Abstract
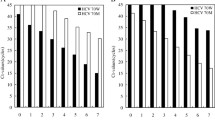
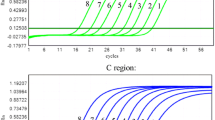
Current antiviral therapies against hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections, such as treatment with nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs) and interferon alpha, can significantly lower HBV DNA titers, eventually to undetectable levels. However, it is still difficult to completely eliminate the stable template of HBV, the covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), and this contributes to viral rebound when treatment is discontinued. HBV pregenomic RNA (pgRNA), which was recently found to be present in the enveloped mature HBV viral particle in blood, is tentatively regarded, with still accumulating clinical evidence, as a novel bona fide virological marker reflecting the amount and status of cccDNA when serum HBV DNA becomes undetectable. HBV pgRNA and DNA share almost identical sequences, and it is therefore difficult to differentiate pgRNA from viral DNA using normal PCR methods. To exclude interference from viral DNA, methods for measuring pgRNA usually require a selective DNA degradation step, which is complicated and time-consuming and also compromises the accuracy of detection. In this study, we developed a simplified quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay with improved accuracy achieved by probing the polyA tail of pgRNA. Using clinical serum samples, we observed that not all patients share the same 3′ sequence, suggesting slight differences between HBV strains in the way they end transcription. We then designed and evaluated a universal primer and probe set for distinguishing HBV pgRNA from HBV DNA. Our results demonstrated that a one-step qRT-PCR assay could selectively amplify HBV pgRNA from a mixture of HBV RNA and DNA, which is valuable for clinical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai L, Zhang X, Kozlowski M, Li W, Wu M, Liu J, Chen L, Zhang J, Huang Y, Yuan Z (2018) Extracellular hepatitis B virus RNAs are heterogeneous in length and circulate as capsid-antibody complexes in addition to virions in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Virol 92:e00798-00718
Block TM, Gish R, Guo H, Mehta A, Cuconati A, Thomas London W, Guo JT (2013) Chronic hepatitis B: what should be the goal for new therapies? Antiviral Res 98:27–34
Butler EK, Gersch J, McNamara A, Luk KC, Holzmayer V, de Medina M, Schiff E, Kuhns M, Cloherty GA (2018) Hepatitis B virus serum DNA and RNA levels in nucleos(t)ide analog-treated or untreated patients during chronic and acute infection. Hepatology 68:2106–2117
Cao Z, Liu Y, Ma L, Lu J, Jin Y, Ren S, He Z, Shen C, Chen X (2017) A potent hepatitis B surface antigen response in subjects with inactive hepatitis B surface antigen carrier treated with pegylated-interferon alpha. Hepatology 66:1058–1066
Chen CL, Yang JY, Lin SF, Sun CA, Bai CH, You SL, Chen CJ, Kao JH, Chen PJ, Chen DS (2015) Slow decline of hepatitis B burden in general population: Results from a population-based survey and longitudinal follow-up study in Taiwan. J Hepatol 63:354–363
Fan H, Lin L, Jia S, Xie M, Luo C, Tan X, Ying R, Guan Y, Li F (2019) Interferon alpha treatment leads to a high rate of hepatitis B surface antigen seroconversion in Chinese children with chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.13165 (in press)
Gholami M, Ravanshad M, Baesi K, Samiee SM, Hosseini Rozbahani N, Mohraz M (2018) Preparation and Evaluation of Ribonuclease-Resistant Viral HIV RNA Standards Based on Armored RNA Technology. Iranian biomedical journal 22:394–400
Giersch K, Allweiss L, Volz T, Dandri M, Lutgehetmann M (2017) Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J Hepatol 66:460–462
Hayer J, Jadeau F, Deleage G, Kay A, Zoulim F, Combet C (2013) HBVdb: a knowledge database for Hepatitis B Virus. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D566–570
Hu J, Liu K (2017) Complete and incomplete hepatitis B virus particles: formation, function, and application. Viruses 9:E56
Jansen L, Kootstra NA, van Dort KA, Takkenberg RB, Reesink HW, Zaaijer HL (2016) Hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA is present in virions in plasma and is associated with a response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a and nucleos(t)ide analogues. J Infect Dis 213:224–232
Jones SA, Hu J (2013) Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase: diverse functions as classical and emerging targets for antiviral intervention. Emerg Microbes Infect 2:e56
Liang X, Gao Z, Xie Q, Zhang J, Sheng J, Cheng J, Chen C, Mao Q, Zhao W, Ren H, Tan D, Niu J, Chen S, Pan C, Tang H, Wang H, Mao Y, Jia J, Ning Q, Xu M, Wu S, Li J, Zhang X, Zhang W, Xiong C, Hou J (2019) Long-term efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B: 5-year results. Hep Intl 13:260–269
Liu S, Zhou B, Valdes JD, Sun J, Guo H (2018) Serum HBV RNA: a new potential biomarker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 69:1816–1827
Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, Gane E, de Man RA, Krastev Z, Germanidis G, Lee SS, Flisiak R, Kaita K, Manns M, Kotzev I, Tchernev K, Buggisch P, Weilert F, Kurdas OO, Shiffman ML, Trinh H, Washington MK, Sorbel J, Anderson J, Snow-Lampart A, Mondou E, Quinn J, Rousseau F (2008) Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 359:2442–2455
