Abstract
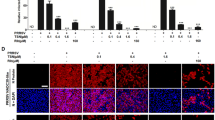
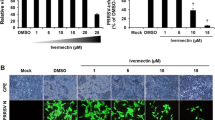
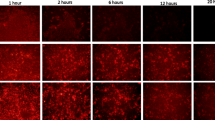
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) continues to cause substantial economic losses to the pig industry worldwide. Current vaccination strategies and antiviral drugs against PRRSV are still inadequate. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new antiviral strategies to control PRRSV. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) Activated Caspase Oligomerizer (DRACO) is a synthetic construct consisting of a dsRNA detection domain, an apoptosis induction domain, and a transduction tag. It has been shown to have broad-spectrum antiviral activity, but there have been no reports regarding its effect on PRRSV. Here, we demonstrate that DRACO exhibits robust antiviral activity against PRRSV infection by suppressing virus RNA and protein synthesis in both Marc-145 cells and porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs). In addition, DRACO still exhibited strong anti-PRRSV activity when viral replication was enhanced by knockdown of interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3) in Marc-145 cells. Furthermore, in PAMs, DRACO was capable of inducing IL-6 expression and reducing Hsp70 expression, which might contribute to the inhibition of PRRSV infection. Collectively, our results imply that DRACO holds promise as a novel anti-PRRSV therapeutic drug.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neumann EJ, Kliebenstein JB, Johnson CD, Mabry JW, Bush EJ, Seitzinger AH, Green AL, Zimmerman JJ (2005) Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States. J Am Vet Med A 227(3):385–392. doi:10.2460/javma.2005.227.385
Murtaugh MP, Genzow M (2011) Immunological solutions for treatment and prevention of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS). Vaccine 29(46):8192–8204. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.09.013
Bosch AA, Biesbroek G, Trzcinski K, Sanders EA, Bogaert D (2013) Viral and bacterial interactions in the upper respiratory tract. Plos Pathog 9(1):e1003057. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003057
Holtkamp D, Kliebenstein J (2011) Pork Checkoff study: PRRS costs industry $664 million annually. J Swine Health Prod 19(6):349
Music N, Gagnon CA (2010) The role of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus structural and non-structural proteins in virus pathogenesis. Anim Health Res Rev 11(2):135–163. doi:10.1017/S1466252310000034
Yun SI, Lee YM (2013) Overview: replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Microbiol 51(6):711–723. doi:10.1007/s12275-013-3431-z
Tian K, Yu X, Zhao T, Feng Y, Cao Z, Wang C, Hu Y, Chen X, Hu D, Tian X, Liu D, Zhang S, Deng X, Ding Y, Yang L, Zhang Y, Xiao H, Qiao M, Wang B, Hou L, Wang X, Yang X, Kang L, Sun M, Jin P, Wang S, Kitamura Y, Yan J, Gao GF (2007) Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PloS One 2(6):e526. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000526
Murtaugh MP, Xiao Z, Zuckermann F (2002) Immunological responses of swine to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Viral Immunol 15(4):533–547. doi:10.1089/088282402320914485
Labarque GG, Nauwynck HJ, Van Reeth K, Pensaert MB (2000) Effect of cellular changes and onset of humoral immunity on the replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the lungs of pigs. J Gen Virol 81(Pt 5):1327–1334
Xiao Z, Batista L, Dee S, Halbur P, Murtaugh MP (2004) The level of virus-specific T-cell and macrophage recruitment in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection in pigs is independent of virus load. J Virol 78(11):5923–5933. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.11.5923-5933.2004
Rider TH, Zook CE, Boettcher TL, Wick ST, Pancoast JS, Zusman BD (2011) Broad-spectrum antiviral therapeutics. PloS One 6(7):e22572. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022572
Samuel CE (2004) Knockdown by RNAi-proceed with caution. Nat Biotechnol 22(3):280–282. doi:10.1038/nbt0304-280
Qiao SL, Feng LL, Bao DK, Guo JQ, Wan B, Xiao ZJ, Yang SZ, Zhang GP (2011) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and bacterial endotoxin act in synergy to amplify the inflammatory response of infected macrophages. Vet Microbiol 149(1–2):213–220. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.11.006
Sadler AJ, Williams BRG (2007) Structure and function of the protein kinase R. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 316:253–292
Ho A, Schwarze SR, Mermelstein SJ, Waksman G, Dowdy SF (2001) Synthetic protein transduction domains: Enhanced transduction potential in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 61(2):474–477
Delogu I, Pastorino B, Baronti C, Nougairede A, Bonnet E, de Lamballerie X (2011) In vitro antiviral activity of arbidol against Chikungunya virus and characteristics of a selected resistant mutant. Antivir Res 90(3):99–107. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.03.182
Costers S, Lefebvre DJ, Delputte PL, Nauwynck HJ (2008) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus modulates apoptosis during replication in alveolar macrophages. Arch Virol 153(8):1453–1465. doi:10.1007/s00705-008-0135-5
Fensterl V, Sen GC (2011) The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family. J Interf Cytokine Res 31(1):71–78. doi:10.1089/jir.2010.0101
Miettinen JJ, Matikainen S, Nyman TA (2012) Global secretome characterization of herpes simplex virus 1-infected human primary macrophages. J Virol 86(23):12770–12778. doi:10.1128/JVI.01545-12
Meulenberg JJ (2000) PRRSV, the virus. Vet Res 31(1):11–21. doi:10.1051/vetres:2000103
Suarez P (2000) Ultrastructural pathogenesis of the PRRS virus. Vet Res 31(1):47–55. doi:10.1051/vetres:2000056
Jourdan SS, Osorio FA, Hiscox JA (2012) Biophysical characterisation of the nucleocapsid protein from a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419(2):137–141. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.126
Dokland T (2010) The structural biology of PRRSV. Virus Res 154(1–2):86–97. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.029
Zhang L, Liu J, Bai J, Du Y, Wang X, Liu X, Jiang P (2013) Poly(I:C) inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication in MARC-145 cells via activation of IFIT3. Antivir Res 99(3):197–206. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.004
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Agriculture Research System (CASR-36) and China Spark Program (2011GA781001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. Guo and L. Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Chen, L., Mo, D. et al. DRACO inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication in vitro . Arch Virol 160, 1239–1247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2392-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2392-4