Abstract
Background
Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is a rare, idiopathic, non-neoplastic histioproliferative disease. Central nervous system (CNS) manifestations are extremely rare. Its low incidence and unknown etiology restrict early diagnosis and optimal therapy.
Methods
In the 1995–2013 period, seven CNS-RDD patients with intracranial and/or spinal lesions were retrospectively analyzed, including the clinical data, laboratory and imaging results, treatment applied and outcome. All seven case samples were screened for the SLC29A3 gene mutation, and the literature was reviewed.
Results
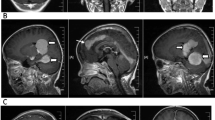
Seven RDD patients (6 male/1 female, aged between 7 and 68) with CNS manifestations are reported. Five of the seven patients (71.4 %) had intracranial lesions (1 with skull erosion and 1 with multiple lesions mimicking meningiomas), and two (28.6 %) had spinal subdural lesions. The patients’ symptoms included headaches, seizures, visual loss, epileptoid convulsions in the lower legs, fever, spastic paraparesis and paraplegia. An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was detected in five of the seven cases. The diagnosis was confirmed by immunohistochemical staining revealing that the characteristic histiocytes were positive for the S100 protein and CD68 and negative for CD1a. All patients were operated on: three recovered completely, two were partially rehabilitated, and two died. No SLC29A3 gene mutations were found in any of the seven samples.
Conclusion
This short series suggests the following: (1) RDD should be included in the differential diagnosis of lesions mimicking intracranial/spinal meningiomas or inflammatory lesions, especially in children; (2) the definitive diagnosis is based on histopathology and immunocytochemistry; (3) surgical resection seems to be the most effective therapy; (4) the exact etiology and adjuvant therapy for relapsing/incompletely resected lesions remain to be established.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Razek M, Matter GA, Azab WA, Katchy KC, Mallik AA (2013) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease: report of two cases and a review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg 23:509–513
Adeleye AOAG, Fraifeld S, Shoshan Y, Umansky F, Spektor S (2010) Diagnosis and management of Rosai-Dorfman disease involving the central nervous system. Neurol Res 32:572–578
Andriko JA, Morrison A, Colegial CH, Davis BJ, Jones RV (2001) Rosai-Dorfman disease isolated to the central nervous system: a report of 11 cases. Mod Pathol 14:172–178
Beros V, Houra K, Rotim K, Zivkovic DJ, Cupic H, Kosec A (2011) Isolated cerebellar intraparenchymal Rosai-Dorfman disease--case report and review of literature. Br J Neurosurg 25:292–296
Camp SJRF, Apostolopoulos V, Weatherall M, Lim S, Nandi D (2012) Intracerebral multifocal Rosai-Dorfman disease. J Clin Neurosci 19:1308–1310
Catalucci A, Lanni G, Ventura L, Ricci A, Galzio RJ, Gallucci M (2012) A rare case of intracranial rosai-dorfman disease mimicking multiple meningiomas. A case report and review of the literature. Neuroradiol J 25:569–574
Chen KT (2003) Crush cytology of Rosai-Dorfman disease of the central nervous system. A report of 2 cases. Acta Cytol 47:1111–1115
Chen YYTX, Li Z, Luo BN, Huang Q (2010) Sporadic meningioangiomatosis-associated atypical meningioma mimicking parenchymal invasion of brain: a case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol 18:39
Dran G, Rasendrarijao D, Vandenbos F, Paquis P (2008) Rosai-Dorfman disease causing spinal cord compression: case report. Neurosurgery 62:E977–E978, discussion E978
Eiras Jda CSA, Lima LL, Tubilla LH, Oliveira RM (2010) Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report. An Bras Dermatol 85:687–690
Favara BEFA, Pauli M, Jaffe ES, Weiss LM, Arico M, Bucsky P, Egeler RM, Elinder G, Gadner H, Gresik M, Henter JI, Imashuku S, Janka-Schaub G, Jaffe R, Ladisch S, Nezelof C, Pritchard J (1997) Contemporary classification of histiocytic disorders. The WHO Committee On Histiocytic/Reticulum Cell Proliferations. Reclassification Working Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol 29:157–166
