Abstract
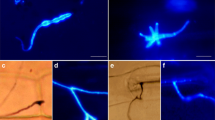
Cereal powdery mildews caused by Blumeria graminis and cereal rusts caused by Puccinia spp. are constant disease threats that limit the production of almost all important cereal crops. Rice is an intensively grown agricultural cereal that is atypical because of its immunity to all powdery mildew and rust fungi. We analyzed the nonhost interactions between rice and the wheat powdery mildew fungus B. graminis f. sp. tritici (Bgt) and the wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina (Ptr) to identify the basis of nonhost resistance (NHR) in rice against cereal powdery mildew and rust fungi at cytological and molecular levels. No visible symptoms were observed on rice leaves inoculated with Bgt or Ptr. Microscopic observations showed that both pathogens exhibited aberrant differentiation and significantly reduced penetration frequencies on rice compared to wheat. The development of Bgt and Ptr was also completely arrested at early infection stages in cases of successful penetration into rice leaves. Attempted infection of rice by Bgt and Ptr induced similar defense responses, including callose deposition, accumulation of reactive oxygen species, and hypersensitive response in rice epidermal and mesophyll cells, respectively. Furthermore, a set of defense-related genes were upregulated in rice against Bgt and Ptr infection. Rice is an excellent monocot model for genetic and molecular studies. Therefore, our results demonstrate that rice is a useful model to study the mechanisms of NHR to cereal powdery mildew and rust fungi, which provides useful information for the development of novel and durable strategies to control these important pathogens.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam L, Somerville SC (1996) Genetic characterization of five powdery mildew disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 9:341–356
Ayliffe M, Singh R, Lagudah E (2008) Durable resistance to wheat stem rust needed. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:187–192
Ayliffe M et al (2011) Determining the basis of nonhost resistance in rice to cereal rusts. Euphytica 179:33–40
Ayliffe M et al (2013) A simple method for comparing fungal biomass in infected plant tissues. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:658–667
Azinheira HGAHG, Silva MCSMC, Talhinhas PTP, Medeira CMC, Maia IMI, Anne-Sophie Petitot ASP, Fernandez DFD (2010) Non-host resistance responses of Arabidopsis thaliana to the coffee leaf rust fungus (Hemileia vastatrix). Botany 88:621–629
Borhan MH, Gunn N, Cooper A, Gulden S, Tor M, Rimmer SR, Holub EB (2008) WRR4 encodes a TIR-NB-LRR protein that confers broad-spectrum white rust resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana to four physiological races of Albugo candida. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:757–768
Borhan MH, Holub EB, Kindrachuk C, Omidi M, Bozorgmanesh-Frad G, Rimmer SR (2010) WRR4, a broad-spectrum TIR-NB-LRR gene from Arabidopsis thaliana that confers white rust resistance in transgenic oilseed Brassica crops. Mol Plant Pathol 11:283–291
Cheng Y et al (2012) Characterization of non-host resistance in broad bean to the wheat stripe rust pathogen. BMC Plant Biol 12:96
Cheng Y, Zhang H, Yao J, Han Q, Wang X, Huang L, Kang Z (2013) Cytological and molecular characterization of non-host resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana against wheat stripe rust. Plant Physiol Biochem 62:11–18
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814
Chuio T et al (2007) Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769:497–505
Collins NC et al (2003) SNARE-protein-mediated disease resistance at the plant cell wall. Nature 425:973–977
Dean R et al (2012) The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:804–804
Durrant WE, Dong X (2004) Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:185–209
Ellis J (2006) Insights into nonhost disease resistance: can they assist disease control in agriculture? Plant Cell 18:523–528
Eric A, Allen HCH, Steadman JR, Stavely RJ (1991) Influence of leaf surface features on spore deposition and the epiphytic growth of phytopathogenic fungi. In: microbial ecology of leaves. Springer, Verlag, New York, pp 87–110
Feys BJ, Moisan LJ, Newman MA, Parker JE (2001) Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4. Embo J 20:5400–5411
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Plant comparative genetics after 10 years. Science 282:656–659
Gan PH, Dodds PN, Hardham AR (2012) Plant infection by biotrophic fungal and oomycete pathogens. In: Silvia Perotto, František Baluška (eds) Signaling and communication in plant symbiosis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 183–212
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JD (1997) Plant disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:575–607
