Abstract
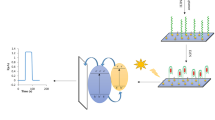
A photoelectrochemical (PEC) aptasensor for Pb(II) detection is described. A nanocomposite consisting of CdS (2.5 μm) and TiO2 nanoparticles (10 nm) was used as a photoactive material, and gold nanochains (Au NCs) as the support for immobilization of the Pb(II)-binding aptamer. The quercetin-copper(II) complex was further employed as the intercalator for the improvement of the photoactivity by embedding it into dsDNA. In the presence of Pb(II), a Pb(II)-stabilized G-quadruplex was formed between Pb(II) and DNA S1. This is accompanied by unwinding of the dsDNA and the release of the quercetin-copper(II) complex from the surface of the sensor. This results in a decrease of the photocurrent that drops linearly from 5.0 × 10−12 to 1.0 × 10−8 mol·L−1 Pb(II) concentration range with a detection limit of 1.6 × 10−12 mol·L−1. The method was applied to the determination of Pb(II) in various samples and gave satisfactory results.

A photoelectrochemical aptasensor was fabricated for the detection of Pb(II) based on CdS-TiO2 nanocomposite modified indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode. Gold nanochains (AuNCs) were used as anchor to immobilize the aptamers S1 and S2 that form a double helix structure by DNA hybridization. After embedding of quercetin-copper(II) complex as intercalator and electron donor, the concentrations of Pb(II) were determined by the changes of photocurrents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao W, Xu J, Chen H (2016) Photoelectrochemical aptasensing. Trends Anal Chem 82:307–315
Yang X, Wu L, Ma L, Li X, Wang T, Liao S (2015) Pd nano-particles (NPs) confined in titanate nanotubes (TNTs) for hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. Catal Commun 59:184–188
Wang W, Savadogo O, Ma Z (2012) The oxygen reduction reaction on Pt/TiOxNy-based electrocatalyst for PEM fuel cell applications. J Appl Electrochem 42:857–866
Li L, Chen R, Zhu X, Liao Q, Ye D, Zhang B, He X, Jiao L, Feng H, Zhang W (2018) A ternary hybrid CdS/SiO2/TiO2 photoanode with enhanced photoelectrochemical activity. Renew Energy 127:524–530
Zou Z, Xie C, Zhang S, Liu Y, Zhang S, Zeng D (2013) Extraordinarily enhanced gas phase photoelectric response of CdS/TiO2 nanocomposite photoelectrode: CdS as a sensitizer and a hole capturer. J Nanopart Res 15:1734–1744
Qi X, She G, Liu Y, Mu L, Shi W (2012) Electrochemical synthesis of CdS/ZnO nanotube arrays with excellent photoelectrochemical properties. Chem Commun 48:242–244
Chen Y, Huang L, Wu W, Ruan Y, Wu Z, Xue Z, Fu F (2014) Speciation analysis of lead in marine animals by using capillary electrophoresis couple on-line with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 35:1346–1352
Tsogas GZ, Giokas DL, Vlessidis AG (2009) Graphite furnace and hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cadmium, lead, and tin traces in natural surface waters: study of preconcentration technique performance. J Hazard Mater 163:988–994
Jiang D, Du X, Chen D, Zhou L, Chen W, Li Y, Hao N, Qian J, Liu Q, Wang K (2016) One-pot hydrothermal route to fabricate nitrogen doped graphene/Ag-TiO2: efficient charge separation and high-performance on-off-on switch system based photoelectrochemical biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 83:149–155
Wang Y, Chen F, Ye X, Wu T, Wu K, Li C (2017) Photoelectrochemical immunosensing of tetrabromobisphenol a based on the enhanced effect of dodecahedral gold nanocrystals/MoS2 nanosheets. Sensors Actuators B 245:205–212
Wang H, Liu P, Jiang W, Li X, Yin H, Ai S (2017) Photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform for M. SssI methyltransferase activity analysis and inhibitor screening based on g-C3N4 and CdS quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B 244:458–465
Duan N, Wu S, Dai S, Miao T, Chen J, Wang Z (2015) Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescenceresonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:917–923
Taghdisi SM, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Ramezani M, Abnous K (2015) An aptasensor for selective, sensitive and fast detection of lead (II) based on polyethyleneimine and gold nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:1206–1211
Zhu Y, Zeng G, Zhang Y, Tang L, Chen J, Cheng M, Zhang L, He L, Guo Y, He X, Lai M, He Y (2014) Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor using a MWCNTs/GNPs-modified electrode for lead (II) detection based on Pb2+-induced G-rich DNA conformation. Analyst 139:5014–5020
Xiao S, Chen L, Xiong X, Zhang Q, Feng J, Deng S, Zhou L (2018) A new impedimetric sensor based on anionic intercalator for detection of lead ions with low cost and high sensitivity. J Electroanal Chem 827:175–180
