Summary.
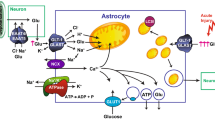
Glutamate uptake into astrocytes and the resulting increase in intracellular Na+ (Na+i) have been identified as a key signal coupling excitatory neuronal activity to increased glucose utilization. Arguments based mostly on mathematical modeling led to the conclusion that physiological concentrations of glutamate more than double astrocytic Na+/K+-ATPase activity, which should proportionally increase its ATP hydrolysis rate. This hypothesis was tested in the present study by fluorescence monitoring of free Mg2+ (Mg2+i), a parameter that inversely correlates with ATP levels. Glutamate application measurably increased Mg2+i (i.e. decreased ATP), which was reversible after glutamate washout. Na+i and ATP changes were then directly compared by simultaneous Na+i and Mg2+ imaging. Glutamate increased both parameters with different rates and blocking the Na+/K+-ATPase during the glutamate-evoked Na+i response, resulted in a drop of Mg2+i levels (i.e. increased ATP). Taken together, this study demonstrates the tight correlation between glutamate transport, Na+ homeostasis and ATP levels in astrocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magistretti, P., Chatton, JY. Relationship between L-glutamate-regulated intracellular Na+ dynamics and ATP hydrolysis in astrocytes. J Neural Transm 112, 77–85 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0171-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0171-6