Hao CZ, Chen YL, Zhang B, Li YF, Zuo H, Qi T, Ma Q (2013) Histochemical comparison of the nonhost tomato with resistant wheat against Blumeria graminis f. sp tritici. Microsc Res Tech 76:514–522
Heath MC (1974) Light and electron microscope studies of the interactions of host and non-host plants with cowpea rust-Uromyces phaseoli var. vignae. Physiol Plant Pathol 4:403–408
Heath MC (1979) Partial characterization of the electron-opaque deposits formed in the non-host plant, French bean, after cowpea rust infection. Physiol Plant Pathol 15:141–144
Heath MC (1981) Resistance of plants to rust infection. Phytopathology 71:971–974
Heath MC (1997) Signalling between pathogenic rust fungi and resistant or susceptible host plants. AoB Plants 80:713–720
Heath MC (2000) Nonhost resistance and nonspecific plant defenses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:315–319
Hemetsberger C, Herrberger C, Zechmann B, Hillmer M, Doehlemann G (2012) The Ustilago maydis effector Pep1 suppresses plant immunity by inhibition of host peroxidase activity. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002684
Hilaire E et al (2001) Vascular defense responses in rice: peroxidase accumulation in xylem parenchyma cells and xylem wall thickening. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:1411–1419
Hood M, Shew H (1996) Applications of KOH-aniline blue fluorescence in the study of plant-fungal interactions. Phytopathology 86:704–708
Hoogkamp T, Chen WQ, Niks R (1998) Specificity of prehaustorial resistance to Puccinia hordei and to two inappropriate rust fungi in barley. Phytopathology 88:856–861
Huckelhoven R, Dechert C, Kogel KH (2001) Non-host resistance of barley is associated with a hydrogen peroxide burst at sites of attempted penetration by wheat powdery mildew fungus. Mol Plant Pathol 2:199–205
Huitema E, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Francis DM, Kamoun S (2003) Active defence responses associated with non-host resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana to the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Mol Plant Pathol 4:487–500
Jafary H, Szabo LJ, Niks RE (2006) Innate nonhost immunity in barley to different heterologous rust fungi is controlled by sets of resistance genes with different and overlapping specificities. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1472–1472
Jafary H, Albertazzi G, Marcel TC, Niks RE (2008) High diversity of genes for nonhost resistance of barley to heterologous rust fungi. Genetics 178:2327–2339
Jwa NS, Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Park CH, Agrawal VP (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel jasmonate inducible pathogenesis-related class 10 protein gene, JIOsPR10, from rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:973–983
Kang Z, Shang H, Li Z (1993) Fluorescence staining technique of wheat rust tissue. Plant Prot 2:27, in Chinese
Koch K et al (2006) Structural analysis of wheat wax (Triticum aestivum, c.v. ‘Naturastar’ L.): from the molecular level to three dimensional crystals. Planta 223:258–270
Koch K, Bhushan B, Barthlott W (2008) Diversity of structure, morphology and wetting of plant surfaces. Soft Matter 4:1943–1963
Koch K, Bhushan B, Barthlott W (2009) Multifunctional surface structures of plants: an inspiration for biomimetics. Prog Mater Sci 54:137–178
Kunkel BN, Brooks DM (2002) Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:325–331
Lee HA et al (2014) Multiple recognition of RXLR effectors is associated with nonhost resistance of pepper against Phytophthora infestans. New Phytol 203:926–938
Lewis JRD BG (1972) Behaviour of uredospore germ-tubes of Puccinia graminis tritici in relation to the fine structure of wheat leaf surfaces. Trans Br Mycol Soc 58:139–145
Lipka V et al (2005) Pre-and postinvasion defenses both contribute to nonhost resistance in Arabidopsis. Science 310:1180
Lipka U, Fuchs R, Lipka V (2008) Arabidopsis non-host resistance to powdery mildews. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:404–411
Lipka U, Fuchs R, Kuhns C, Petutschnig E, Lipka V (2010) Live and let die—Arabidopsis nonhost resistance to powdery mildews. Eur J Cell Biol 89:194–199
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-[Delta][Delta] CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Loehrer M, Langenbach C, Goellner K, Conrath U, Schaffrath U (2008) Characterization of nonhost resistance of Arabidopsis to the Asian soybean rust. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:1421–1430
Mellersh DG, Heath MC (2003) An investigation into the involvement of defense signaling pathways in components of the nonhost resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana to rust fungi also reveals a model system for studying rust fungal compatibility. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:398–404
Mendgen K, Hahn M, Deising H (1996) Morphogenesis and mechanisms of penetration by plant pathogenic fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:367–386
