Abstract
Background
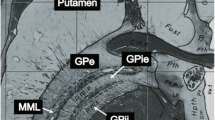
Deep-brain stimulation (DBS) of the internal globus pallidus (GPi) has shown remarkable therapeutic benefits for treatment-resistant neurological disorders including dystonia and Parkinson’s disease (PD). The success of the DBS is critically dependent on the reliable visualization of the GPi.
The aim of the study was to evaluate promising 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods for pre-stereotactic visualization of the GPi using a standard installation protocol.
Methods
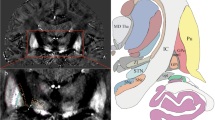
MRI at 3.0 T of nine healthy individuals and of one patient with PD was acquired (FLAIR, T1-MPRAGE, T2-SPACE, T2*-FLASH2D, susceptibility-weighted imaging mapping (SWI)). Image quality and visualization of the GPi for each sequence were assessed by two neuroradiologists independently using a 6-point scale. Axial, coronal, and sagittal planes of the T2*-FLASH2D images were compared. Inter-rater reliability, contrast-to-noise ratios (CNR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) for the GPi were determined. For illustration, axial T2*-FLASH2D images were fused with a section schema of the Schaltenbrand-Wahren stereotactic atlas.
Results
The GPi was best and reliably visualized in axial and to a lesser degree on coronal T2*-FLASH2D images. No major artifacts in the GPi were observed in any of the sequences. SWI offered a significantly higher CNR for the GPi compared to standard T2-weighted imaging using the standard parameters. The fusion of the axial T2*-FLASH2D images and the atlas projected the GPi clearly in the boundaries of the section schema.
Conclusions
Using a standard installation protocol at 3.0 T T2*-FLASH2D imaging (particularly axial view) provides optimal and reliable delineation of the GPi.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease Study Group (2001) Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 345:956–963
Abosch A, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, Harel N (2010) An assessment of current brain targets for deep brain stimulation surgery with susceptibility-weighted imaging at 7 tesla. Neurosurgery 67:1745–1756, discussion 1756
Amirnovin R, Williams ZM, Cosgrove GR, Eskandar EN (2006) Experience with microelectrode guided subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery 58:ONS96–102, discussion ONS196-102
Andrade P, Carrillo-Ruiz JD, Jimenez F (2009) A systematic review of the efficacy of globus pallidus stimulation in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Clin Neurosci 16:877–881
Ashkan K, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L, Tisch S, Yousry T, Limousin-Dowsey P, Hariz MI (2007) Variability of the subthalamic nucleus: the case for direct MRI guided targeting. Br J Neurosurg 21:197–200
Bachmann R, Reilmann R, Schwindt W, Kugel H, Heindel W, Kramer S (2006) FLAIR imaging for multiple sclerosis: a comparative MR study at 1.5 and 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol 16:915–921
Balachandran R, Welch EB, Dawant BM, Fitzpatrick JM (2010) Effect of MR distortion on targeting for deep-brain stimulation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:1729–1735
Bejjani BP, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Yelnik J, Damier P, Arnulf I, Bonnet AM, Marsault C, Agid Y, Philippon J, Cornu P (2000) Bilateral subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson's disease by using three-dimensional stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 92:615–625
Bejjani BP, Gervais D, Arnulf I, Papadopoulos S, Demeret S, Bonnet AM, Cornu P, Damier P, Agid Y (2000) Axial parkinsonian symptoms can be improved: the role of levodopa and bilateral subthalamic stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68:595–600
Benazzouz A, Hallett M (2000) Mechanism of action of deep brain stimulation. Neurology 55:S13–16
Bergman H, Feingold A, Nini A, Raz A, Slovin H, Abeles M, Vaadia E (1998) Physiological aspects of information processing in the basal ganglia of normal and parkinsonian primates. Trends Neurosci 21:32–38
Bhidayasiri R (2006) Dystonia: genetics and treatment update. Neurologist 12:74–85
Bhidayasiri R, Tarsy D (2006) Treatment of dystonia. Expert Rev Neurother 6:863–886
Biswas J, Nelson CB, Runge VM, Wintersperger BJ, Baumann SS, Jackson CB, Patel T (2005) Brain tumor enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) at 1.5 versus 3 tesla. Invest Radiol 40:792–797
Bour LJ, Contarino MF, Foncke EM, de Bie RM, van den Munckhof P, Speelman JD, Schuurman PR (2010) Long-term experience with intraoperative microrecording during DBS neurosurgery in STN and GPi. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:2069–2077
Bushberg JT, Seibert JT, Leidholdt EM Jr, Boone JM (2001) The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Chen N, Wyrwicz AM (1999) Removal of intravoxel dephasing artifact in gradient-echo images using a field-map based RF refocusing technique. Magn Reson Med 42:807–812
