Abstract
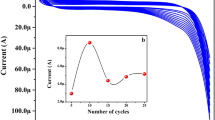
An electrochemiluminescence (ECL) nanoprobe was fabricated for the determination of clenbuterol (CLB). A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) film was coated on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode modified with CdTe-doped multiwall carbon nanotubes. The MIP film with CLB as the template molecule improves the selectivity of the nanoprobe, CdTe is used as ECL signal amplifier, and MWCNT works as the carrier. The ECL intensity is altered by elution and reabsorption of CLB. The possible reaction mechanism and experimental parameters of the nanoprobe are discussed. Under optimized conditions, the quenched ECL intensity and the CLB concentration have a linear relationship in the range 2.3 × 10−9 to 1.5 × 10−5 mol·L−1, and the detection limit is 1.0 × 10−9 mol·L−1 (S/N = 3). The nanoprobe was successfully applied to the determination of CLB in pork samples.

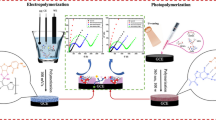
Schematic representation of the molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe based on complexes consisting of CdTe and multiwall carbon nanotube used to determinate clenbuterol.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Elliott C, McCaughey W, Shortt H (1993) Residues of the beta-agonist clenbuterol in tissues of medicated farm animals. Food Addit Contam 10:231–244
López-Erroz C, Viñas P, Cerdán FJ, Hernández-Córdoba M (2000) Determination of clenbuterol in pharmaceutical preparations by reaction with o-phthalaldehyde using a flow-injection fluorimetric procedure. Talanta 53:47–53
Zhou JY, Wang XS, Xiao Y (2007) Competitive immunoassay for clenbuterol using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B 848:226–231
Zhao L, Zhao J, Huangfu WG, Wu YL (2010) Simultaneous determination of melamine and clenbuterol in animal feeds by GC–MS. Chromatogr 72:365–368
Blanca J, Muñoz P, Morgado M, Méndez N, Aranda A, Reuvers T, Hooghuis H (2005) Determination of clenbuterol, ractopamine and zilpaterol in liver and urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 529:199–205
Sirichai S, Khanatharana P (2008) Rapid analysis of clenbuterol, salbutamol, procaterol and fenoterol in pharmaceuticals and human urine by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 76:1194–1198
Ge Y, Camarada MB, Xu L, Qu M, Liang H, Zhao E, Wen Y (2018) A highly stable black phosphorene nanocomposite for voltammetric detection of clenbuterol. Microchim Acta 185:566
Ji RY, Chen S, Xu W, Qin Z, Qiu JF, Li CR (2018) A voltammetric immunonanoprobe for clenbuterol based on the use of a MoS2-AuPt nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 185:209
Jin XC, Fang GZ, Pan MF, Yang YK, Bai XY, Wang S (2018) A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe based on upconversion nanoparticles enhanced by electrodeposited rGO for selective and ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol. Biosens Bioelectron 102:357–364
Yan FF, Zhang YC, Zhang S, Zhao JH, Liu SL, He LH, Feng XZ, Zhang HZ, Zhang ZH (2015) Carboxyl-modified graphene for use in an immunoassay for the illegal feed additive clenbuterol using surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 182:855–862
Tian L, Wang XR, Wu KX, Hu Y, Wang Y, Lu J (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence bionanoprobe for dopamine based on ZnSe, graphene oxide@multi walled carbon nanotube and Ru(bpy)32+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 286:266–271
Wang ZH, Qian YX, Wei XL, Zhang YF, Wu GF, Lu XQ (2017) An “on-off” Electrochemiluminescence Bionanoprobe Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Recycling Amplifications for Determination of Dopamine. Electrochim Acta 250:309–319
Kitte SA, Gao WY, Zholudov YT, Qi LM, Nsabimana A, Liu ZY, Xu GB (2017) Stainless steel electrode for sensitive luminol electrochemiluminescent detection of H2O2. Glucose, and Glucose Oxidase Activity, Anal Chem 89:9864–9869
Zhao XC, Zhou WJ, Lu C (2017) Fabrication of noncoplanar molecule aggregates with inherent porous structures for electrochemiluminescence signal amplification. Anal Chem 89:10078–10084
Wu L, Ding F, Yin WM, Ma J, Wang BR, Nie AX, Han HY (2017) From electrochemistry to electroluminescence: development and application in a ratiometric aptananoprobe for aflatoxin B1. Anal Chem 89:7578–7585
Jiang XY, Wang ZL, Wang HJ, Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2017) A novel metal–organic framework loaded with abundant N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol) as a high-efficiency electrochemiluminescence indicator for sensitive detection of mucin1 on cancer cells. Chem Commun 53:9705–9708
