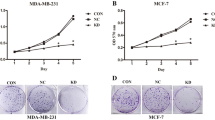
Abstract
Epstein–Barr virus immediate-early protein Zta plays an active role in altering cellular gene expression, which may be fundamentally linked to the viral life cycle, cell cycle, cell growth, and differentiation. HER2 is associated with a wide variety of human cancers, and its knockdown significantly reverses the malignant features of HER2-positive cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential role of Zta in regulating HER2 expression and phenotype changes of MDA-MB-453 cells. Our results indicate that ectopic expression of Zta resulted in downregulation of the HER2 protein in cancer cells (MDA-MB-453, SKBR-3, BT474, and SKOV-3). The Zta protein significantly decreased HER2 mRNA and protein expression in MDA-MB-453 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanistically, Zta recognized and targeted the promoter of HER2 gene, reducing the transcriptional activity of the HER2 gene. Zta induced G0/G1 arrest of MDA-MB-453 cells, inhibiting their proliferation and migration activity. These data suggest that Zta may act as a transforming suppressor of the HER2 gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Shannon-Lowe C, Rickinson AB, Bell AI (2017) Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0271
Yanagi A, Nishikawa J, Shimokuri K, Shuto T, Takagi T, Takagi F et al (2019) Clinicopathologic characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer over the past decade in Japan. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090305
Khan G, Fitzmaurice C, Naghavi M, Ahmed LA (2020) Global and regional incidence, mortality and disability-adjusted life-years for Epstein-Barr virus-attributable malignancies, 1990–2017. BMJ Open 10(8):e037505. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037505
Al Hamad M, Matalka I, Al Zoubi MS, Armogida I, Khasawneh R, Al-Husaini M et al (2020) Human mammary tumor virus, human papilloma virus, and Epstein-Barr Virus infection are associated with sporadic breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer (Auckl). https://doi.org/10.1177/1178223420976388
Gopalakrishnan Mahalingam KK, Sankar LS, Masthan KMK, Mahalakshmi K, Naveen Kumar V (2021) Epstein–Barr viral load in exfoliated cells of oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral potentially malignant disorders—a cross-sectional study. J Clin Virol Plus 1(4):100051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcvp.2021.100051
Godfrey A, Osborn K, Sinclair AJ (2021) Interaction sites of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta transcription factor with the host genome in epithelial cells. Access Microbiol 3(11):000282. https://doi.org/10.1099/acmi.0.000282
Zhou Y, Heesom K, Osborn K, AlMohammed R, Sweet SM, Sinclair AJ (2020) Identifying the cellular interactome of Epstein–Barr virus lytic regulator zta reveals cellular targets contributing to viral replication. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00927-19
Ramasubramanyan S, Osborn K, Al-Mohammad R, Naranjo Perez-Fernandez IB, Zuo J, Balan N et al (2015) Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor Zta acts through distal regulatory elements to directly control cellular gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):3563–3577. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv212
Cayrol C, Flemington E (1996) The Epstein-Barr virus bZIP transcription factor Zta causes G0/G1 cell cycle arrest through induction of cyclin‐dependent kinase inhibitors. EMBO J 15(11):2748–2759
Tsai S-C, Lin S-J, Chen P-W, Luo W-Y, Yeh T-H, Wang H-W, Chen C-J, Tsai C-H (2009) EBV Zta protein induces the expression of interleukin-13, promoting the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 114(1):109–118
Kang M-S, Kieff E (2015) Epstein–Barr virus latent genes. Exp Mol Med 47(1):e131–e. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2014.84
Young LS, Murray PG (2003) Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene 22(33):5108–5121. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206556
Marquitz AR, Mathur A, Shair KH, Raab-Traub N (2012) Infection of Epstein-Barr virus in a gastric carcinoma cell line induces anchorage independence and global changes in gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(24):9593–9598. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1202910109
Luo Y, Liu Y, Wang C, Gan R (2021) Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01793-3
Cayrol C, Flemington EK (1996) The Epstein-Barr virus bZIP transcription factor Zta causes G0/G1 cell cycle arrest through induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Embo J 15(11):2748–2759
Rodriguez A, Jung EJ, Yin Q, Cayrol C, Flemington EK (2001) Role of c-myc regulation in Zta-mediated induction of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27 and cell growth arrest. Virology 284(2):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.2001.0923
Mauser A, Holley-Guthrie E, Zanation A, Yarborough W, Kaufmann W, Klingelhutz A, Seaman WT, Kenney S (2002) The Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein BZLF1 induces expression of E2F-1 and other proteins involved in cell cycle progression in primary keratinocytes and gastric carcinoma cells. J Virol 76(24):12543–12552. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.76.24.12543-12552.2002
Sundaresan S, Penuel E, Sliwkowski MX (1999) The biology of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Curr Oncol Rep 1(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-999-0005-7
Lee J, Dull TJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A (1989) HER2 cytoplasmic domain generates normal mitogenic and transforming signals in a chimeric receptor. Embo J 8(1):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03361.x
De Potter IY, Poumay Y, Squillace KA, Pittelkow MR (2001) Human EGF receptor (HER) family and heregulin members are differentially expressed in epidermal keratinocytes and modulate differentiation. Exp Cell Res 271(2):315–328. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.2001.5390
Villa-Moruzzi E (2011) Tyrosine phosphatases in the HER2-directed motility of ovarian cancer cells: Involvement of PTPN12, ERK5 and FAK. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 34(3):101–112. https://doi.org/10.3233/acp-2011-0008
Carpenter RL, Han W, Paw I, Lo HW (2013) HER2 phosphorylates and destabilizes pro-apoptotic PUMA, leading to antagonized apoptosis in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 8(11):e78836. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078836
