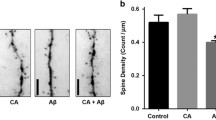
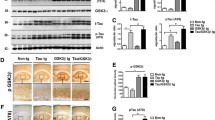
Summary.
Increased production and reduced clearance of amyloid β (Aβ) plays a central role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We have recently shown that the neurotrophic peptide mixture Cerebrolysin™ (Cbl) has the ability of improving synaptic functioning and reducing amyloid deposition in a transgenic (tg) animal model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Since in AD, potentially toxic Aβ aggregates accumulate not only around neurons but also in the blood vessels, then it is important to investigate whether bioactive compounds such as Cbl might have the capacity to ameliorate the age-related cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) in tg models. To this end, tg mice expressing mutant human amyloid precursor protein (APP) under the Thy1 promoter were treated with Cbl or saline alone starting at 7 or 12 months of age for a total of three months. Neuropathological analysis with an antibody against Aβ showed that Cbl decreased amyloid deposition around the blood vessels in a time dependant manner. These effects were accompanied by a reduction in perivascular microgliosis and astrogliosis and increased expression of markers of vascular fitness such as CD31 and ZO-1. No lymphocytic infiltration was observed associated with Aβ in the vessels. Consistent with these findings, ultrastructural analysis showed that while in tg mice treated with saline alone there was an abundant accumulation of amyloid fibers in the vascular wall accompanied by thickening of the basal membrane and endothelial cell damage, in Cbl-treated mice there was considerable reduction in the subcellular alterations of endothelial and smooth muscle cells with preservation of basal membranes and intercellular junctions. Taken together, these results suggest that Cbl treatment might have beneficial effects in patients with cognitive impairment due to cerebrovascular amyloidosis by reducing Aβ accumulation and promoting the preservation of the cerebrovasculature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rockenstein, E., Adame, A., Mante, M. et al. Amelioration of the cerebrovascular amyloidosis in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with the neurotrophic compound Cerebrolysin™. J Neural Transm 112, 269–282 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0181-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0181-4