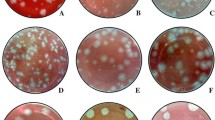
Abstract
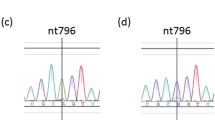
A previous investigation showed that MX10 virus, recently isolated in China, belongs to the Oriental-Australian (O/A) genotype of Sindbis virus (SINV) (Wang Jinglin, 2011, ATMH). Similar to the MRE16 isolate, the prototype O/A genotype of SINV, two derivate viruses with obviously different plaque morphologies were derived from MX10 virus, which were accordingly denoted as MX10-LP and MX10-SP. MX10-LP virus exhibited higher neurovirulence in neonatal mice than MX10-SP virus. Analysis of the complete genome revealed seven nucleotide differences between MX10-LP and MX10-SP. Compared with MRE16 virus, MRE16SP virus has a deletion of 30 aa in the E2 gene (200-229), which has been shown to be the molecular basis for the different plaque morphology. However, the MX10-SP virus did not have the 30-amino-acid deletion in the E2 gene. These results demonstrate that the molecular basis for the different plaque morphology of MX10 virus, the first strain of the O/A genotype of SINV isolated from China, is different from that of the prototype MRE16 virus.


Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Buckley A, Dawson A, Moss SR, Hinsley SA, Bellamy PE, Gould EA (2003) Serological evidence of West Nile virus, Usutu virus and Sindbis virus infection of birds in the UK. J Gen Virol 84:2807–2817
Byrnes AP, Griffin DE (1998) Binding of Sindbis virus to cell surface heparan sulfate. J Virol 72:7349–7356
Davis NL, Pence DF, Meyer WJ, Schmaljohn AL, Johnston RE (1987) Alternative forms of a strain-specific neutralizing antigenic site on the Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein. Virology 161:101–108
Lastarza MW, Grakoui A, Rice CM (1994) Deletion and duplication mutations in the C-terminal nonconserved region of Sindbis virus nsP3: effects on phosphorylation and on virus replication in vertebrate and invertebrate cells. Virology 202(1):224–232
Lastarza MW, Lemm JA, Rice CM (1994) Genetic analysis of the nsP3 region of Sindbis virus: evidence for roles in minus-strand and subgenomic RNA synthesis. J Virol 68(9):5781–5791
Levine B, Jiang HH, Kleeman L, Yang G (1996) Effect of E2 envelope glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain mutations on Sindbis virus pathogenesis. J Virol 70:1255–1260
Lvov DK, Berezina LK, Yakovlev BI, Aristova VA, Gushchina EL (1984) Isolation of Karelian fever agent from Aedes communis mosquitoes. Lancet 2:399–400
Morioka K, Fukai K, Ohashi S, Sakamoto K, Tsuda T, Yoshida K (2008) Comparison of the characters of the plaque-purified viruses from foot-and-mouth disease virus O/JPN/2000. J Vet Med Sci 70:653–658
Myles KM, Pierro DJ, Olson KE (2003) Deletions in the putative cell receptor-binding domain of Sindbis virus strain MRE16 E2 glycoprotein reduce midgut infectivity in Aedes aegypti. J Virol 77:8872–8881
Sammels LM, Lindsay MD, Poidinger M, Coelen RJ, Mackenzie JS (1999) Geographic distribution and evolution of Sindbis virus in Australia. J Gen Virol 80:739–748
Skogh M, Espmark A (1982) Ockelbo disease: epidemic arthritis exanthema syndrome in Sweden caused by Sindbis-virus like agent. Lancet 1:795–796
Smith TJ, Cheng RH, Olson NH, Peterson P, Chase E, Kuhn RJ, Baker TS (1995) Putative receptor binding sites on alphaviruses as visualized by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10648–10652
Strauss EG, Stec DS, Schmaljohn AL, Strauss JH (1991) (1991) Identification of ntigenically important domains in the glycoproteins of Sindbis virus by analysis of antibody escape variants. J Virol 65:4654–4664
Strauss JH, Strauss EG (1994) The alphaviruses: gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol Rev 58:491–562
Wang JL, Zhang HL, Sun XH, Fu SH, Wang HQ, Feng Y (2011) Distribution of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne arboviruses in Yunnan Province near the China-Burma-Laos border. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84:738–746
Zhu WY, Fu SH, Wang JL, He Y, Tang Q (2009) Effects of the nsP2-726 Pro mutation on infectivity and pathogenesis of Sindbis virus derived from a fulllength infectious cDNA clone. Virus Res 142:204–207
Zhu WY, Wang LH, Yang YL, Jia J, Fu SH (2010) Interaction of E2 Glycoprotein with Heparan Sulfate Is Crucial for Cellular Infection of Sindbis Virus. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9656
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81160353; 30970160), China Mega-Project for Infectious Disease (2011ZX10004-001), a Development Grant of State Key Laboratory for Infectious Disease Prevention and Control (2008SKLID105; 2011SKLID205) and China CDC-US CDC Cooperative Agreement U19-GH000004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. Jinglin and Z. Wuyang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinglin, W., Wuyang, Z., Fu, S. et al. Phenotypic and molecular characteristics of plaque-purified MX10 virus, an Oriental-Australian genotype of Sindbis virus from Yunnan, China. Arch Virol 158, 71–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1464-y