Okoth OK, Yan K, Feng J, Zhang J (2018) Label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensing of diclofenca based on gold nanoparticles and graphene-doped CdS. Sensors Actuators B 256:334–341
Li F, Feng Y, Zhao C, Tang B (2011) Crystal violet as a G-quadruplex-selective probe for sensitive amperometric sensing of lead. Chem Commun 47:11909–11911
Li H, Xue Y, Wang W (2014) Femtomole level photoelectrochemical aptasensing for mercury ions using quercetin-copper (II) complex as the DNA intercalator. Biosens Bioelectron 54:317–322
Srinivasan SS, Wade J, Stefanakos EK (2006) Visible light photocatalysis via CdS/TiO2 nanocomposite materials. J Nanomater 2006:87326. https://doi.org/10.1155/JNM/2006/87326
Lang QQ, Chen YH, Huang TL, Yang LN, Zhong SX, Wu LJ, Chen JR, Bai S (2018) Graphene “bridge” in transferring hot electrons from plasmonic Ag nanocubes to TiO2 nanosheets for enhanced visible light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B 220:182–190
Zhang ZM, Jiang YH, Yu QH, Ding YH, Jiang Y, Yin JR, Zhang P (2017) Facile preplaration of exposed {001} facet TiO2 nanobelts coated by monolayer carbon and its high-performance photocatalytic activity. J Mater Sci 52:13586–13595
You DT, Pan B, He YS, Wang XX, Su WY (2017) Enhanced visible light photocatalytic H2 evolution over CeO2 loaded with Pt and CdS. Res Chem Intermed 43:5103–5112
Malashchonak MV, Mazanik AV, Korolik OV, Streltsov EA, Kulak AI (2015) Influence of wide band gap oxide substrates on the photoelectrochemical properties and structural disorder of CdS nanoparticles grown by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Beilstein J Nanotech 6:2252–2262
Pang X, Bian H, Wang W, Liu C, Khan MS, Wang Q, Qi J, Wei Q, Du B (2017) A bio-chemical application of N-GQDs and g-C3N4 QDs sensitized TiO2 nanopillars for the quantitative detection of pcDNA3-HBV. Biosens Bioelectron 91:456–464
Xin Y, Zhao Y, Qiu B, Zhang Z (2017) Sputtering gold nanoparticles on nanoporous bismuth vanadate for sensitive and selective photoelectrochemical aptasensing of thrombin. Chem Commun 53:8898–8901
Cai H, Lee TMH, Hsing IM (2006) Label-free protein recognition using an aptamer-based impedance measurement assay. Sensors Actuators B 114:433–437
Lin Z, Li X, Kraatz HB (2011) Impedimetric immobilized DNA-based sensor for simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Ag+ and Hg2+. Anal Chem 83:6896–6901
Zang Y, Lei J, Hao Q, Ju H (2014) “Signal-on” photoelectrochemical sensing strategy based on target-dependent aptamer conformational conversion for selective detection of lead (II) ion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:15991–15997
Li M, Zhou X, Guo S, Wu N (2013) Detection of lead (II) with a “turn-on” fluorescent biosensor based on energy transfer from CdSe/ZnS quantum dots to graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 43:69–74
Pang S, Liu S, Su X (2015) An ultrasensitive sensing strategy for the detection of lead (II) ions based on the intermolecular G-quadruplex and graphene oxide. Sensors Actuators B 208:415–420
Qian ZS, Shan XY, Chai LJ, Chen JR, Feng H (2015) A fluorescent nanosensor based on graphene quantum dots-aptamer probe and graphene oxide platform for detection of lead (II) ion. Biosens Bioelectron 68:225–231
Wang S, Si S (2013) Aptamer biosensing platform based on carbon nanotube longrange energy transfer for sensitive, selective and multicolor fluorescent heavy metal ion analysis. Anal Methods 5:2947–2953
Zhou B, Yang XY, Wang YS, Yi JC, Zeng Z, Zhang H, Chen YT, Hu XJ, Suo QL (2019) Label-free fluorescent aptasensor of Cd2+ detection based on the conformational switching of aptamer probe and SYBR green I. Microchem J 144:377–382
Lotfi Zadeh Zhad HR, Rodríguez Torres YM, Lai RY (2017) A reagentless and reusable electrochemical aptamer-based sensor for rapid detection of cd(II). J Electroanal Chem 803:89–94
Wu Y, Zhan S, Wang L, Zhou P (2014) Selection of a DNA aptamer for cadmium detection based on cationic polymer mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Analyst 139:1550–1561
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21665007), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (219QN207), and Key Science and Technology Program of Haikou City (2017042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 234 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, Y., Luo, G., Xie, H. et al. Photoelectrochemical aptasensor for lead(II) by exploiting the CdS nanoparticle-assisted photoactivity of TiO2 nanoparticles and by using the quercetin-copper(II) complex as the DNA intercalator. Microchim Acta 186, 826 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3951-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3951-2