Marcellin P, Ahn SH, Ma X, Caruntu FA, Tak WY, Elkashab M, Chuang WL, Lim SG, Tabak F, Mehta R, Petersen J, Foster GR, Lou L, Martins EB, Dinh P, Lin L, Corsa A, Charuworn P, Subramanian GM, Reiser H, Reesink HW, Fung S, Strasser SI, Trinh H, Buti M, Gaeta GB, Hui AJ, Papatheodoridis G, Flisiak R, Chan HL, Study I (2016) Combination of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and peginterferon alpha-2a increases loss of hepatitis B surface antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 150(134–144):e110
Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST (2013) Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology 57:1333–1342
Ni YH, Chang MH, Wu JF, Hsu HY, Chen HL, Chen DS (2012) Minimization of hepatitis B infection by a 25-year universal vaccination program. J Hepatol 57:730–735
Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST (2012) Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine 30:2212–2219
Papatheodoridis GV, Manolakopoulos S, Su TH, Siakavellas S, Liu CJ, Kourikou A, Yang HC, Kao JH (2018) Significance of definitions of relapse after discontinuation of oral antivirals in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 68:415–424
Revill PA, Chisari FV, Block JM, Dandri M, Gehring AJ, Guo H, Hu J, Kramvis A, Lampertico P, Janssen HLA, Levrero M, Li W, Liang TJ, Lim SG, Lu F, Penicaud MC, Tavis JE, Thimme R, Members of the ICEHBVWG, Chairs I-HSG, Advisors I-HS, Zoulim F (2019) A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B. LKancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:545–558
Seto WK, Lo YR, Pawlotsky JM, Yuen MF (2018) Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 392:2313–2324
Tong S, Revill P (2016) Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J Hepatol 64:S4–S16
Trépo C, Chan HLY, Lok A (2014) Hepatitis B virus infection. The Lancet 384:2053–2063
Tu T, Budzinska MA, Shackel NA, Urban S (2017) HBV DNA integration: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Viruses 9:E75
van Bommel F, Bartens A, Mysickova A, Hofmann J, Kruger DH, Berg T, Edelmann A (2015) Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels as an early predictor of hepatitis B envelope antigen seroconversion during treatment with polymerase inhibitors. Hepatology 61:66–76
Wang FS, Fan JG, Zhang Z, Gao B, Wang HY (2014) The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology 60:2099–2108
Wang J, Shen T, Huang X, Kumar GR, Chen X, Zeng Z, Zhang R, Chen R, Li T, Zhang T, Yuan Q, Li PC, Huang Q, Colonno R, Jia J, Hou J, McCrae MA, Gao Z, Ren H, Xia N, Zhuang H, Lu F (2016) Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J Hepatol 65:700–710
Wang J, Yu Y, Li G, Shen C, Li J, Chen S, Zhang X, Zhu M, Zheng J, Song Z, Wu J, Shao L, Meng Z, Wang X, Huang Y, Zhang J, Qiu C, Zhang W (2018) Natural history of serum HBV-RNA in chronic HBV infection. J Viral Hepat 25:1038–1047
Wei Y, Yang C, Wei B, Huang J, Wang L, Meng S, Zhang R, Li J (2008) RNase-resistant virus-like particles containing long chimeric RNA sequences produced by two-plasmid coexpression system. J Clin Microbiol 46:1734–1740
Wirth S, Zhang H, Hardikar W, Schwarz KB, Sokal E, Yang W, Fan H, Morozov V, Mao Q, Deng H, Huang Y, Yang L, Frey N, Nasmyth-Miller C, Pavlovic V, Wat C (2018) Efficacy and safety of peginterferon Alfa-2a (40KD) in children with chronic hepatitis B: the PEG-B-ACTIVE Study. Hepatology 68:1681–1694
Zhang W, Xie Q, Ning Q, Dou X, Chen X, Jia J, Xie Y, Ren H (2017) The role of peginterferon in nucleos(t)ide-analogue-treated chronic hepatitis B patients: a review of published literature. J Viral Hepat 24:618–623
Zhang X, Lu W, Zheng Y, Wang W, Bai L, Chen L, Feng Y, Zhang Z, Yuan Z (2016) In situ analysis of intrahepatic virological events in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Investig 126:1079–1092
Acknowledgments
We thank all of the study participants for their donation of blood samples. This work was supported by the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program (No. 201707010348), by a National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant (No. 81670536 and 81770593) and by the National Grand Program on Key Infectious Disease Control (2017ZX10202203-004-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ming Gao and Chengqian Feng performed detection, conditional optimization, and data analysis. Ruosu Ying, Ying Zhu and Yujuan Guan managed patient sample collection from the clinic. Yuan Nie and Xizi Deng helped generate the standard. Fengyu Hu and Feng Li conceived, designed, and supervised the study. Xiaoping Tang contributed critical intelligence to review the study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Zhongjie Shi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Feng, C., Ying, R. et al. A novel one-step quantitative reverse transcription PCR assay for selective amplification of hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA from a mixture of HBV DNA and RNA in serum. Arch Virol 164, 2683–2690 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04372-0