Abstract
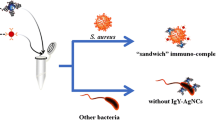
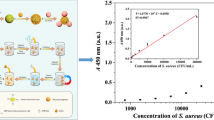
A colorimetric test is described for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus (SA). Gold nanorods (AuNRs) are first labeled with urease and yolk immunoglobulin (IgY). This probe can specifically bind SA. In the next step, nonspecific magnetic beads and sample are added. This leads to the formation of the AuNR-IgY-SA-nMB immunocomplex which is then magnetically separated. Finally, a solution of urea is added to the supernatant. Ureases catalyzes the decomposition of urea which results in an increase in the pH value. The increase in the pH value is detected by using a phenolphthalein test paper which undergoes a color change from white to pink. The analytical process can be completed within 20 min. The method is highly specific and can detect as little as 476 cfu·mL−1. It was verified by analyzing contaminated Chinese cabbage and beef samples, and 1000 cfu·mL−1 of SA were accurately detected.

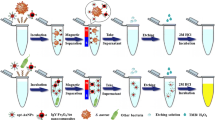
Schematic representation of a colorimetric method for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on the immunocomplex formed from dual-labeled gold nanorod (AuNR) probe, bacteria and non-specific magnetic bead (nMB). This method can be completed within 20 min.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suaifan GA, Alhogail S, Zourob M (2017) Rapid and low-cost biosensor for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 90:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.047
Principato M, Qian BF (2014) Staphylococcal enterotoxins in the etiopathogenesis of mucosal autoimmunity within the gastrointestinal tract. Toxins 6:1471–1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6051471
Chaibenjawong P, Foster SJ (2011) Desiccation tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus. Arch Microbiol 193:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0653-x
Becker K, Schaumburg F, Fegeler C, Friedrich AW, Kock R (2017) Staphylococcus aureus from the German general population is highly diverse. Int J Med Microbiol 307:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.11.007
Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Widdowson MA, Roy SL, Jones JL, Griffin PM (2011) Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--major pathogens. Emerg Infec Dis 17:7–15. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1701.P11101
Byrd-Bredbenner C, Berning J, Martin-Biggers J, Quick V (2013) Food safety in home kitchens: a synthesis of the literature. Int J Env Res Pub He 10:4060–4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10094060
Saraiva MM, De Leon CM, Santos SC, Stipp DT, Souza MM, Santos Filho L, Gebreyes WA, Oliveira CJ (2018) Accuracy of PCR targeting different markers for Staphylococcus aureus identification: a comparative study using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry as the gold standard. J Vet Diagn Investig 30:252–255. https://doi.org/10.1177/1040638717732370
Liu Y, Wei Y, Cao Y, Zhu D, Ma W, Yu Y, Guo M (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of Staphylococcus aureus via enzyme-free branched DNA signal amplification probe. Biosens Bioelectron 117:830–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.008
Ward AC, Hannah AJ, Kendrick SL, Tucker NP, MacGregor G, Connolly P (2018) Identification and characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus on low cost screen printed carbon electrodes using impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 110:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.048
Gill AAS, Singh S, Thapliyal N, Karpoormath R (2019) Nanomaterial-based optical and electrochemical techniques for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review. Mikrochim Acta 186:114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3186-7
Bhaisare ML, Gedda G, Khan MS, Wu HF (2016) Fluorimetric detection of pathogenic bacteria using magnetic carbon dots. Anal Chim Acta 920:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.02.025
Srisa-Art M, Boehle KE, Geiss BJ, Henry CS (2018) Highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a colorimetric paper-based analytical device coupled with Immunomagnetic separation. Anal Chem 90:1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04628
Wang R, Xu Y, Liu H, Peng J, Irudayaraj J, Cui F (2017) An integrated microsystem with dielectrophoresis enrichment and impedance detection for detection of Escherichia coli. Biomed Microdevices 19:34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0167-2
Aldewachi H, Chalati T, Woodroofe MN, Bricklebank N, Sharrack B, Gardiner P (2017) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensors. Nanoscale 10:18–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr06367a
Wu Y, Guo W, Peng W, Zhao Q, Piao J, Zhang B, Wu X, Wang H, Gong X, Chang J (2017) Enhanced fluorescence ELISA based on HAT triggering fluorescence "turn-on" with enzyme-antibody dual labeled AuNP probes for ultrasensitive detection of AFP and HBsAg. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:9369–9377. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16236
Chen Q, Huang F, Cai G, Wang M, Lin J (2018) An optical biosensor using immunomagnetic separation, urease catalysis and pH indication for rapid and sensitive detection of listeria monocytogenes. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 258:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.087
Hu R, Wen W, Wang Q, Xiong H, Zhang X, Gu H, Wang S (2014) Novel electrochemical aptamer biosensor based on an enzyme-gold nanoparticle dual label for the ultrasensitive detection of epithelial tumour marker MUC1. Biosens Bioelectron 53:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.015
Gagner JE, Lopez MD, Dordick JS, Siegel RW (2011) Effect of gold nanoparticle morphology on adsorbed protein structure and function. Biomaterials 32:7241–7252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.05.091
Hinterwirth H, Stubiger G, Lindner W, Lammerhofer M (2013) Gold nanoparticle-conjugated anti-oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies for targeted lipidomics of oxidative stress biomarkers. Anal Chem 85:8376–8384. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401778f
Joshi PP, Yoon SJ, Hardin WG, Emelianov S, Sokolov KV (2013) Conjugation of antibodies to gold nanorods through fc portion: synthesis and molecular specific imaging. Bioconjug Chem 24:878–888. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc3004815
Fu K, Zheng Y, Li J, Liu Y, Pang B, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Zhao C (2018) Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of vibrio parahemolyticus based on Mn(2+) mediates the assembly of gold nanoparticles. J Agr Food Chem 66:9516–9521. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02494
Liu Y, Wang J, Song X, Xu K, Chen H, Zhao C, Li J (2018) Colorimetric immunoassay for listeria monocytogenes by using core gold nanoparticles, silver nanoclusters as oxidase mimetics, and aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 185:360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2896-1
Feng L, Xuan Z, Ma J, Chen J, Cui D, Su C, Guo J, Zhang Y (2013) Preparation of gold nanorods with different aspect ratio and the optical response to solution refractive index. J Exp Nanosci 10:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2013.824619
Pang B, Fu K, Liu Y, Ding X, Hu J, Wu W, Xu K, Song X, Wang J, Mu Y, Zhao C, Li J (2018) Development of a self-priming PDMS/paper hybrid microfluidic chip using mixed-dye-loaded loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for multiplex foodborne pathogens detection. Anal Chim Acta 1040:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.07.024
Zhang S, Niu H, Hu Z, Cai Y, Shi Y (2010) Preparation of carbon coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their application for solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1217:4757–4764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.05.035
Tan L, Chen Z, Zhang C, Wei X, Lou T, Zhao Y (2017) Colorimetric detection of Hg(2+) based on the growth of aptamer-coated AuNPs: the effect of prolonging aptamer strands. Small 13:1603370. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603370
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 81872668, 81473018), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Item (Grant No.: 20170204003SF) and Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (Grant No.: 101832018C061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5260 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, B., Zheng, Y., Wang, J. et al. Colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus using gold nanorods labeled with yolk immunoglobulin and urease, magnetic beads, and a phenolphthalein impregnated test paper. Microchim Acta 186, 611 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3722-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3722-0