Foucar ERJ, Dorfman RF (1978) Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Arch Otolaryngol 104:687–693
Foucar ERJ, Dorfman R (1990) Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol 7:19–73
Foucar ERJ, Dorfman RF, Brynes RK (1982) The neurologic manifestations of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Neurology 32:365–372
Gaetani P, Tancioni F, Di Rocco M, Rodriguez y Baena R (2000) Isolated cerebellar involvement in Rosai-Dorfman disease: case report. Neurosurgery 46:479–481
Gaitonde S (2007) Multifocal, extranodal sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131:1117–1121
Geara AR, Ayoubi MA, Achram MC, Chamseddine NM (2004) Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking neurofibromatosis: case presentation and review of the literature. Clin Radiol 59:625–630
Griffiths SJTW, Parameswaran R, Kelsey A, West CG (2004) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking meningioma in a child. Br J Neurosurg 18:293–297
Gupta K, Bagdi N, Sunitha P, Ghosal N (2011) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking meningioma in a child: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Radiol 84:e138–e141
Gupta DK, Suri A, Mahapatra AK, Mehta VS, Garg A, Sarkar C, Ahmad FU (2006) Intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease in a child mimicking bilateral giant petroclival meningiomas: a case report and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1194–1200
Jabali YSV, Pradna J (2005) Rosai-Dorfman disease: successful long-term results by combination chemotherapy with prednisone, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate, and vinblastine: a case report. Int J Surg Pathol 13:285–289
Joubert C, Dagain A, Faivre A, Nguyen AT, Fesselet J, Figarella-Branger D (2013) Intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking multiple meningiomas. Rev Med Brux 34:112–114
Juskevicius RFJ (2001) Rosai-Dorfman disease of the parotid gland: cytologic and histopathologic findings with immunohistochemical correlation. Arch Pathol Lab Med 125:1348–1350
Kidd DPRT, Miller NR (2006) Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting with widespread intracranial and spinal cord involvement. Neurology 67:1551–1555
Kim M, Provias J, Bernstein M (1995) Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking multiple meningioma: case report. Neurosurgery 36:1185–1187
Konishi EIN, Yamamoto S, Scheithauer BW (2003) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease (sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:515–518
Levine PHJN, Murari P, Manak M, Jaffe ES (1992) Detection of human herpesvirus 6 in tissues involved by sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). J Infect Dis 166:291–295
Lungren MPPJ, Cummings TJ, Grant GA (2009) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease in a child. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:E148–E149
McPherson CM, Brown J, Kim AW, DeMonte F (2006) Regression of intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease following corticosteroid therapy. Case report. J Neurosurg 104:840–844
Middel PHB, Fayyazi A, Kaboth U, Radzun HJ (1999) Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: evidence for its relationship to macrophages and for a cytokine-related disorder. Histopathology 35:525–533
Morgan NVMM, Cangul H, Gleeson D, Straatman-Iwanowska A, Davies N, Keenan S, Pasha S, Rahman F, Gentle D, Vreeswijk MP, Devilee P, Knowles MA, Ceylaner S, Trembath RC, Dalence C, Kismet E, Köseoğlu V, Rossbach HC, Gissen P, Tannahill D, Maher ER (2010) Mutations in SLC29A3, encoding an equilibrative nucleoside transporter ENT3, cause a familial histiocytosis syndrome (Faisalabad histiocytosis) and familial Rosai-Dorfman disease. PLoS Genet 6, e1000833
Petzold ATM, Powell M, Plant GT (2001) Relapsing intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:538–541
Raslan OASD, Fuller GN, Ketonen LM (2011) Rosai-Dorfman disease in neuroradiology: imaging findings in a series of 10 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:W187–W193
Rastogi VSR, Misra SR, Yadav L, Sharma V (2014) Emperipolesis—a review. J Clin Diagn Res 8:ZM01–ZM02
