Abstract
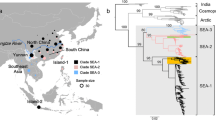
Rabies is a fatal disease caused by infection with rabies virus (RABV), and human rabies is still a critical public-health concern in China. Although there have been some phylogenetic studies about RABV transmission patterns, with the accumulation of more rabies sequences in recent years, there is an urgent need to update and clarify the spatial and temporal patterns of RABV circulating in China on a national scale. In this study, we collected all available RABV nucleoprotein gene sequences from China and its neighboring countries and performed comparative analysis. We identified six significant subclades of RABV circulating in China and found that each of them has a specific geographical distribution, reflecting possible physical barriers to gene flow. The phylogeographic analysis revealed minimal viral movement among different geographical locations. An analysis using Bayesian coalescent methods indicated that the current RABV strains in China may come from a common ancestor about 400 years ago, and currently, China is amid the second event of increasing RABV population since the 1950s, but the population has decreased gradually. We did not detect any evidence of recombination in the sequence dataset, nor did we find any evidence for positive selection during the expansion of RABV. Overall, geographic location and neutral genetic drift may be the main factors in shaping the phylogeography of RABV transmission in China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourhy H, Reynes JM, Dunham EJ, Dacheux L, Larrous F, Huong VTO, Xu GL, Yan JX, Miranda MEG, Holmes EC (2008) The origin and phylogeography of dog rabies virus. J Gen Virol 89:2673–2681
Hampson K, Coudeville L, Lembo T, Sambo M, Kieffer A, Attlan M, Barrat J, Blanton JD, Briggs DJ, Cleaveland S, Costa P, Freuling CM, Hiby E, Knopf L, Leanes F, Meslin FX, Metlin A, Miranda ME, Muller T, Nel LH, Recuenco S, Rupprecht CE, Schumacher C, Taylor L, Vigilato MAN, Zinsstag J, Dushoff J, Par GARC (2015) Estimating the global burden of endemic canine rabies. Plos Neglect Trop Dis 9(4):3709
Yin WW, Dong J, Tu CC, Edwards J, Guo FS, Zhou H, Yu HJ, Vong S, Board RTA (2013) Challenges and needs for China to eliminate rabies. Infect Dis Poverty 2:23
Abbas SS, Kakkar M (2015) Rabies control in India: a need to close the gap between research and policy. B World Health Organ 93(2):131–132
Knobel DL, Cleaveland S, Coleman PG, Fevre EM, Meltzer MI, Miranda MEG, Shaw A, Zinsstag J, Meslin FX (2005) Re-evaluating the burden of rabies in Africa and Asia. B World Health Organ 83(5):360–368
Troupin C, Dacheux L, Tanguy M, Sabeta C, Blanc H, Bouchier C, Vignuzzi M, Duchene S, Holmes EC, Bourhy H (2016) Large-scale phylogenomic analysis reveals the complex evolutionary history of rabies virus in multiple carnivore hosts. PLoS Pathog 12(12):e1006041
Zhang Y, Vrancken B, Feng Y, Dellicour S, Yang Q, Yang W, Zhang Y, Dong L, Pybus OG, Zhang H, Tian H (2017) Cross-border spread, lineage displacement and evolutionary rate estimation of rabies virus in Yunnan Province, China. Virol J 14(1):102
Zhang JM, Zhang ZS, Deng YQ, Wu SL, Wang W, Yan YS (2017) Incidence of human rabies and characterization of rabies virus nucleoprotein gene in dogs in Fujian Province, Southeast China, 2002–2012. BMC Infect Dis 17:599
Liu Y, Zhang HP, Zhang SF, Wang JX, Zhou HN, Zhang F, Wang YM, Ma L, Li N, Hu RL (2016) Rabies outbreaks and vaccination in domestic camels and cattle in Northwest China. Plos Neglect Trop Dis 10(9):e0004890
Feng Y, Shi YY, Yu MY, Xu WD, Gong WJ, Tu ZZ, Ding LX, He B, Guo HC, Tu CC (2016) Livestock rabies outbreaks in Shanxi province, China. Arch Virol 161(10):2851–2854
Yu JN, Li H, Tang Q, Rayner S, Han N, Guo ZY, Liu HZ, Adams J, Fang W, Tao XY, Wang SM, Liang GD (2012) The spatial and temporal dynamics of rabies in China. Plos Neglect Trop Dis 6(5):1640
Yao HW, Yang Y, Liu K, Li XL, Zuo SQ, Sun RX, Fang LQ, Cao WC (2015) The spatiotemporal expansion of human rabies and its probable explanation in mainland China, 2004–2013. Plos Neglect Trop Dis 9(2):e0003502
