Abstract
A voltammetric sandwich immunoassay is described for the biomarker cardiac troponin I (cTnI). The gold nanocube-functionalized graphene oxide (AuNC/GO) is employed as a substrate to accelerate the electron transfer and to immobilize more primary antibodies. It also employs composite materials prepared from bimetallic gold/silver core-shell nanocubes and nitrogen and sulfur co-doped reduced graphene oxide as the signal amplifier. The introduction of N and S into GO enlarges the active surface and accelerates the electron transfer rate. Such unique characteristics render the material an effective support substrate to load more Au@AgNC and to immobilize an increasing number of second antibodies via Ag-N bonds. After specific binding with cTnI, the immunosensor was incubated in a labeled cTnI secondary antibody solution. The amperometric signal change is then measured at 0.34 V (vs. SCE) using o-phenylenediamine and hydrogen peroxide as an electrochemical probe. Response is linear in the concentration range from 100 fg∙mL−1 to 250 ng∙mL−1, and the detection limit is 33 fg∙mL−1.

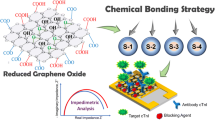
Schematic presentation of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) electrochemical immunosensor based on gold nanocube-functionalized graphene oxide (AuNC/GO) as substrate material, bimetallic gold/silver core-shell nanocubes and nitrogen and sulfur co-doped reduced graphene oxide (Au@AgNC/N, S-rGO) as signal amplifier, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and o-phenylenediamine (o-PD) as redox probe.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheng Q, Qiao X, Zhou M, Zheng J (2017) Recent progress in electrochemical sensing of cardiac troponin by using nanomaterial-induced signal amplification. Microchim Acta 184(6):1573–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2219-y
Rezaei B, Shoushtari AM, Rabiee M, Uzun L, Mak WC, Turner APF (2018) An electrochemical immunosensor for cardiac troponin I using electrospun carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotube -whiskered nanofibres. Talanta 182:178–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2012.05.033
Gao F, Fan T, Ou S, Wu J, Zhang X, Luo J, Li N, Yao Y, Mou Y, Liao X (2017) Highly efficient electrochemical sensing platform for sensitive detection DNA methylation, and methyltransferase activity based on Ag NPs decorated carbon nanocube. Biosens Bioelectron 99:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.063
Hong Q, Yang L, Ge L, Liu Z, Li F (2018) Direct-laser-writing of three-dimensional porous graphene frameworks on indium-tin oxide for sensitive electrochemical biosensing. Analyst 142(5):780–786. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN00888D
Wei Z, Guo S, Asaka K (2014) An insight into the capacitive properties of reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2248–2254. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4057562
Singh S, Tuteja SK, Sillu D, Deep A, Suri CR (2016) Gold nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide based electrochemical immunosensor for the cardiac biomarker myoglobin. Microchim Acta 183(5):1729–1738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1803-x
Lv H, Li Y, Zhang X, Gao Z, Zhang C, Zhang S, Dong Y (2018) Enhanced peroxidase-like properties of Au@Pt DNs/NG/Cu2+ and application of sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of CEA. Biosens Bioelectron 112:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.025
Chen B, Jiang Z, Zhou L, Deng B, Jiang ZJ, Huang J, Liu M (2018) Electronic coupling induced high performance of N, S-codoped graphene supported CoS2 nanoparticles for catalytic reduction and evolution of oxygen. J Power Sources 389:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.010
Huo J, Zheng P, Wang X, Guo S (2018) Three-dimensional Sulphur/nitrogen co-doped reduced graphene oxide as high-performance supercapacitor binder-free electrodes. Appl Surf Sci 442:575–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.221
Jiang L, Han J, Li F, Gao J, Li Y, Dong Y, Wei Q (2015) A sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on multiple signal amplification for α-fetoprotein labeled by platinum hybrid multiwalled carbon nanotubes adhered copper oxide. Electrochim Acta 160:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.02.050
Zhang X, Lv H, Li Y, Zhang C, Wang P, Liu Q, Ai B, Xu Z, Zhao Z (2019) Ultrasensitive sandwich-type immunosensor for cardiac troponin I based on enhanced electrocatalytic reduction of H2O2 by β-cyclodextrins functionalized 3D porous graphene supported Pd@Au nanocubes. J Mater Chem B 7(9):1460–1468. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB03362E
Zhang Y, Shuai Z, Zhou H, Luo Z, Liu B, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Chen S, Chao J, Weng L (2018) Single-molecule analysis of MicroRNA and logic operations using a smart plasmonic nanobiosensor. J Am Chem Soc 140(11):3988–3993. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b12772
Zhang X, Li Y, Lv H, Feng J, Gao Z, Wang P, Dong Y, Liu Q, Zhao Z (2018) Sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on Au@Ag supported on functionalized phenolic resin microporous carbon spheres for ultrasensitive analysis of α-fetoprotein. Biosens Bioelectron 106:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.02.001
Lin T, Zhang M, Xu F, Wang X, Xu Z, Guo L (2018) Colorimetric detection of benzoyl peroxide based on the etching of silver nanoshells of Au@Ag nanorods. Sensors Actuators B Chem 261:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.172
Xu H, Song P, Fernandez C, Wang J, Zhu M, Shiraishi Y, Du Y (2018) Sophisticated construction of binary PdPb alloy Nanocube as robust Electrocatalysts toward ethylene glycol and glycerol oxidation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:12659–12665. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00532