Resnick DK, Johnson BL, Lovely TJ (1996) Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting with multiple orbital and intracranial masses. Acta Neuropathol 91:554–557
Rosai JDR (1969) Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy:a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol 87:63–70
Russo N, Giangaspero F, Beccaglia MR, Santoro A (2009) Intracranial dural histiocytosis. Br J Neurosurg 23:449–454
Said RA-FF, Talwar J, Attallah JP, Dilawari A (2011) Intracranial Rosai-Dorfman: a clinical challenge. Neurologist 17:117–119
Sandoval-Sus JDS-LA, Chapman JR, Velazquez-Vega J, Borja MJ, Rosenberg S, Lossos A, Lossos IS (2014) Rosai-Dorfman disease of the central nervous system: report of 6 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:165–175
Sato A, Sakurada K, Sonoda Y, Saito S, Kayama T, Jokura H, Yoshimoto T, Nakazato Y (2003) Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting with multiple intracranial and intraspinal masses: a case report. No Shinkei Geka 31:1199–1204
Sharma MSPM, Jha AN (2005) Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking a sphenoid wing meningioma. Neurol India 53:110–111
Shaver EGRS, Yachnis AT, Sutton LN (1993) Isolated extranodal intracranial sinus histiocytosis in a 5-year-old boy. Case report. J Neurosurg 79:769–773
Song SKSI, Strauchen JA, Huang YP, Sachdev V, Daftary DR, Vas CJ (1989) Meningeal nodules with features of extranodal sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Am J Surg Pathol 13:406–412
Theeler BJKJ, Yoest SM (2008) Teaching NeuroImage: isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking a meningioma. Neurology 70, e42
Tian Y, Wang J, Ge J, Ma Z, Ge M (2015) Intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking multiple meningiomas in a child: a case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 31:317–323
Toh CHCY, Wong HF, Wei KC, Ng SH, Wan YL (2005) Rosai-Dorfman disease with dural sinus invasion. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 102:550–554
Türe USA, Bozkurt SU, Uneri C, Sav A, Pamir MN (2004) Giant intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease. J Clin Neurosci 11:563–566
Udono H, Fukuyama K, Okamoto H, Tabuchi K (1999) Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting multiple intracranial lesions with unique findings on magnetic resonance imaging. Case report. J Neurosurg 91:335–339
Wan STX, Zhan R, Yu J, Gu J, Zhang K (2008) Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking suprasellar meningioma: case report with review of the literature. J Int Med Res 36:1134–1139
Wang Y, Gao X, Tang W, Jiang C (2010) Rosai-Dorfman disease isolated to the central nervous system: a report of six cases. Neuropathology 30:154–158
Woodcock RJ Jr, Mandell JW, Lipper MH (1999) Sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease) of the suprasellar region: MR imaging findings—a case report. Radiology 213:808–810
Wu M, Anderson AE, Kahn LB (2001) A report of intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease with literature review. Ann Diagn Pathol 5:96–102
Zhang XJ, Piao YS, Chen L, Tang GC, Wei LF, Yang H, Lu DH (2011) Multiple intracranial lesions: a clinicalpathologic study of 62 cases. Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi 40:599–603
Zhang JT, Tian HJ, Lang SY, Wang XQ (2010) Primary intracerebral Rosai-Dorfman disease. J Clin Neurosci 17:1286–1288
Zheng MBR, Li W, Landeck L, Chen JQ, Lao LM, Cai SQ, Yao YG, Man XY (2013) Generalized pure cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: a link between inflammation and cancer not associated with mitochondrial DNA and SLC29A3 gene mutation? Disc Med 16:193–200
Acknowledgments
Dr. Yongji Tian (first author) was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30900479) , Beijing Nova-Plan Program (No. 2010B121), National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2013BAI09B03) and BIBD-PXM 2013_014226_07_000084.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Wang, J., Li, M. et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease involving the central nervous system: seven cases from one institute. Acta Neurochir 157, 1565–1571 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2511-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2511-8