Abstract
A new and efficient assay is proposed for the photometric determination of Cr6+ by employing polyethylenimine-stabilized Ag nanoclusters (PEI-AgNCs) as an oxidoreductase mimic. Cr6+ with certain oxidicability is able to specifically react with 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), giving a color change from colorless to blue indicating the presence of Cr6+. However, the redox kinetics is so slow that the sensitivity obtained for Cr6+ determination is very poor. It is interestingly found that PEI-AgNCs can act as an oxidoreductase-like nanozyme to significantly promote the sluggish reaction, making it possible to rapidly detect toxic Cr6+ with remarkably enhanced performance. With the use of PEI-AgNCs, fast and convenient determination of Cr6+ was realized, with a limit of detection as low as 1.1 μM. Additionally, the proposed assay exhibited excellent selectivity; other ions, including Cr3+, hardly affected the determination of Cr6+.

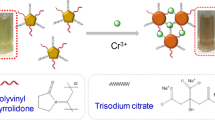
Polyethylenimine-stabilized silver nanoclusters (PEI-AgNCs) act as an oxidoreductase mimic to catalyze the redox reaction of Cr6+ and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), enabling the high-performance colorimetric determination of toxic Cr6+.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha R, Nandi R, Saha B (2011) Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J Coord Chem 64:1782–1806
Zhitkovich A (2011) Chromium in drinking water: sources, metabolism, and cancer risks. Chem Res Toxicol 24:1617–1629
Zhang JF, Li SL (2019) Sensors for detection of Cr(VI) in water: a review. Intern J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1675652
Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2016) Ultrasound assisted-deep eutectic solvent based on emulsification liquid phase microextraction combined with microsample injection flame atomic absorption spectrometry for valence speciation of chromium(III/VI) in environmental samples. Talanta 160:680–685
Ma JX, Wang Z, Li Q, Gai RY, Li XH (2014) On-line separation and preconcentration of hexavalent chromium on a novel mesoporous silica adsorbent with determination by solution-cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 29:2315–2322
Zhuang YT, Chen S, Jiang R, Yu YL, Wang JH (2019) Ultrasensitive colorimetric chromium chemosensor based on dye color switching under the Cr(VI)-stimulated Au NPs catalytic activity. Anal Chem 91:5346–5353
Mutuyimana FP, Liu JJ, Nsanzamahoro S, Na M, Chen HL, Chen XG (2019) Yellow-emissive carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for chromium(VI). Microchim Acta 186:163
Alex SA, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2018) Using gold nanorod-based colorimetric sensor for determining chromium in biological samples. J Mol Liq 264:119–126
Guo JF, Hou CJ, Yang M, Huo DQ, Li JJ, Fa HB, Luo HB, Yang P (2016) Colorimetric sensing of chromium(VI) ions in aqueous solution based on the leaching of protein-stabled gold nanoparticles. Anal Methods 8:5526–5532
Zhang XH, Liu W, Li XM, Zhang Z, Shan DL, Xia H, Zhang ST, Lu XQ (2018) Ultrahigh selective colorimetric quantification of chromium(VI) ions based on gold amalgam catalyst oxidoreductase-like activity in water. Anal Chem 90:14309–14315
Li S, Wei T, Ren GJ, Chai F, Wu HB, Qu FY (2017) Gold nanoparticles based colorimetric probe for Cr(III) and Cr(VI) detection. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 535:215–224
Guo JF, Huo DQ, Yang M, Hou CJ, Li JJ, Fa HB, Luo HB, Yang P (2016) Colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) based on the leaching of gold nanoparticles using a paper-based sensor. Talanta 161:819–825
Rong MC, Lin LP, Song XH, Wang YR, Zhong YX, Yan JW, Feng YF, Zeng XY, Chen X (2015) Fluorescence sensing of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid using graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a fluorescent “switch”. Biosens Bioelectron 68:210–217
Huang S, Qiu HN, Zhu FW, Lu SY, Xiao Q (2015) Graphene quantum dots as on-off-on fluorescent probes for chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 182:1723–1731
Gong XJ, Liu Y, Yang ZH, Shuang SM, Zhang ZY, Dong C (2017) An “on-off-on” fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dual-doped carbon quantum dot. Anal Chim Acta 968:85–96
Zhang JR, Zeng AL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2016) Fluorescent silver nanoclusters for ultrasensitive determination of chromium(VI) in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 304:66–72
Zhu LJ, Peng X, Li HT, Zhang YY, Yao SZ (2017) On-off-on fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for recognition of chromium(VI) and hydrogen sulfide based on the inner filter effect. Sens Actuators B Chem 238:196–203
