Abstract
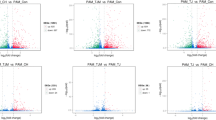
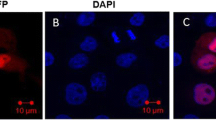
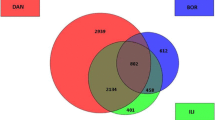
Since the highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (HP-PRRSV) variant emerged in 2006, it has caused death in more than 20 million pigs in China and other Southeast Asian countries, making it the most destructive swine pathogen currently in existence. To characterize the cellular responses to HP-PRRSV infection, the gene expression profile of porcine alveolar macrophage (PAM) cells, the primary target cells of PRRSV, was analyzed in HP-PRRSV-infected and uninfected PAMs by suppression subtractive hybridization. After confirmation by Southern blot, genes that were differentially expressed in the HP-PRRSV-infected and uninfected PAMs were sequenced and annotated. Genes that were upregulated mainly in HP-PRRSV-infected PAM cells were related to immunity and cell signaling. Among the differentially expressed genes, Mx1 and HSP70 protein expression was confirmed by western blotting, and IL-8 expression was confirmed by ELISA. In PAM cells isolated from HP-PRRSV-infected piglets, the differential expression of 21 genes, including IL-16, TGF-beta type 1 receptor, epidermal growth factor, MHC-I SLA, Toll-like receptor, hepatoma-derived growth factor, FTH1, and MHC-II SLA-DRB1, was confirmed by real-time PCR. To our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate differential gene expression between HP-PRRSV-infected and uninfected PAMs in vivo. The results indicate that HP-PRRSV infection excessively stimulates genes involved in the innate immune response, including proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An TQ, Tian ZJ, Leng CL, Peng JM, Tong GZ (2011) Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, Asia. Emerg Infect Dis 17(9):1782–1784
Bahn SC, Bae MS, Park YB, Oh SI, Jeung JU, Bae JM, Chung YS, Shin JS (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel low temperature-induced gene, blti2, from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:134–137
Cavanagh D (1997) Nidovirales: a new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Arch Virol 142:629–633
Cheung CY, Poon LL, Lau AS, Luk W, Lau YL, Shortridge KF, Gordon S, Guan Y, Peiris JS (2002) Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease? Lancet 360:1831–1837
Cilloniz C, Pantin-Jackwood MJ, Ni C, Carter VS, Korth MJ, Swayne DE, Tumpey TM, Katze MG (2012) Molecular signatures associated with Mx1-mediated resistance to highly pathogenic influenza virus infection: mechanisms of survival. J Virol 86(5):2437–2446
Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E, Kuchinsky A, Landys N, Workman C, Christmas R, Avila-Campilo I, Creech M, Gross B, Hanspers K, Isserlin R, Kelley R, Killcoyne S, Lotia S, Maere S, Morris J, Ono K, Pavlovic V, Pico AR, Vailaya A, Wang PL, Adler A, Conklin BR, Hood L, Kuiper M, Sander C, Schmulevich I, Schwikowski B, Warner GJ, Ideker T, Bader GD (2007) Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc 2:2366–2382
Dash P, Barnett PV, Denyer MS, Jackson T, Stirling CM, Hawes PC, Simpson JL, Monaghan P, Takamatsu HH (2010) Foot-and-mouth disease virus replicates only transiently in well differentiated porcine nasal epithelial cells. J Virol 84(18):9149–9160
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA (2003) DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol 4:P3
Duan X, Nauwynck H, Pensaert M (1997) Effects of origin and state of differentiation and activation of monocytes/macrophages on their susceptibility to PRRSV. Arch Virol 142:2483–2497
Genini S, Delputte PL, Malinverni R, Cecere M, Stella A, Nauwynck HJ, Giuffra E (2008) Genome-wide transcriptional response of primary alveolar macrophages following infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Gen Virol 89:2550–2564
Gracey AY, Troll JV, Somero GN (2001) Hypoxia-induced gene expression profiling in the euryoxic fish Gillichthys mirabilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(4):1993–1998
Guo BQ, Chen ZS, Liu WX, Cui YZ (1996) Isolation and identification of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus from aborted fetuses suspected of PRRS. Chin J Infect Diseases Anim Poult 18:1–5 (in Chinese)
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37(1):1–13
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57
Kash JC, Tumpey TM, Proll SC, Carter V, Perwitasari O, Thomas MJ, Basler CF, Palese P, Taubenberger JK, García-Sastre A, Swayne DE, Katze MG (2006) Genomic analysis of increased host immune and cell death responses induced by 1918 influenza virus. Nature 443(7111):578–581
Keffaber KK (1989) Reproductive failure of unknown etiology. Am Assoc Swine Pract Newslett 1:1–10
Kobasa D, Jones SM, Shinya K, Kash JC, Copps J (2007) Aberrant innate immune response in lethal infection of macaques with the 1918 influenza virus. Nature 445(7125):319–323
Lavoie JP, Lefebvre-Lavoie J, Leclere M, Lavoie-Lamoureux A, Chamberland A, Laprise C, Lussier J (2012) Profiling of differentially expressed genes using suppression subtractive hybridization in an equine model of chronic asthma. PLoS ONE 7(1):e29440
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data us-ing real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Loo YM, Gale M Jr (2007) Fatal immunity and the 1918 virus. Nature 445(7125):267–268
