Abstract
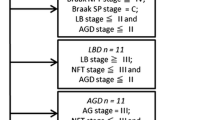
Immunocytochemistry for transactive response binding protein-43 (TDP43) was assessed in the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus in 250 cases displaying hippocampal pathology identified by haematoxylin–eosin staining. 18%, nearly one in five displayed TDP43 immunoreactive pathology in the granular cell layer of hippocampus. This percentage increased to 43% when only subjects with hippocampal pathology other than vascular in origin were included. When only subjects with severe Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology were included, 42% displayed TDP43-immunoreactive pathology, increasing to 60% when concomitant Alzheimer’s disease and α-synuclein pathology were present. Within this setting, TDP43-immunoreactive pathology was observed to be present in 6% of subjects with hippocampal pathology but without any cognitive impairment. Our findings justify assessment of TDP43 pathology in every case where a pathological alteration is observed in the hippocampus using a routine stain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alafuzoff I, Helisalmi S, Mannermaa A, Riekkinen P Sr, Soininen H (1999) Beta-amyloid load is not influenced by the severity of cardiovascular disease in aged and demented patients. Stroke 30:613–618
Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T, Al-Sarraj S et al (2008) Staging of neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Brain Pathol 18:484–496
Alafuzoff I, Thal DR, Arzberger T et al (2009a) Assessment of β-amyloid deposits in human brain: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Acta Neuropathol 117:309–320
Alafuzoff I, Ince PG, Arzberger T et al (2009b) Staging/typing of Lewy body related alpha-synuclein pathology: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Acta Neuropathol 117:635–652
Amador-Ortiz C, Lin WL, Ahmed Z et al (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 61:435–445
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H et al (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:602–611
Arai T, Mackenzie IR, Hasegawa M et al (2009) Phosphorylated TDP-43 in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 117:125–136
Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T et al (2006) Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol 112:389–404
Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2010) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6(4):211–220
Freeman SH, Spires-Jones T, Hyman BT et al (2008) TAR-DNA binding protein 43 in Pick disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:62–67
Fujishiro H, Uchikado H, Arai T et al (2009) Accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 in brains of patients with argyrophilic grain disease. Acta Neuropathol 117:151–158
Geser F, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2010) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a spectrum of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Neuropathology 30(2):103–112
Hatanpää KJ, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ et al (2008) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 immunohistochemistry reveals extensive neuritic pathology in FTLD-U: a midwest-southwest consortium for FTLD study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:271–279
Higashi S, Iseki E, Yamamoto R et al (2007) Concurrence of TDP-43, tau and alpha-synuclein pathology in brains of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res 1184:284–294
Hu WT, Josephs KA, Knopman DS et al (2008) Temporal lobar predominance of TDP-43 neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol 116:215–220
Josephs KA, Holton JL, Rossor MN et al (2004) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration and ubiquitin immunohistochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:369–373
Josephs KA, Whitwell JL, Knopman DS et al (2008) Abnormal TDP-43 immunoreactivity in AD modifies clinicopathologic and radiologic phenotype. Neurology 70:1850–1857
Kadokura A, Yamazaki T, Lemere CA et al (2009) Regional distribution of TDP-43 inclusions in Alzheimer disease (AD) brains: their relation to AD common pathology. Neuropathology 29:566–573
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1241–1253
Kuusisto E, Kauppinen T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Use of p62/SQSTM1 antibodies for neuropathological diagnosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34:169–180
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Bigio EH et al (2010) Nomenclature and nosology for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: an update. Acta Neuropathol 119:1–4
Mateen FJ, Josephs KA (2009) TDP-43 is not present in brain tissue of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 108:297–298
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Nakashima-Yasuda H, Uryu K, Robinson J et al (2007) Co-morbidity of TDP-43 proteinopathy in Lewy body related diseases. Acta Neuropathol 114:221–229
Nelson PT, Abner EL, Schmitt FA et al (2010) Modeling the association between 43 different clinical and pathological variables and the severity of cognitive impairment in a large autopsy cohort of elderly persons. Brain Pathol 20:66–79
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK et al (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Parkkinen L, Soininen H, Laakso M et al (2001) Alpha-synuclein pathology is highly dependent on the case selection. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27:314–325
Paulson HL (2009) The spinocerebellar ataxias. J Neuroophthalmol 29:227–237
Tolnay M, Clavaguera F (2004) Argyrophilic grain disease: a late-onset dementia with distinctive features among tauopathies. Neuropathology 24:269–283
Uryu K, Nakashima-Yasuda H, Forman MS et al (2008) Concomitant TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology is present in Alzheimer disease and corticobasal degeneration but not in other tauopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:555–564
Wang HY, Wang IF, Bose J, Shen CK (2004) Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics 83:130–139
Williams DR, Lees AJ (2009) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinicopathological concepts and diagnostic challenges. Lancet Neurol 8:270–279
Acknowledgments
We thank medical laboratory technologist Tarja Kauppinen, Mrs. Merja Fali, Mr. Heikki Luukkonen and Mr. Hannu Tiainen for their skilful technical assistance, Vesa Kiviniemi PhD for his assistance with the statistical analyses and Ewen MacDonald PhD for critical reading of the manuscript. This study has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of Kuopio University Hospital and the Finnish National Authority for Medicolegal Affairs. This study has been supported by UCB Pharma Nordic Epilepsy Grant 2008 and EVO funds from Kuopio University Hospital
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rauramaa, T., Pikkarainen, M., Englund, E. et al. TAR-DNA binding protein-43 and alterations in the hippocampus. J Neural Transm 118, 683–689 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0574-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0574-5