Kunte S, Abraham J, Montero AJ (2020) Novel HER2-targeted therapies for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer 126(19):4278–4288. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.33102
Faltus T, Yuan J, Zimmer B, Krämer A, Loibl S, Kaufmann M, Strebhardt K (2004) Silencing of the HER2/neu gene by siRNA inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in HER2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 6(6):786–795. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.04313
Rossing M, Sørensen CS, Ejlertsen B, Nielsen FC (2019) Whole genome sequencing of breast cancer. Apmis 127(5):303–315
Ferrari A, Vincent-Salomon A, Pivot X, Sertier A-S, Thomas E, Tonon L et al (2016) A whole-genome sequence and transcriptome perspective on HER2-positive breast cancers. Nat Commun 7(1):1–9
Timms JF, White SL, O'Hare MJ, Waterfield MD (2002) Effects of ErbB-2 overexpression on mitogenic signalling and cell cycle progression in human breast luminal epithelial cells. Oncogene 21(43):6573–6586. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205847
Kalkan A, Ozdarendeli A, Bulut Y, Yekeler H, Cobanoglu B, Doymaz MZ (2005) Investigation of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in formalin-fixed and paraffin- embedded breast cancer tissues. Med Princ Pract 14(4):268–271. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085748
Preciado MV, Chabay PA, De Matteo EN, Gonzalez P, Grinstein S, Actis A, Gass HD (2005) Epstein-Barr virus in breast carcinoma in Argentina. Arch Pathol Lab Med 129(3):377–381. https://doi.org/10.5858/2005-129-377-evibci
Ayee R, Ofori MEO, Wright E, Quaye O (2020) Epstein Barr virus associated lymphomas and epithelia cancers in humans. J Cancer 11(7):1737–1750. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.37282
Tavakoli A, Monavari SH, Solaymani Mohammadi F, Kiani SJ, Armat S, Farahmand M (2020) Association between Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 20(1):493. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07013-x
Nkosi D, Sun L, Duke LC, Patel N, Surapaneni SK, Singh M, Meckes DG Jr (2020) Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 promotes syntenin-1- and Hrs-induced extracellular vesicle formation for its own secretion to increase cell proliferation and migration. mBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00589-20
Tsai SC, Lin SJ, Chen PW, Luo WY, Yeh TH, Wang HW, Chen CJ, Tsai CH (2009) EBV Zta protein induces the expression of interleukin-13, promoting the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Blood 114(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-12-193375
Arbach H, Viglasky V, Lefeu F, Guinebretière JM, Ramirez V, Bride N et al (2006) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome and expression in breast cancer tissue: effect of EBV infection of breast cancer cells on resistance to paclitaxel (Taxol). J Virol 80(2):845–853. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.80.2.845-853.2006
Guo Q, Qian L, Guo L, Shi M, Chen C, Lv X et al (2010) Transactivators Zta and Rta of Epstein-Barr virus promote G0/G1 to S transition in Raji cells: a novel relationship between lytic virus and cell cycle. Mol Immunol 47(9):1783–1792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2010.02.017
Eichelberg MR, Welch R, Guidry JT, Ali A, Ohashi M, Makielski KR et al (2019) Epstein-Barr virus infection promotes epithelial cell growth by attenuating differentiation-dependent exit from the cell cycle. mBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01332-19
Lin JH, Tsai CH, Chu JS, Chen JY, Takada K, Shew JY (2007) Dysregulation of HER2/HER3 signaling axis in Epstein-Barr virus-infected breast carcinoma cells. J Virol 81(11):5705–5713. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00076-07
Leong MML, Lung ML (2021) The impact of Epstein–Barr virus infection on epigenetic regulation of host cell gene expression in epithelial and lymphocytic malignancies. Front Oncol 11:629780. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.629780
Heather J, Flower K, Isaac S, Sinclair AJ (2009) The Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle activator Zta interacts with methylated ZRE in the promoter of host target gene egr1. J Gen Virol 90(Pt 6):1450–1454. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.007922-0
Cayrol C, Flemington EK (1995) Identification of cellular target genes of the Epstein-Barr virus transactivator Zta: activation of transforming growth factor beta igh3 (TGF-beta igh3) and TGF-beta 1. J Virol 69(7):4206–4212. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.69.7.4206-4212.1995
Liu P, Speck SH (2003) Synergistic autoactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early BRLF1 promoter by Rta and Zta. Virology 310(2):199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00145-4
Bonnet M, Guinebretiere JM, Kremmer E, Grunewald V, Benhamou E, Contesso G, Joab I (1999) Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in invasive breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 91(16):1376–1381. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/91.16.1376
Wu Y, Wang D, Wei F, Xiong F, Zhang S, Gong Z et al (2020) EBV-miR-BART12 accelerates migration and invasion in EBV-associated cancer cells by targeting tubulin polymerization-promoting protein 1. Faseb j 34(12):16205–16223. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001508R
Bridgewater HE, Date KL, O’Neil JD, Hu C, Arrand JR, Dawson CW, Young LS (2020) The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 protein activates the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) signalling pathway to promote carcinoma cell migration. Pathogens. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070594
Funding
This work was supported by the Jinan Clinical Medical Science and Technology Innovation Plan (Grant numbers 202019071 and 202019172) and the Shandong Province Medical and Health Technology Development Plan (grant number 202106010191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BY and QG contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by all authors. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HZ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Graciela Andrei.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Zhao, H., Zhang, W. et al. Epstein–Barr virus immediate-early protein Zta mediates the proliferation and migration of HER2-overexpressing cancer cells. Arch Virol 168, 150 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05774-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05774-x