Korshoj LE, Zaitouna AJ, Lai RY (2015) Methylene blue-mediated electrocatalytic detection of hexavalent chromium. Anal Chem 87:2560–2564
Huang S, Yang EL, Yao JD, Chu X, Liu Y, Xiao Q (2019) Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur tri-doped carbon dots are specific and sensitive fluorescent probes for determination of chromium(VI) in water samples and in living cells. Microchim Acta 186:851
Jin W, Wu GS, Chen AC (2014) Sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of chromium(VI) based on gold nanoparticle-decorated titania nanotube arrays. Analyst 139:235–241
Li JJ, Wang YX, Jiao YF, Jia R, Chen Z (2017) Core-shell Cu@Au nanoparticles as an optical probe for ultrasensitive detection of chromium(VI) via an etching effect. Microchim Acta 184:3817–3823
Joshi P, Sarkar S, Soni SK, Kumar D (2016) Label-free colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) in aqueous systems based on flower shaped silver nanoparticles. Polyhedron 120:142–149
Dong C, Wu GH, Wang ZQ, Ren WZ, Zhang YJ, Shen ZY, Li TH, Wu AG (2016) Selective colorimetric detection of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) using gallic acid capped gold nanoparticles. Dalton Trans 45:8347–8354
Niu XH, He YF, Li X, Zhao HL, Pan JM, Qiu FX, Lan MB (2019) A peroxidase-mimicking nanosensor with Hg2+-triggered enzymatic activity of cysteine-decorated ferromagnetic particles for ultrasensitive Hg2+ detection in environmental and biological fluids. Sens Actuators B Chem 281:445–452
Li X, Wang LJ, Du D, Ni L, Pan JM, Niu XH (2019) Emerging applications of nanozymes in environmental analysis: opportunities and trends. Trends Anal Chem 120:115653
Wei H, Wang EK (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42:6060–6093
Huang YY, Ren JS, Qu XG (2019) Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem Rev 119:4357–4412
Liang MM, Yan XY (2019) Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc Chem Res 52:2190–2200
Li ZX, Feng KZ, Zhang W, Ma M, Gu N, Zhang Y (2018) Catalytic mechanism and application of nanozymes. Chin Sci Bull 63:2128–2139
Xu XC, Wang LJ, Zou XB, Wu SW, Pan JM, Li X, Niu XH (2019) Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of arsenite based on reassembly-induced oxidase-mimicking activity inhibition of dithiothreitol-capped Pd nanozyme. Sens Actuators B Chem 298:126876
Long YJ, Li YF, Liu Y, Zheng JJ, Tang J, Huang CZ (2011) Visual observation of the mercury-stimulated peroxidase mimetic activity of gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 47:11939–11941
Zhang ST, Zhang DX, Zhang XH, Shang DH, Xue ZH, Shan DL, Lu XQ (2017) Ultratrace naked-eye colorimetric detection of Hg2+ in wastewater and serum utilizing mercury-stimulated peroxidase mimetic activity of reduced graphene oxide-PEI-Pd nanohybrids. Anal Chem 89:3538–3544
Li CR, Hai J, Fan L, Li SL, Wang BD, Yang ZY (2019) Amplified colorimetric detection of Ag+ based on Ag+-triggered peroxidase-like catalytic activity of ZIF-8/GO nanosheets. Sens Actuators B Chem 284:213–219
Choi K, Lee S, Park JO, Park JA, Cho SH, Lee SY, Lee JH, Choi JW (2018) Chromium removal from aqueous solution by a PEI-silica nanocomposite. Sci Rep 8:1438
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DL, Perrett S, Yan XY (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Niu XH, He YF, Pan JM, Li X, Qiu FX, Yan YS, Shi LB, Zhao HL, Lan MB (2016) Uncapped nanobranch-based CuS clews used as an efficient peroxidase mimic enable the visual detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose with fast response. Anal Chim Acta 947:42–49
Song HW, Li ZB, Peng YX, Li X, Xu XC, Pan JM, Niu XH (2019) Enzyme-triggered in situ formation of Ag nanoparticles with oxidase-mimicking activity for amplified detection of alkaline phosphatase activity. Analyst 144:2416–2422
Vernekar AA, Das T, Ghosh S, Mugesh G (2016) A remarkably efficient MnFe2O4-based oxidase nanozyme. Chem Asian J 11:72–76
Yang HK, Xiao JY, Su L, Feng T, Lv QY, Zhang XJ (2017) Oxidase-mimicking activity of the nitrogen-doped Fe3C@C composites. Chem Commun 53:3882–3885
Funding
The work was supported in part by the Social Development Fund of Zhenjiang City (No. SH2018011). Xiangheng Niu was supported by the Cultivation Project for Excellent Young Teachers of Jiangsu University (No. 4111310004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no completing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 296 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Q., Li, X., Peng, Y. et al. Polyethylenimine-stabilized silver nanoclusters act as an oxidoreductase mimic for colorimetric determination of chromium(VI). Microchim Acta 187, 263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04232-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04232-8