Cho ZH, Min HK, Oh SH, Han JY, Park CW, Chi JG, Kim YB, Paek SH, Lozano AM, Lee KH (2010) Direct visualization of deep brain stimulation targets in Parkinson disease with the use of 7-tesla magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 113:639–647
Cohen JA (1960) A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas 20:37–46
Coubes P, Cif L, Azais M, Roubertie A, Hemm S, Diakonoya N, Vayssiere N, Monnier C, Hardouin E, Ganau A, Tuffery S, Claustre M, Echenne B (2002) Treatment of dystonia syndrome by chronic electric stimulation of the internal globus pallidus. Arch Pediatr 9(Suppl 2):84s–86s
Cuny E, Guehl D, Burbaud P, Gross C, Dousset V, Rougier A (2002) Lack of agreement between direct magnetic resonance imaging and statistical determination of a subthalamic target: the role of electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 97:591–597
Dormont D, Ricciardi KG, Tande D, Parain K, Menuel C, Galanaud D, Navarro S, Cornu P, Agid Y, Yelnik J (2004) Is the subthalamic nucleus hypointense on T2-weighted images? A correlation study using MR imaging and stereotactic atlas data. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1516–1523
Drayer B, Burger P, Darwin R, Riederer S, Herfkens R, Johnson GA (1986) MRI of brain iron. AJR Am J Roentgenol 147:103–110
Drayer BP (1989) Basal ganglia: significance of signal hypointensity on T2-weighted MR images. Radiology 173:311–312
Duyn JH, van Gelderen P, Li TQ, de Zwart JA, Koretsky AP, Fukunaga M (2007) High-field MRI of brain cortical substructure based on signal phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11796–11801
Gavarini S, Vayssiere N, Delort P, Cif L, Biolsi B, Tancu C, Vasques X, Plagnol S, Bonafe A, Coubes P (2008) Stereotactic MRI in DYT1 dystonia: focal signal abnormalities in the basal ganglia do not contraindicate deep brain stimulation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86:245–252
Griffiths PD, Dobson BR, Jones GR, Clarke DT (1999) Iron in the basal ganglia in Parkinson's disease. An in vitro study using extended X-ray absorption fine structure and cryo-electron microscopy. Brain 122(Pt 4):667–673
Gringel T, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Elolf E, Frolich A, Dechent P, Helms G (2009) Optimized high-resolution mapping of magnetization transfer (MT) at 3 Tesla for direct visualization of substructures of the human thalamus in clinically feasible measurement time. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:1285–1292
Gross RE, Krack P, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Rezai AR, Benabid AL (2006) Electrophysiological mapping for the implantation of deep brain stimulators for Parkinson's disease and tremor. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 14):S259–283
Guo T, Finnis KW, Deoni SC, Parrent AG, Peters TM (2006) Comparison of different targeting methods for subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 9:768–775
Haacke EM, Ayaz M, Khan A, Manova ES, Krishnamurthy B, Gollapalli L, Ciulla C, Kim I, Petersen F, Kirsch W (2007) Establishing a baseline phase behavior in magnetic resonance imaging to determine normal vs. abnormal iron content in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:256–264
Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR (2004) Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med 52:612–618
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3:41–51
Hamani C, Richter EO, Andrade-Souza Y, Hutchison W, Saint-Cyr JA, Lozano AM (2005) Correspondence of microelectrode mapping with magnetic resonance imaging for subthalamic nucleus procedures. Surg Neurol 63:249–253, discussion 253
Haneder S, Attenberger UI, Biffar A, Dietrich O, Fink C, Schoenberg SO, Michaely HJ (2011) Gadofosveset: Parameter Optimization for Steady-State Imaging of the Thoracic and Abdominal Vasculature. Invest Radiol 46:678–685
Hariz MI, Bergenheim AT (1990) A comparative study on ventriculographic and computerized tomography-guided determinations of brain targets in functional stereotaxis. J Neurosurg 73:565–571
Hirabayashi H, Tengvar M, Hariz MI (2002) Stereotactic imaging of the pallidal target. Mov Disord 17(Suppl 3):S130–134
Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Roberts DW, Darcey TM (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for target localization in functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 45:290–297, discussion 297–298
Hutchison WD, Lozano AM, Davis KD, Saint-Cyr JA, Lang AE, Dostrovsky JO (1994) Differential neuronal activity in segments of globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease patients. Neuroreport 5:1533–1537
Katayama S, Watanabe C, Khoriyama T, Oka M, Mao JJ, Yamamura Y, Tahara E, Nakamura S (1998) Slowly progressive L-DOPA nonresponsive pure akinesia due to nigropallidal degeneration: a clinicopathological case study. J Neurol Sci 161:169–172