Lunney JK, Fritz ER, Reecy JM, Kuhar D, Prucnal E, Molina R, Christopher-Hennings J, Zimmerman J, Rowland RR (2010) Interleukin-8, interleukin-1beta, and interferon-gamma levels are linked to PRRS virus clearance. Viral Immunol 23(2):127–134
Meulenberg JJ, Hulst MM, de Meijer EJ, Moonen PL, den Besten A, de Kluyver EP, Wensvoort G, Moormann RJ (1993) Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology 192(1):62–72
Meulenberg JJ, Hulst MM, de Meijer EJ, Moonen PL, den Besten A, de Kluyver EP, Wensvoort G, Moormann RJ (1994) Lelystad virus belongs to a new virus family, comprising lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus, equine arteritis virus, and simian hemorrhagic fever virus. Arch Virol 9:441–448
Mikami Y, Somei M, Takagi M (2009) A new synthetic compound, SST-VEDI-1, inhibits osteoblast differentiation with a down-regulation of the Osterix expression. J Biochem 145(2):239–247
Miller LC, Neill JD, Harhay GP, Lager KM, Laegreid WW, Kehrli ME Jr (2010) In-depth global analysis of transcript abundance levels in porcine alveolar macrophages following infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Adv Virol 864181:2010. doi:10.1155//864181
Monteiro RA, Balsanelli E, Tuleski T, Faoro H, Cruz LM, Wassem R, de Baura VA, Tadra-Sfeir MZ, Weiss V, DaRocha WD, Muller-Santos M, Chubatsu LS, Huergo LF, Pedrosa FO, de Souza EM (2012) Genomic comparison of the endophyte Herbaspirillum seropedicae SmR1 and the phytopathogen Herbaspirillum rubrisubalbicans M1 by suppressive subtractive hybridization and partial genome sequencing. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80(2):441–451
Nelsen CJ, Murtaugh MP, Faaberg KS (1999) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus comparison: divergent evolution on two continents. J Virol 73:270–280
Opriessnig T, Patel D, Wang R, Halbur PG, Meng XJ, Stein DA, Zhang YJ (2011) Inhibition of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection in piglets by a peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomer. Antiviral Res 91(1):36–42
Palm M, Garigliany MM, Cornet F, Desmecht D (2010) Interferon-induced Sus scrofa Mx1 blocks endocytic traffic of incoming influenza A virus particles. Vet Res 41(3):29
Pavlovic J, Haller O, Staeheli P (1992) Human and mouse Mx proteins inhibit different steps of the influenza virus multiplication cycle. J Virol 66(4):2564–2569
Perrone LA, Plowden JK, García-Sastre A, Katz JM, Tumpey TM (2008) H5N1 and 1918 pandemic influenza virus infection results in early and excessive infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils in the lungs of mice. PLoS Pathog 4(8):e1000115
Snijder EJ, Meulenberg JJ (1998) The molecular biology of arteriviruses. J Gen Virol 79(Pt 5):961–979
Snijder EJ, van Tol H, Pedersen KW, Raamsman MJ, de Vries AA (1999) Identification of a novel structural protein of arteriviruses. J Virol 73(8):6335–6345
Tian K, Yu X, Zhao T, Feng Y, Cao Z, Wang C, Hu Y, Chen X, Hu D, Tian X, Liu D, Zhang S, Deng X, Ding Y, Yang L, Zhang Y, Xiao H, Qiao M, Wang B, Hou L, Wang X, Yang X, Kang L, Sun M, Jin P, Wang S, Kitamura Y, Yan J, Gao GF (2007) Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS ONE 2:e526
Tong GZ, Zhou YJ, Hao XF, Tian ZJ, An TQ, Qiu HJ (2007) Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, China. Emerg Infect Dis 13(9):1434–1436
Voicu IL, Silim A, Morin M, Elazhary MA (1994) Interaction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus with swine monocytes. Vet Rec 134:422–423
Wensvoort G, Wensvoort G, Terpstra C, Pol JM, ter Laak EA, Bloemraad M, de Kluyver EP, Kragten C, van Buiten L, den Besten A, Wagenaar F (1991) Mystery swine disease in the Netherlands: the isolation of Lelystad virus. Vet Q 13:121–130
Wu WH, Fang Y, Farwell R, Steffen-Bien M, Rowland RR, Christopher-Hennings J, Nelson EA (2001) A 10-kDa structural protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus encoded by ORF2b. Virology 287(1):183–191
Xiao S, Jia J, Mo D, Wang Q, Qin L, He Z, Zhao X, Huang Y, Li A, Yu J, Niu Y, Liu X, Chen Y (2010) Understanding PRRSV infection in porcine lung based on genome-wide transcriptome response identified by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 5(6):e11377
Xiao S, Mo D, Wang Q, Jia J, Qin L, Yu X, Niu Y, Zhao X, Liu X, Chen Y (2010) Aberrant host immune response induced by highly virulent PRRSV identified by digital gene expression tag profiling. BMC Genomics 11:544
Zhou P, Zhai S, Zhou X, Lin P, Jiang T, Hu X, Jiang Y, Wu B, Zhang Q, Xu X, Li JP, Liu B (2011) Molecular characterization of transcriptome-wide interactions between highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and porcine alveolar macrophages in vivo. Int J Biol Sci 7(7):947–959
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30901080, 31270045) and the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 20090451026, 201003467). The authors thank Dr. Qing-Men Meng and Fu-Shan Tan for technical support with the Southern blotting experiments, and Sheng-Zhi Zhang for the real-time RT-PCR analyses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., An, TQ., Tian, ZJ. et al. The gene expression profile of porcine alveolar macrophages infected with a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus indicates overstimulation of the innate immune system by the virus. Arch Virol 160, 649–662 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2309-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2309-7