Hong J, Ming L, Tu YF (2014) Intensification of the electrochemiluminescence of luminol on hollow TiO2 nanoshell-modified indium tin oxide electrodes. Talanta 128:242–247
Wu FF, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2018) Electrochemiluminescence peptide-based bionanoprobe with hetero-nanostructures as coreaction accelerator for the ultrasensitive determination of Tryptase. Anal Chem 90:2263–2270
Tian KL, Li DJ, Tang TT, Nie F, Zhou Y, Du JX, Zheng JB (2018) A novel electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system of luminol-graphene quantum dot composite and its application in H2O2 detection. Talanta 185:446–452
Haghighi B, Tavakoli A, Bozorgzadeh S (2015) Cathodic electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol on glassy carbon electrode modified with cobalt nanoparticles decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim Acta 154:259–265
Wang YF, Sha HF, Ke H, Jia NQ (2018) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunonanoprobe based on platinum nickel nanocubes-L-cysteine-luminol nanocomposite. Talanta 186:322–329
Tang HJ, Chen WX, Li DD, Duan XL, Ding SJ, Zhao M, Zhang J (2019) Luminol-based ternary electrochemiluminescence nanospheres as signal tags and target-triggered strand displacement reaction as signal amplification for highly sensitive detection of helicobacter pylori DNA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 293:304–311
Xing B, Zhu WJ, Zheng XP, Zhu YY, Wei Q, Wu D (2018) Electrochemiluminescence immunonanoprobe based on quenching effect of SiO2@PDA on SnO2/rGO/au NPs-Luminol for insulin detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 265:403–411
Huang XM, Deng X, Qi WJ, Wu D (2018) Highly sensitive luminol electrochemiluminescence immunonanoprobe based on platinum-gold alloy hybrid functionalized zinc oxide nanocomposites for catalytic amplification. Sens Actuators B 273:466–472
Wu BW, Wang ZH, Xue ZH, Zhou XB, Du J, Liu XH, Lu XQ (2012) A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe for isoniazid detection. Analyst 137:3644–3652
Li SH, Liu CH, Yin GH, Zhang Q, Luo JH, Wu NC (2017) Aptamer-molecularly imprinted nanoprobe base on electrogenerated chemiluminescence energy transfer for detection of lincomycin. Biosens Bioelectron 91:687–691
Babamiri B, Salimi A, Hallaj R (2018) A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe for ultrasensitive HIV-1 gene detection using EuS nanocrystals as luminophore. Biosens Bioelectron 117:332–339
Lopes F, Pacheco JG, Rebelo P, Delerue-Matos C (2017) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical nanoprobe prepared on a screen printed carbon electrode for naloxone detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:745–752
Yang JJ, Li Y, Wang JC, Sun XL, Cao R, Sun H, Huang CN, Chen JP (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres prepared by Pickering emulsion polymerization for selective solid-phase extraction of eight bisphenols from human urine samples. Anal Chim Acta 872:35–45
Nolvachai Y, Kulsing C, Boysen RI, Hearn MTW, Marriott PJ (2014) Miniaturized molecularly imprinted polymer extraction method for the gas chromatographic analysis of flavonoids. J Sep Sci 8:1018–1025
Yang YK, Fang GZ, Wang XM, Zhang FY, Liu JM, Zheng WJ, Wang S (2017) Electrochemiluminescent graphene quantum dots enhanced by MoS2 as sensing platform: a novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe for 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid assay. Electrochim Acta 228:107–113
Lian S, Huang ZY, Lin ZZ, Chen X, Oyama M, Chen XM (2016) A highly selective melamine nanoprobe relying on intensified electrochemiluminescence of the silica nanoparticles doped with [Ru(bpy)3]2+/molecularly imprinted polymer modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 236:614–620
Hua M, Yang S, Ma J, He W, Kuang L, Hua D (2018) Highly selective and sensitive determination of uranyl ion by the probe of CdTe quantum dot with a specific size. Talanta 190:278–283
Zhu Q, Cai FD, Zhang J, Zhao K, Deng AP, Li JG (2016) Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent immunonanoprobe based on gold nanoparticles-functionalized zinc oxide nanorod and poly(amidoamine)-graphene for detecting brombuterol. Biosens Bioelectron 86:899–906
Funding
This study was funded by Jilin Provincial Department of Education “Thirteen Five Years” Scientific Research Project (JJKH20181173KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Wu, K., Hu, Y. et al. A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe based on complexes consisting of CdTe and multiwall carbon nanotube for sensitive determination of clenbuterol. Microchim Acta 187, 358 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04319-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04319-2