Katsakiori PF, Kefalopoulou Z, Markaki E, Paschali A, Ellul J, Kagadis GC, Chroni E, Constantoyannis C (2009) Deep brain stimulation for secondary dystonia: results in 8 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:473–478, discussion 478
Kitajima M, Korogi Y, Kakeda S, Moriya J, Ohnari N, Sato T, Hayashida Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Yamashita Y (2008) Human subthalamic nucleus: evaluation with high-resolution MR imaging at 3.0 T. Neuroradiology 50:675–681
Kosta P, Argyropoulou MI, Markoula S, Konitsiotis S (2006) MRI evaluation of the basal ganglia size and iron content in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 253:26–32
Krauss JK, Yianni J, Loher TJ, Aziz TZ (2004) Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. J Clin Neurophysiol 21:18–30
Kringelbach ML, Jenkinson N, Green AL, Owen SL, Hansen PC, Cornelissen PL, Holliday IE, Stein J, Aziz TZ (2007) Deep brain stimulation for chronic pain investigated with magnetoencephalography. Neuroreport 18:223–228
Kringelbach ML, Jenkinson N, Owen SL, Aziz TZ (2007) Translational principles of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:623–635
Kumar R, Lang AE, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Lozano AM, Limousin P, Pollak P, Benabid AL, Guridi J, Ramos E, van der Linden C, Vandewalle A, Caemaert J, Lannoo E, van den Abbeele D, Vingerhoets G, Wolters M, Obeso JA (2000) Deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus pars interna in advanced Parkinson's disease. Neurology 55:S34–39
Kupsch A, Benecke R, Muller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Muller JU, Deuschl G, Pinsker MO, Skogseid IM, Roeste GK, Vollmer-Haase J, Brentrup A, Krause M, Tronnier V, Schnitzler A, Voges J, Nikkhah G, Vesper J, Naumann M, Volkmann J (2006) Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med 355:1978–1990
Kurian MA, McNeill A, Lin JP, Maher ER (2011) Childhood disorders of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Dev Med Child Neurol 53:394–404
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 33:363–374
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lee JY, Kim JW, Lim YH, Kim C, Kim DG, Jeon BS, Paek SH (2010) Is MRI a reliable tool to locate the electrode after deep brain stimulation surgery? Comparison study of CT and MRI for the localization of electrodes after DBS. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:2029–2036
Lee KH, Blaha CD, Garris PA, Mohseni P, Horne AE, Bennet KE, Agnesi F, Bledsoe JM, Lester DB, Kimble C, Min HK, Kim YB, Cho ZH (2009) Evolution of Deep Brain Stimulation: Human Electrometer and Smart Devices Supporting the Next Generation of Therapy. Neuromodulation 12:85–103
Lozano A, Hutchison W, Kiss Z, Tasker R, Davis K, Dostrovsky J (1996) Methods for microelectrode-guided posteroventral pallidotomy. J Neurosurg 84:194–202
Manova ES, Habib CA, Boikov AS, Ayaz M, Khan A, Kirsch WM, Kido DK, Haacke EM (2009) Characterizing the mesencephalon using susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:569–574
McIntyre CC, Savasta M, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Vitek JL (2004) Uncovering the mechanism(s) of action of deep brain stimulation: activation, inhibition, or both. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1239–1248
McNeill A, Chinnery PF (2011) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Handb Clin Neurol 100:161–172
Mehdorn HM, Goebel S, Falk D, Volkmann J, Leplow B, Pinsker MO (2008) Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and its neuropsychological implications. Acta Neurochir Suppl 101:9–12
Miyagi Y, Shima F, Sasaki T (2007) Brain shift: an error factor during implantation of deep brain stimulation electrodes. J Neurosurg 107:989–997
Ordidge RJ, Gorell JM, Deniau JC, Knight RA, Helpern JA (1994) Assessment of relative brain iron concentrations using T2-weighted and T2*-weighted MRI at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 32:335–341
Papavassiliou E, Rau G, Heath S, Abosch A, Barbaro NM, Larson PS, Lamborn K, Starr PA (2004) Thalamic deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: relation of lead location to outcome. Neurosurgery 54:1120–1129, discussion 1129–1130
Park JH, Chung SJ, Lee CS, Jeon SR (2011) Analysis of hemorrhagic risk factors during deep brain stimulation surgery for movement disorders: comparison of the circumferential paired and multiple electrode insertion methods. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:1573–1578
Pinsker MO, Volkmann J, Falk D, Herzog J, Steigerwald F, Deuschl G, Mehdorn HM (2009) Deep brain stimulation of the internal globus pallidus in dystonia: target localisation under general anaesthesia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:751–758
Rehncrona S, Johnels B, Widner H, Tornqvist AL, Hariz M, Sydow O (2003) Long-term efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation for tremor: double-blind assessments. Mov Disord 18:163–170