Midoh N, Iwata M (1996) Cloning and characterization of a probenazole-inducible gene for an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 37:9–18
Mysore KS, Ryu CM (2004) Nonhost resistance: how much do we know? Trends Plant Sci 9:97–104
Niks R (1983a) Comparative histology of partial resistance and the nonhost reaction to leaf rust pathogens in barley and wheat seedlings. Phytopathology 73:60–64
Niks R (1983b) Haustorium formation by Puccinia hordei in leaves of hypersensitive, partially resistant, and nonhost plant genotypes. Phytopathology 73:64–66
Qiu DY et al (2007) OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:492–499
Roelfs AP, Bushnell WR (1985) The cereal rusts. Vol. II: diseases, distribution, epidemiology and control. Academic Press, Orlando
Schulze-Lefert P, Panstruga R (2011) A molecular evolutionary concept connecting nonhost resistance, pathogen host range, and pathogen speciation. Trends Plant Sci 16:117–125
Shafiei R, Hang C, Kang JG, Loake GJ (2007) Identification of loci controlling non-host disease resistance in Arabidopsis against the leaf rust pathogen Puccinia triticina. Mol Plant Pathol 8:773–784
Sohn KH, Saucet SB, Clarke CR, Vinatzer BA, O’Brien HE, Guttman DS, Jones JDG (2012) HopAS1 recognition significantly contributes to Arabidopsis nonhost resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pathogens. New Phytol 193:58–66
Staples RC (2000) Research on the rust fungi during the twentieth century. Annu Rev Phytopathol 38:49–69
Staub T, Dahmen H, Schwinn F (1974) Light-and scanning electron microscopy of cucumber and barley powdery mildew on host and nonhost plants. Phytopathology 64:364–372
Stein M et al (2006) Arabidopsis PEN3/PDR8, an ATP binding cassette transporter, contributes to nonhost resistance to inappropriate pathogens that enter by direct penetration. Plant Cell 18:731–746
Stokstad E (2007) Deadly wheat fungus threatens world’s breadbaskets. Science 315:1786–1787
Thaler JS, Owen B, Higgins VJ (2004) The role of the jasmonate response in plant susceptibility to diverse pathogens with a range of lifestyles. Plant Physiol 135:530–538
Thordal-Christensen H (2003) Fresh insights into processes of nonhost resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:351–357
Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Collinge DB (1997) Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant J 11:1187–1194
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Voegele RT, Mendgen KW (2011) Nutrient uptake in rust fungi: how sweet is parasitic life? Euphytica 179:41–55
Wang CF, Huang LL, Buchenauer H, Han QM, Zhang HC, Kang ZS (2007) Histochemical studies on the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (O2 − and H2O2) in the incompatible and compatible interaction of wheat—Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 71:230–239
Wei CF, Kvitko BH, Shimizu R, Crabill E, Alfano JR, Lin NC, Martin GB, Huang HC, Collmer A (2007) A Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 mutant lacking the type III effector HopQ1-1 is able to cause disease in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J 51:32–46
Wroblewski T et al (2009) Comparative large-scale analysis of interactions between several crop species and the effector repertoires from multiple pathovars of Pseudomonas and Ralstonia. Plant Physiol 150:1733–1749
Wyand RA, Brown JK (2003) Genetic and forma specialis diversity in Blumeria graminis of cereals and its implications for host-pathogen co-evolution. Mol Plant Pathol 4:187–198
Yuan YX et al (2007) Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility Plant. Biotechnol J 5:313–324
Yun BW, Atkinson HA, Gaborit C, Greenland A, Read ND, Pallas JA, Loake GJ (2003) Loss of actin cytoskeletal function and EDS1 activity, in combination, severely compromises non-host resistance in Arabidopsis against wheat powdery mildew. Plant J 34:768–777
Zhang H et al (2011) Histological and molecular studies of the non-host interaction between wheat and Uromyces fabae. Planta 234:979–991
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333
Zimmerli L, Stein M, Lipka V, Schulze-Lefert P, Somerville S (2004) Host and non-host pathogens elicit different jasmonate/ethylene responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 40:633–646
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB127700), the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System in China (No. CARS-3-1-11), and the 111 Project from the Ministry of Education of China (No. B07049).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Adrienne R. Hardham
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Yao, J., Zhang, H. et al. Cytological and molecular analysis of nonhost resistance in rice to wheat powdery mildew and leaf rust pathogens. Protoplasma 252, 1167–1179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0750-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0750-9