de Sargassum (Phaeophyta, Fucales) do litoral dos estados do Rio de Janeiro e São Paulo, Brasil. Rev Bras Bot 23(2):121–132
Thibaut T, Pinedo S, Torras X, Ballesteros E (2005) Long-term decline of the populations of Fucales (Cystoseira spp. and Sargassum spp.) in the Albères coast (France, North-western Mediterranean). Mar Pollut Bull 50:1472–1489
Toth G, Pavia H (2000) Lack of phlorotannin induction in the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum in response to increased copper concentrations. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 192:119–126
Vieira RHSF, Volesky B (2000) Biosorption: a solution to pollution? Int Microbiol 3:17–24
Vijayaraghavan K, Teo TT, Balasubramanian R, Joshi UM (2009) Application of Sargassum biomass to remove heavy metal ions from synthetic multi-metal solutions and urban storm water runoff. J Hazard Mater 164:1019–1023
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the staff of the Central Laboratory of Electron Microscopy (LCME), Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil, for the use of their scanning electron microscopy. Éder C. Schmidt holds a postdoctoral fellowship from CAPES. Giulia B. Costa holds a Master’s degree fellowship from CAPES. Zenilda L. Bouzon is a CNPq fellow. Fungyi Chow is a FAPESP fellow. This study is part of the MSc dissertation of the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Andreas Holzinger
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, G.B., de Felix, M.R.L., Simioni, C. et al. Effects of copper and lead exposure on the ecophysiology of the brown seaweed Sargassum cymosum . Protoplasma 253, 111–125 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0795-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0795-4