Rossi M, Ruottinen H, Elovaara I, Ryymin P, Soimakallio S, Eskola H, Dastidar P (2010) Brain Iron Deposition and Sequence Characteristics in Parkinsonism: Comparison of SWI, T2* Maps, T2-Weighted-, and FLAIR-SPACE. Invest Radiol 45:795–802
Rouaud T, Dondaine T, Drapier S, Haegelen C, Lallement F, Peron J, Raoul S, Sauleau P, Verin M (2010) Pallidal stimulation in advanced Parkinson's patients with contraindications for subthalamic stimulation. Mov Disord 25:1839–1846
Runge VM, Wood ML, Kaufman DM, Traill MR, Nelson KL (1988) The straight and narrow path to good head and spine MRI. Radiographics 8:507–531
Rutledge JN, Hilal SK, Silver AJ, Defendini R, Fahn S (1987) Study of movement disorders and brain iron by MR. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:365–379
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren, W. (1977) Atlas for Stereotaxy of the Human Brain. Thieme Stuttgart
Slavin KV, Thulborn KR, Wess C, Nersesyan H (2006) Direct visualization of the human subthalamic nucleus with 3 T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:80–84
Stark DD, Bradley WG (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging. C.V. Mosby, St. Louis
Starr PA, Vitek JL, DeLong M, Bakay RA (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging-based stereotactic localization of the globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus. Neurosurgery 44:303–313, discussion 313–304
Strassmann G (1949) Iron and calcium deposits in the brain; their pathologic significance. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 8:428–435, illust
Tang JK, Moro E, Mahant N, Hutchison WD, Lang AE, Lozano AM, Dostrovsky JO (2007) Neuronal firing rates and patterns in the globus pallidus internus of patients with cervical dystonia differ from those with Parkinson's disease. J Neurophysiol 98:720–729
Terao T, Takahashi H, Yokochi F, Taniguchi M, Okiyama R, Hamada I (2003) Hemorrhagic complication of stereotactic surgery in patients with movement disorders. J Neurosurg 98:1241–1246
Tisch S, Rothwell JC, Limousin P, Hariz MI, Corcos DM (2007) The physiological effects of pallidal deep brain stimulation in dystonia. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 15:166–172
Tisch S, Silberstein P, Limousin-Dowsey P, Jahanshahi M (2004) The basal ganglia: anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. Psychiatr Clin North Am 27:757–799
Tisch S, Zrinzo L, Limousin P, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Ashkan K, Hariz M (2007) Effect of electrode contact location on clinical efficacy of pallidal deep brain stimulation in primary generalised dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1314–1319
Toda H, Sawamoto N, Hanakawa T, Saiki H, Matsumoto S, Okumura R, Ishikawa M, Fukuyama H, Hashimoto N (2009) A novel composite targeting method using high-field magnetic resonance imaging for subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg 111:737–745
Trepanier LL, Kumar R, Lozano AM, Lang AE, Saint-Cyr JA (2000) Neuropsychological outcome of GPi pallidotomy and GPi or STN deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Brain Cogn 42:324–347
Vayssiere N, Hemm S, Cif L, Picot MC, Diakonova N, El Fertit H, Frerebeau P, Coubes P (2002) Comparison of atlas- and magnetic resonance imaging-based stereotactic targeting of the globus pallidus internus in the performance of deep brain stimulation for treatment of dystonia. J Neurosurg 96:673–679
Vertinsky AT, Coenen VA, Lang DJ, Kolind S, Honey CR, Li D, Rauscher A (2009) Localization of the subthalamic nucleus: optimization with susceptibility-weighted phase MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1717–1724
Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, Lagrange C, Tezenas du Montcel S, Dormont D, Grand S, Blond S, Detante O, Pillon B, Ardouin C, Agid Y, Destee A, Pollak P (2005) Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med 352:459–467
Volkmann J, Benecke R (2002) Deep brain stimulation for dystonia: patient selection and evaluation. Mov Disord 17(Suppl 3):S112–115
Xiaowu H, Xiufeng J, Xiaoping Z, Bin H, Laixing W, Yiqun C, Jinchuan L, Aiguo J, Jianmin L (2010) Risks of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with Parkinson's disease receiving deep brain stimulation and ablation. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:96–100
Zhang W, Sun SG, Jiang YH, Qiao X, Sun X, Wu Y (2009) Determination of brain iron content in patients with Parkinson's disease using magnetic susceptibility imaging. Neurosci Bull 25:353–360
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ingo S. Nölte and Lars Gerigk contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nölte, I.S., Gerigk, L., Al-Zghloul, M. et al. Visualization of the internal globus pallidus: sequence and orientation for deep brain stimulation using a standard installation protocol at 3.0 Tesla. Acta Neurochir 154, 481–494 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1242-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1242-8