Guo ZY, Tao XY, Yin CP, Han N, Yu JN, Li H, Liu HZ, Fang W, Adams J, Wang J, Liang GD, Tang Q, Rayner S (2013) National borders effectively halt the spread of rabies: the current rabies epidemic in China is dislocated from cases in neighbouring countries. Plos Neglect Trop Dis 7(1):e2039
Wang LH, Tang Q, Liang GD (2014) Rabies and rabies virus in wildlife in mainland China, 1990–2013. Int J Infect Dis 25:122–129
Meng SL, Sun Y, Wu XF, Tang JR, Xu GL, Lei YL, Wu J, Yan JX, Yang XM, Rupprecht CE (2011) Evolutionary dynamics of rabies viruses highlights the importance of China rabies transmission in Asia. Virology 410(2):403–409
Finke S, Conzelmann KK (2005) Replication strategies of rabies virus. Virus Res 111(2):120–131
Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M, Khoosal A, Muhire B (2015) RDP4: detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol 1(1):vev003
Li WZ, Godzik A (2006) Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22(13):1658–1659
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Rambaut A, Lam TT, Carvalho LM, Pybus OG (2016) Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol 2(1):vew007
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32(1):268–274
Xia XH (2017) DAMBE6: new tools for microbial genomics, phylogenetics, and molecular evolution. J Hered 108(4):431–437
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14(6):587
Minh BQ, Nguyen MAT, von Haeseler A (2013) Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol Biol Evol 30(5):1188–1195
Yu GC, Smith DK, Zhu HC, Guan Y, Lam TTY (2017) GGTREE: an R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol Evol 8(1):28–36
Suchard MA, Lemey P, Baele G, Ayres DL, Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2018) Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol 4(1):vey016
Baele G, Lemey P, Bedford T, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Alekseyenko AV (2012) Improving the accuracy of demographic and molecular clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty. Mol Biol Evol 29(9):2157–2167
Baele G, Li WL, Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Lemey P (2013) Accurate model selection of relaxed molecular clocks in bayesian phylogenetics. Mol Biol Evol 30(2):239–243
Bielejec F, Baele G, Vrancken B, Suchard MA, Rambaut A, Lemey P (2016) Sprea D3: interactive visualization of spatiotemporal history and trait evolutionary processes. Mol Biol Evol 33(8):2167–2169
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3(5):418–426
Weaver S, Shank SD, Spielman SJ, Li M, Muse SV, Pond SLK (2018) Datamonkey 2.0: a modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol Biol Evol 35(3):773–777
Pond SLK, Frost SDW (2005) Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol Biol Evol 22(5):1208–1222
Murrell B, Wertheim JO, Moola S, Weighill T, Scheffler K, Pond SLK (2012) Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. Plos Genet 8(7):e1002764
Murrell B, Moola S, Mabona A, Weighill T, Sheward D, Pond SLK, Scheffler K (2013) FUBAR: a fast, unconstrained bayesian approximation for inferring selection. Mol Biol Evol 30(5):1196–1205
Tsai KJ, Hsu WC, Chuang WC, Chang JC, Tu YC, Tsai HJ, Liu HF, Wang FI, Lee SH (2016) Emergence of a sylvatic enzootic formosan ferret badger-associated rabies in Taiwan and the geographical separation of two phylogenetic groups of rabies viruses. Vet Microbiol 182:28–34
Zhou H, Vong S, Liu K, Li Y, Mu D, Wang LP, Yin WW, Yu HJ (2016) Human Rabies in China, 1960–2014: a descriptive epidemiological study. Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases 10(8):e0004874
Perez-Losada M, Arenas M, Galan JC, Palero F, Gonzalez-Candelas F (2015) Recombination in viruses: mechanisms, methods of study, and evolutionary consequences. Infect Genet Evol 30:296–307
Baghi HB, Bazmani A, Aghazadeh M (2016) The fight against rabies: the Middle East needs to step up its game. Lancet 388(10054):1880
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Diego G. Diel.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Wu, X., Bao, J. et al. Phylodynamic and transmission pattern of rabies virus in China and its neighboring countries. Arch Virol 164, 2119–2129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04297-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04297-8