Chen P, Wang T, Zheng X, Tian D, Xia F, Zhou C (2018) An ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on C60-modified polyamidoamine dendrimer and Au NPs for co-catalytic silver deposition. New J Chem 42(6):4653–4660. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ00059J
Wang P, Li M, Pei F, Li Y, Liu Q, Dong Y, Chu Q, Zhu H (2017) An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification system of double-deck gold film and thionine unite with platinum nanowire inlaid globular SBA-15 microsphere. Biosens Bioelectron 91:424–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.057
Li M, Wang P, Pei F, Yu H, Dong Y, Li Y, Liu Q, Chen P (2018) A novel signal amplification system fabricated immunosensor based on Au nanoparticles and mesoporous trimetallic PdPtCu nanospheres for sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Sensors Actuators B Chem 261:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.136
Fan F-R, Liu D-Y, Wu Y-F, Duan S, Xie Z-X, Jiang Z-Y, Tian Z-Q (2008) Epitaxial growth of heterogeneous metal nanocrystals: from gold nano-octahedra to palladium and silver nanocube. J Am Chem Soc 130(22):6949–6951. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja801566d
Zhang R, Zhang C, Zheng F, Li X, Sun C-L, Chen W (2018) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene nanoribbons: a novel metal-free catalyst for high performance electrochemical detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT). Carbon 126:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.10.042
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Chen J, Kong L, Sun X, Feng J, Chen Z, Fan D, Wei Q (2018) Ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical immunosensor of cardiac troponin I detection based on dual inhibition effect of Ag@Cu2O core-shell submicron-particles on CdS QDs sensitized TiO2 nanosheets. Biosens Bioelectron 117:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.037
Sandil D, Srivastava S, Malhotra B, Sharma S, Puri NK (2018) Biofunctionalized tungsten trioxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for sensitive electrochemical immunosensing of cardiac biomarker. J Alloys Compd 763:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.293
Jiang M-H, Lu P, Lei Y-M, Chai Y-Q, Yuan R, Zhuo Y (2018) Self-accelerated electrochemiluminescence emitters of Ag@SnO2 nanoflowers for sensitive detection of cardiac troponin T. Electrochim Acta 271:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.03.177
Kazemi SH, Ghodsi E, Abdollahi S, Nadri S (2016) Porous graphene oxide nanostructure as an excellent scaffold for label-free electrochemical biosensor: detection of cardiac troponin I. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 69:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.07.005
Liu G, Meng Q, Zhang Y, Cao C, Goldys EM (2016) Nanocomposites of gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide towards an stable label-free electrochemical immunosensor for detection of cardiac marker troponin-I. Anal Chim Acta 909:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.12.023
Yan H, Tang X, Zhu X, Zeng Y, Lu X, Yin Z, Lu Y, Yang Y, Li L (2018) Sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive determination of cardiac troponin I using carboxyl-terminated ionic liquid and helical carbon nanotube composite as platform and ferrocenecarboxylic acid as signal label. Sensors Actuators B Chem 277:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2018.09.010
Chekin F, Vasilescu A, Jijie R, Singh SK, Kurungot S, Iancu M, Badea G, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2018) Sensitive electrochemical detection of cardiac troponin I in serum and saliva by nitrogen-doped porous reduced graphene oxide electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 262:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.215
Singal S, Srivastava AK, Gahtori B, Rajesh (2016) Immunoassay for troponin I using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a hybrid film consisting of graphene and multiwalled carbon nanotubes and decorated with platinum nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(4):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1759-x
Singal S, Srivastava AK, Dhakate S, Biradar AM, Rajesh R (2015) Electroactive graphene-multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid supported impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of human cardiac troponin-I. RSC Adv 5(92):74994–75003. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15449A
Zhang T, Ma N, Ali A, Wei Q, Wu D, Ren X (2018) Electrochemical ultrasensitive detection of cardiac troponin I using covalent organic frameworks for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 119:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.020
Saxberg BE, Kowalski B (1979) Generalized standard addition method. Anal Chem 51(7):1031–1038. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a059
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2018GSF120001, 2018GNC110038), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21575079). All of the authors express their deep thanks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
All experiments were performed in compliance with relevant laws or guidelines of Shandong University of Technology and approved by the ethics committee at Shandong University of Technology, China. Moreover, informed consent was obtained from human participants of this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.33 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, H., Zhang, X., Li, Y. et al. An electrochemical sandwich immunosensor for cardiac troponin I by using nitrogen/sulfur co-doped graphene oxide modified with Au@Ag nanocubes as amplifiers. Microchim Acta 186, 416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3526-2